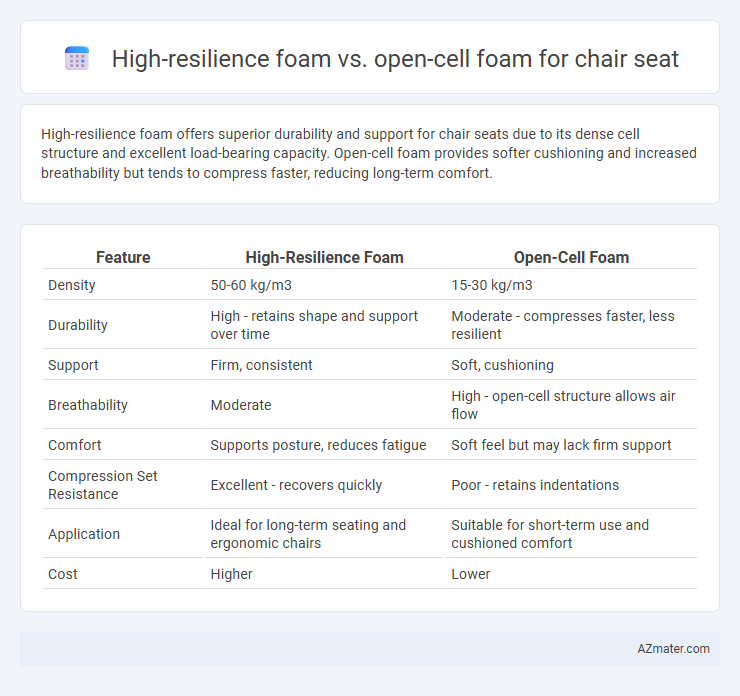
High-resilience foam offers superior durability and support for chair seats due to its dense cell structure and excellent load-bearing capacity. Open-cell foam provides softer cushioning and increased breathability but tends to compress faster, reducing long-term comfort.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | High-Resilience Foam | Open-Cell Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 50-60 kg/m3 | 15-30 kg/m3 |
| Durability | High - retains shape and support over time | Moderate - compresses faster, less resilient |
| Support | Firm, consistent | Soft, cushioning |
| Breathability | Moderate | High - open-cell structure allows air flow |
| Comfort | Supports posture, reduces fatigue | Soft feel but may lack firm support |
| Compression Set Resistance | Excellent - recovers quickly | Poor - retains indentations |
| Application | Ideal for long-term seating and ergonomic chairs | Suitable for short-term use and cushioned comfort |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Chair Seat Foams
High-resilience foam offers superior durability and support due to its dense structure and high rebound rate, making it ideal for long-lasting chair seats. Open-cell foam provides a softer, more breathable cushioning experience with enhanced airflow but tends to compress faster under weight. Choosing between high-resilience and open-cell foam depends on balancing comfort, longevity, and breathability requirements for chair seating.
What is High-Resilience Foam?
High-resilience foam is a high-density polyurethane foam known for its excellent durability, support, and quick recovery, making it ideal for chair seats that require long-lasting comfort. This foam features a resilient, open-cell structure with an ILD (Indentation Load Deflection) typically ranging from 25 to 45, providing firm yet responsive cushioning. Compared to standard open-cell foam, high-resilience foam maintains its shape and support over extended use, reducing sagging and improving ergonomic seating.
Understanding Open-Cell Foam
Open-cell foam features a porous structure that allows air to flow easily, providing enhanced breathability and softer cushioning compared to high-resilience foam. This type of foam compresses more under pressure, offering a plush seating experience but with less support and durability over time. Understanding open-cell foam highlights its suitability for chairs prioritizing comfort and ventilation, though it may not retain shape as effectively as high-resilience foam.
Comfort Comparison: HR vs Open-Cell Foam
High-resilience (HR) foam offers superior support and durability compared to open-cell foam, making it ideal for chair seats that require long-lasting comfort. HR foam's higher density and responsive nature provide better weight distribution and cushioning, reducing pressure points during extended sitting. Open-cell foam is softer and more breathable but tends to compress faster, resulting in diminished comfort over time.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
High-resilience foam offers superior durability and longevity for chair seats due to its dense cell structure and high rebound capability, maintaining shape and support over extended use. Open-cell foam, while softer and more breathable, tends to compress and degrade faster, reducing seat comfort and lifespan under constant pressure. For long-term seating applications, high-resilience foam provides consistent performance and better resistance to wear and tear compared to open-cell foam.
Breathability and Temperature Regulation
High-resilience foam offers moderate breathability with its dense structure, providing firm support but potentially trapping heat during extended seating. Open-cell foam excels in temperature regulation due to its porous design, allowing superior airflow that enhances breathability and keeps the chair seat cooler. Choosing open-cell foam improves comfort in warm environments by facilitating heat dissipation and reducing moisture buildup.
Support and Ergonomics for Seating
High-resilience foam offers superior support and durability for chair seats, providing consistent firmness that helps maintain proper spinal alignment and reduces pressure points during extended use. Open-cell foam, while softer and more breathable, tends to compress more quickly under weight, offering less ergonomic support and potentially causing discomfort over time. Choosing high-resilience foam enhances ergonomic seating by ensuring optimal cushioning and support, critical for maintaining posture and reducing fatigue.
Maintenance and Care Differences
High-resilience foam offers greater durability and resistance to sagging, making it easier to maintain with simple spot cleaning and occasional fluffing to preserve its shape. Open-cell foam, being softer and more porous, requires more frequent replacement as it absorbs moisture and dirt more readily, leading to quicker wear and tear. Proper care of high-resilience foam involves minimal effort compared to open-cell foam, which demands regular airing and protection from spills to extend its lifespan in chair seats.
Cost Efficiency and Value Assessment
High-resilience (HR) foam offers superior durability and support compared to open-cell foam, typically resulting in a longer lifespan and reduced replacement costs for chair seats. Although HR foam has a higher upfront cost, its resilience and ability to maintain shape contribute to enhanced value and comfort over time. Open-cell foam, being less dense and cheaper, may require more frequent replacement, increasing long-term expenses and potentially lowering overall cost efficiency.
Which Foam is Better for Your Chair Seat?
High-resilience foam offers superior durability, support, and shape retention, making it ideal for chair seats subjected to frequent use and heavier weight. Open-cell foam provides a softer, more breathable cushioning but tends to compress faster and lose firmness over time. For long-lasting comfort and structural integrity, high-resilience foam is generally better suited for chair seats.
Infographic: High-resilience foam vs Open-cell foam for Chair seat
 azmater.com
azmater.com