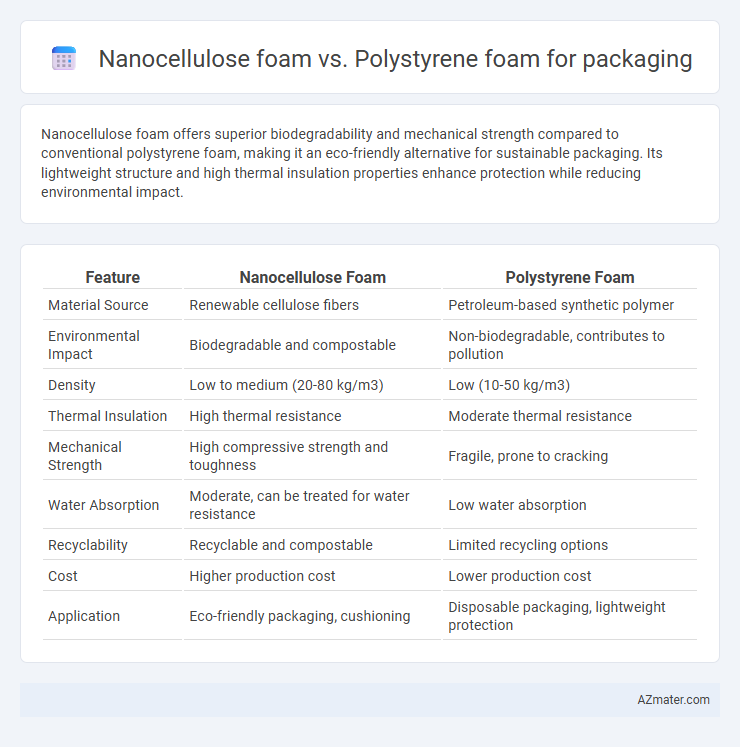
Nanocellulose foam offers superior biodegradability and mechanical strength compared to conventional polystyrene foam, making it an eco-friendly alternative for sustainable packaging. Its lightweight structure and high thermal insulation properties enhance protection while reducing environmental impact.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nanocellulose Foam | Polystyrene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Renewable cellulose fibers | Petroleum-based synthetic polymer |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable and compostable | Non-biodegradable, contributes to pollution |
| Density | Low to medium (20-80 kg/m3) | Low (10-50 kg/m3) |
| Thermal Insulation | High thermal resistance | Moderate thermal resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | High compressive strength and toughness | Fragile, prone to cracking |
| Water Absorption | Moderate, can be treated for water resistance | Low water absorption |
| Recyclability | Recyclable and compostable | Limited recycling options |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Lower production cost |
| Application | Eco-friendly packaging, cushioning | Disposable packaging, lightweight protection |
Introduction to Foam Materials in Packaging
Nanocellulose foam and polystyrene foam are prominent materials in packaging due to their lightweight and cushioning properties. Nanocellulose foam is derived from renewable cellulose fibers, offering biodegradability and high mechanical strength, while polystyrene foam, a petroleum-based polymer, provides excellent thermal insulation and shock absorption. The sustainable nature of nanocellulose foam makes it a promising alternative to conventional polystyrene foam, addressing environmental concerns in packaging applications.
What is Nanocellulose Foam?
Nanocellulose foam is an innovative, biodegradable packaging material derived from cellulose fibers extracted from plant sources, offering exceptional strength and lightweight properties. Unlike traditional polystyrene foam, nanocellulose foam provides superior environmental sustainability due to its renewable origin and complete biodegradability. Its porous structure delivers effective cushioning and thermal insulation, making it a promising alternative to conventional plastic-based foams in packaging applications.
Understanding Polystyrene Foam
Polystyrene foam, widely used in packaging, is a lightweight material known for its excellent cushioning and insulation properties, but it poses significant environmental challenges due to its non-biodegradable nature and difficulty in recycling. Nanocellulose foam, derived from renewable plant fibers, offers a sustainable alternative with comparable cushioning performance and superior biodegradability, making it an innovative solution for eco-friendly packaging. Understanding the chemical composition and environmental impact of polystyrene foam underscores the urgency for adopting greener materials like nanocellulose foam in packaging industries.
Environmental Impact: Biodegradability and Sustainability
Nanocellulose foam offers significant environmental advantages over polystyrene foam due to its biodegradability and renewable sourcing from cellulose fibers. Unlike polystyrene, which can persist in ecosystems for hundreds of years and contributes to microplastic pollution, nanocellulose foam decomposes naturally within months under composting conditions. The sustainable production process of nanocellulose foam reduces carbon footprint and reliance on fossil fuels, making it a more eco-friendly alternative for packaging applications.
Mechanical Properties and Performance Comparison
Nanocellulose foam exhibits superior mechanical properties with higher tensile strength and better elasticity compared to polystyrene foam, allowing for enhanced impact resistance and cushioning during packaging. Its lightweight yet strong structure offers improved compression recovery and durability, reducing risk of deformation under load. Polystyrene foam, while cost-effective and widely used, often shows weaker mechanical resilience and lower environmental sustainability in packaging applications.
Thermal Insulation and Protective Capabilities
Nanocellulose foam offers superior thermal insulation properties compared to polystyrene foam due to its highly porous structure and low thermal conductivity, enhancing energy efficiency in packaging applications. Its biodegradability and high mechanical strength provide excellent protective capabilities, cushioning fragile items effectively while reducing environmental impact. Polystyrene foam, although widely used for its lightweight and shock absorption, falls short in sustainability and may release harmful chemicals, making nanocellulose foam a promising eco-friendly alternative in advanced packaging solutions.
Cost Analysis: Nanocellulose vs Polystyrene
Nanocellulose foam generally incurs higher initial production costs compared to polystyrene foam due to raw material extraction and processing complexities. Polystyrene benefits from established mass manufacturing infrastructure, which significantly reduces unit costs and enables economies of scale. However, rising environmental regulations and recycling challenges are driving potential long-term cost increases for polystyrene, making nanocellulose a competitively sustainable alternative in packaging.
Regulatory and Safety Considerations
Nanocellulose foam offers significant advantages over polystyrene foam in regulatory compliance and safety due to its biodegradable nature and non-toxic composition, meeting increasingly stringent environmental regulations such as those enforced by the EPA and EU REACH. Polystyrene foam faces regulatory scrutiny for its persistence in ecosystems and potential leaching of styrene, a suspected carcinogen, leading to bans or restrictions in multiple regions worldwide. Choosing nanocellulose foam for packaging enhances adherence to evolving safety standards and reduces regulatory risk associated with chemical hazards and environmental pollution.
Future Prospects and Technological Innovations
Nanocellulose foam offers significant advantages over polystyrene foam in packaging due to its biodegradability, renewable source, and superior mechanical strength, positioning it as a sustainable alternative with growing market demand. Technological innovations such as advanced cellulose nanofiber extraction processes and enhanced foam formulation techniques are driving improvements in durability, thermal insulation, and cost-efficiency. Future prospects include increased adoption in food and electronics packaging as environmental regulations tighten and consumer preference shifts toward eco-friendly materials.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Packaging Foam
Nanocellulose foam offers superior biodegradability, lightweight properties, and enhanced mechanical strength compared to traditional polystyrene foam, making it an eco-friendly alternative for sustainable packaging. Polystyrene foam remains cost-effective with excellent shock absorption and insulation, ideal for applications requiring high durability and low production costs. Selecting the right packaging foam depends on balancing environmental impact, product protection needs, and budget constraints to achieve optimized performance and sustainability.
Infographic: Nanocellulose foam vs Polystyrene foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com