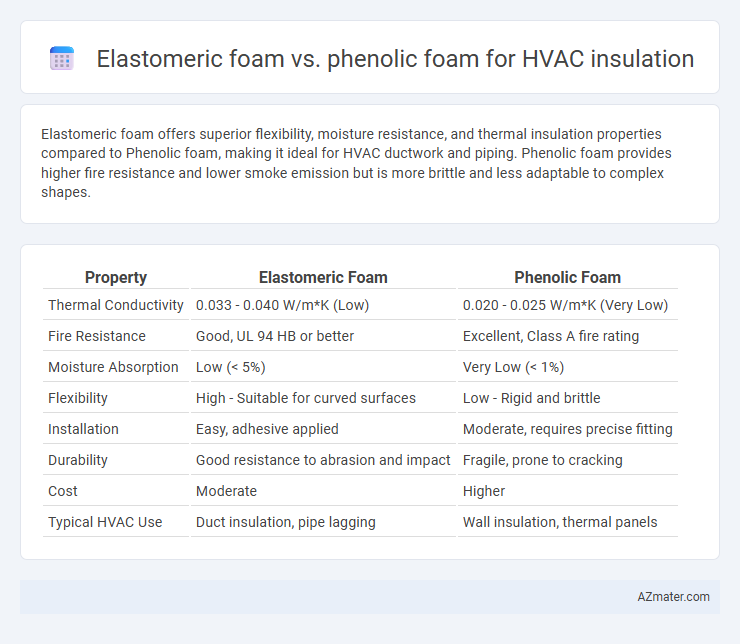
Elastomeric foam offers superior flexibility, moisture resistance, and thermal insulation properties compared to Phenolic foam, making it ideal for HVAC ductwork and piping. Phenolic foam provides higher fire resistance and lower smoke emission but is more brittle and less adaptable to complex shapes.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Elastomeric Foam | Phenolic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.033 - 0.040 W/m*K (Low) | 0.020 - 0.025 W/m*K (Very Low) |
| Fire Resistance | Good, UL 94 HB or better | Excellent, Class A fire rating |
| Moisture Absorption | Low (< 5%) | Very Low (< 1%) |
| Flexibility | High - Suitable for curved surfaces | Low - Rigid and brittle |
| Installation | Easy, adhesive applied | Moderate, requires precise fitting |
| Durability | Good resistance to abrasion and impact | Fragile, prone to cracking |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
| Typical HVAC Use | Duct insulation, pipe lagging | Wall insulation, thermal panels |
Introduction to HVAC Insulation Materials
Elastomeric foam and phenolic foam are commonly used HVAC insulation materials, each offering unique thermal and moisture resistance properties essential for energy-efficient heating and cooling systems. Elastomeric foam, known for its flexibility and closed-cell structure, provides excellent vapor barrier capabilities and durability against condensation. Phenolic foam distinguishes itself with superior fire resistance, low smoke emission, and high thermal insulation value, making it ideal for stringent safety standards in commercial HVAC applications.
What is Elastomeric Foam?
Elastomeric foam is a flexible, closed-cell insulation material widely used in HVAC systems to prevent heat loss and control condensation. Its unique rubber-like properties offer excellent thermal insulation, moisture resistance, and sound absorption, making it ideal for ductwork and piping applications. Compared to phenolic foam, elastomeric foam provides superior flexibility and durability, especially in environments with temperature fluctuations and mechanical stress.
What is Phenolic Foam?
Phenolic foam is a rigid, closed-cell insulation material characterized by its excellent thermal resistance and fire-retardant properties, making it ideal for HVAC applications. This foam features a low smoke emission and high dimensional stability, which enhances safety and durability in ductwork and piping insulation. Its inherently higher R-value per inch compared to elastomeric foam ensures superior energy efficiency and long-term performance in temperature control.
Thermal Performance: Elastomeric vs Phenolic
Elastomeric foam offers superior thermal performance for HVAC insulation due to its low thermal conductivity, typically around 0.034 to 0.040 W/m*K, providing excellent resistance to heat transfer and preventing condensation. Phenolic foam also delivers effective insulation with thermal conductivity values generally ranging from 0.022 to 0.030 W/m*K, making it highly efficient in reducing energy loss. While phenolic foam boasts a lower thermal conductivity, elastomeric foam's flexibility and vapor barrier properties often make it more suitable for dynamic or moisture-sensitive HVAC applications.
Fire Resistance Comparison
Elastomeric foam offers superior fire resistance with low smoke emission and self-extinguishing properties, making it ideal for HVAC insulation where safety is crucial. Phenolic foam provides excellent fire retardant capabilities, including a high char yield that slows flame spread and reduces heat release. Both materials meet stringent fire safety standards, but elastomeric foam is often preferred for applications requiring enhanced smoke control.
Moisture and Vapor Resistance
Elastomeric foam offers superior moisture and vapor resistance compared to phenolic foam, making it highly effective in preventing condensation and maintaining insulation integrity in HVAC systems. Its closed-cell structure minimizes water absorption and vapor permeability, reducing the risk of mold growth and corrosion. Phenolic foam, while providing good thermal insulation, tends to be more hygroscopic and less resilient against moisture infiltration, which can compromise long-term performance in humid environments.
Installation and Handling Differences
Elastomeric foam offers greater flexibility and ease of installation due to its lightweight and pliable nature, making it ideal for wrapping around complex HVAC ductwork with minimal cutting and fitting. Phenolic foam, while providing superior fire resistance and thermal insulation, is more rigid and brittle, requiring careful handling and specialized tools to avoid cracking or damage during installation. Elastomeric foam's moisture-resistant properties ensure fewer issues with condensation, whereas phenolic foam demands additional protective measures to maintain durability in humid environments.
Longevity and Maintenance
Elastomeric foam offers superior longevity in HVAC insulation due to its resistance to moisture, UV exposure, and microbial growth, reducing maintenance frequency. Phenolic foam provides excellent thermal performance but tends to be more brittle and susceptible to cracking over time, increasing the need for repairs. Maintenance costs for elastomeric foam are typically lower, making it a more durable and cost-effective solution for long-term HVAC system protection.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Elastomeric foam offers superior environmental benefits for HVAC insulation due to its low Global Warming Potential (GWP) and zero Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP), often manufactured with CFC-free blowing agents that contribute to sustainability. Phenolic foam, while having good thermal performance, generally contains formaldehyde and other organic compounds that can pose environmental and health risks during production and disposal. Choosing elastomeric foam supports greener building practices by minimizing harmful emissions and enhancing energy efficiency over the product lifecycle.
Cost Considerations and ROI
Elastomeric foam offers lower upfront costs and flexibility benefits for HVAC insulation but may incur higher maintenance expenses over time compared to phenolic foam. Phenolic foam presents a higher initial investment with superior thermal resistance and fire performance, potentially reducing energy costs and enhancing ROI through long-term efficiency gains. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including installation, durability, and energy savings, is critical for optimizing HVAC insulation investments.
Infographic: Elastomeric foam vs Phenolic foam for HVAC insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com