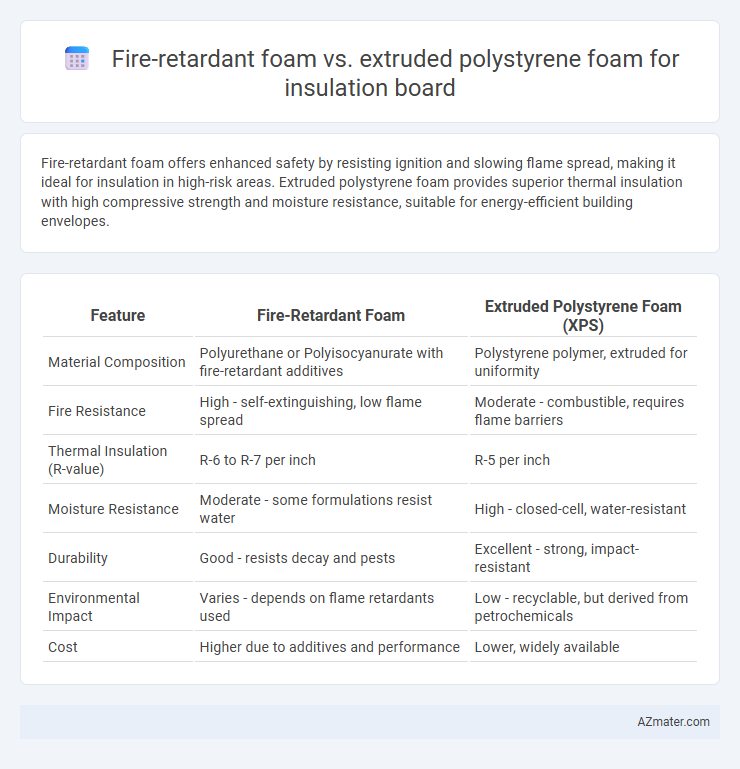
Fire-retardant foam offers enhanced safety by resisting ignition and slowing flame spread, making it ideal for insulation in high-risk areas. Extruded polystyrene foam provides superior thermal insulation with high compressive strength and moisture resistance, suitable for energy-efficient building envelopes.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fire-Retardant Foam | Extruded Polystyrene Foam (XPS) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polyurethane or Polyisocyanurate with fire-retardant additives | Polystyrene polymer, extruded for uniformity |
| Fire Resistance | High - self-extinguishing, low flame spread | Moderate - combustible, requires flame barriers |
| Thermal Insulation (R-value) | R-6 to R-7 per inch | R-5 per inch |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate - some formulations resist water | High - closed-cell, water-resistant |
| Durability | Good - resists decay and pests | Excellent - strong, impact-resistant |
| Environmental Impact | Varies - depends on flame retardants used | Low - recyclable, but derived from petrochemicals |
| Cost | Higher due to additives and performance | Lower, widely available |
Introduction to Insulation Materials
Fire-retardant foam and extruded polystyrene foam are key insulation materials used in building construction for thermal resistance and fire safety. Fire-retardant foam contains additives that enhance its ability to resist ignition and slow fire spread, making it suitable for applications requiring stringent fire codes compliance. Extruded polystyrene foam offers high compressive strength, moisture resistance, and excellent thermal insulation, widely used for wall sheathing, roofing, and below-grade insulation.
What is Fire-Retardant Foam?
Fire-retardant foam is a type of insulation material engineered to resist ignition and slow the spread of fire, enhancing building safety by meeting stringent fire codes and standards. Unlike extruded polystyrene foam, which primarily provides thermal insulation but is combustible, fire-retardant foam incorporates chemical additives or proprietary formulations to improve flame resistance while maintaining effective thermal performance. This specialized foam is widely used in applications demanding higher fire safety, such as commercial buildings and industrial insulation systems.
Understanding Extruded Polystyrene Foam (XPS)
Extruded Polystyrene Foam (XPS) is a closed-cell insulation board known for its high compressive strength, moisture resistance, and thermal performance with an R-value typically around 5 per inch. Fire-retardant foams offer enhanced fire resistance but may have lower insulation efficiency compared to XPS, which balances durability and energy efficiency in building applications. Understanding the specific fire rating and thermal properties of XPS ensures optimal selection for insulation boards in construction projects requiring moisture control and mechanical stability.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Fire-retardant foam insulation boards exhibit enhanced thermal stability with a typical R-value ranging from 3.5 to 4.0 per inch, maintaining integrity under elevated temperatures. Extruded polystyrene (XPS) foam offers a higher R-value, approximately 5 per inch, providing superior thermal resistance but with lower fire resistance compared to fire-retardant foams. The choice between these materials depends on balancing higher thermal efficiency of XPS against the improved fire safety profile of fire-retardant foam in building insulation applications.
Fire Resistance and Safety Considerations
Fire-retardant foam offers enhanced fire resistance through chemical additives that slow ignition and reduce flame spread, making it a safer choice in high-risk environments compared to extruded polystyrene foam (XPS), which is inherently flammable and can emit toxic gases when burned. While XPS provides excellent thermal insulation and moisture resistance, it generally requires additional fire barriers or treatments to meet safety standards in building applications. Prioritizing fire-retardant foam in insulation boards improves occupant safety by minimizing fire hazards and complying with stringent fire codes.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Fire-retardant foam typically contains chemical additives that may release harmful substances during production and disposal, raising environmental concerns compared to extruded polystyrene foam (XPS), which is generally more stable but derived from non-renewable petroleum resources. XPS insulation boards offer superior thermal resistance and moisture resistance, contributing to building energy efficiency and lower carbon footprints over time, yet their environmental impact is heightened by the difficulty of recycling and persistence in landfills. Sustainable alternatives emphasize the balance between fire safety, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and end-of-life recyclability, with increasing interest in bio-based or recycled-content foams that minimize ecological harm.
Moisture and Mold Resistance
Fire-retardant foam insulation offers enhanced resistance to moisture absorption and mold growth due to its chemical additives that inhibit microbial development. Extruded polystyrene foam (XPS) demonstrates superior water resistance with a low water vapor permeability rating of approximately 0.1 perm, effectively preventing moisture intrusion and reducing mold risk. Both materials provide reliable moisture control, but XPS typically surpasses fire-retardant foams in sustained moisture resistance and long-term mold prevention in insulation board applications.
Installation Methods and Applications
Fire-retardant foam insulation boards require careful installation using specialized adhesives and protective gear to ensure safety and proper curing, making them ideal for high-risk fire zones and industrial settings. Extruded polystyrene (XPS) foam boards are installed with mechanical fasteners or compatible adhesives and are commonly used in residential walls, roofs, and below-grade applications due to their moisture resistance and structural rigidity. Both materials demand precise cutting and sealing techniques to maximize thermal performance and long-term durability in their respective applications.
Cost Analysis and Longevity
Fire-retardant foam insulation boards typically cost more upfront due to specialized additives that enhance flame resistance, while extruded polystyrene (XPS) foam offers a more economical initial investment with strong thermal performance. In terms of longevity, XPS provides excellent moisture resistance and durability, often lasting 25 to 30 years, whereas fire-retardant foam's lifespan can vary widely depending on the specific formulation and environmental exposure. Balancing cost and longevity, XPS foam generally delivers better long-term value in standard insulation applications, while fire-retardant foam is preferred where enhanced fire safety is a critical concern.
Choosing the Right Insulation Board
Fire-retardant foam offers superior fire resistance and thermal insulation, making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced safety and compliance with strict fire codes. Extruded polystyrene foam (XPS) excels in moisture resistance and compressive strength, suitable for below-grade or high-load environments like foundations and roofs. Choosing the right insulation board depends on balancing fire safety standards, moisture exposure, and structural requirements to optimize energy efficiency and durability.
Infographic: Fire-retardant foam vs Extruded polystyrene foam for Insulation board
 azmater.com
azmater.com