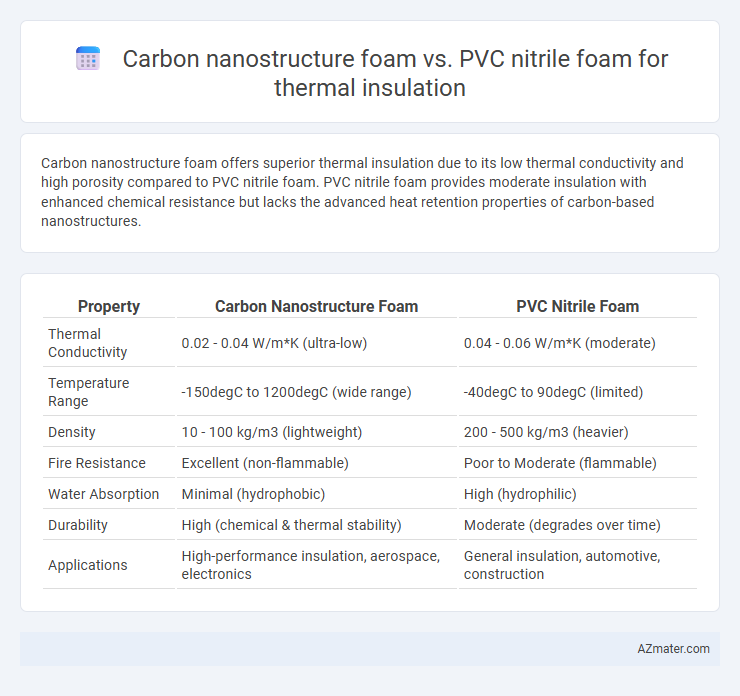
Carbon nanostructure foam offers superior thermal insulation due to its low thermal conductivity and high porosity compared to PVC nitrile foam. PVC nitrile foam provides moderate insulation with enhanced chemical resistance but lacks the advanced heat retention properties of carbon-based nanostructures.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Nanostructure Foam | PVC Nitrile Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.02 - 0.04 W/m*K (ultra-low) | 0.04 - 0.06 W/m*K (moderate) |
| Temperature Range | -150degC to 1200degC (wide range) | -40degC to 90degC (limited) |
| Density | 10 - 100 kg/m3 (lightweight) | 200 - 500 kg/m3 (heavier) |
| Fire Resistance | Excellent (non-flammable) | Poor to Moderate (flammable) |
| Water Absorption | Minimal (hydrophobic) | High (hydrophilic) |
| Durability | High (chemical & thermal stability) | Moderate (degrades over time) |
| Applications | High-performance insulation, aerospace, electronics | General insulation, automotive, construction |
Introduction to Thermal Insulation Materials
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits exceptional thermal insulation properties due to its low thermal conductivity and high porosity, making it ideal for advanced insulating applications. PVC nitrile foam, commonly used for thermal insulation in construction and industrial settings, provides effective heat resistance and durability but generally has higher thermal conductivity compared to carbon nanostructures. The choice between these materials depends on the balance between thermal performance, mechanical strength, and cost efficiency in insulation design.
Overview of Carbon Nanostructure Foam
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits exceptional thermal insulation properties due to its low density, high porosity, and superior heat resistance compared to traditional PVC nitrile foam. Its unique hierarchical porous network significantly reduces thermal conductivity while maintaining mechanical strength and durability in extreme temperatures. This makes carbon nanostructure foam highly suitable for advanced insulation applications in aerospace, electronics, and cryogenics.
Key Properties of PVC Nitrile Foam
PVC nitrile foam offers exceptional thermal insulation due to its closed-cell structure, which effectively minimizes heat transfer and provides excellent resistance to moisture and chemicals. Its flexibility, durability, and resistance to oil and abrasion make it ideal for demanding industrial environments where thermal performance and mechanical strength are critical. Unlike carbon nanostructure foams, PVC nitrile foam combines thermal insulation with enhanced mechanical properties, ensuring long-term stability and energy efficiency in thermal management applications.
Thermal Conductivity: Carbon Nanostructure vs PVC Nitrile
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits significantly lower thermal conductivity, typically around 0.02 W/m*K, compared to PVC nitrile foam, which ranges from 0.035 to 0.05 W/m*K, making it more effective for thermal insulation. The unique porous architecture and high surface area of carbon nanostructure foam enable superior heat dissipation and reduced heat transfer. PVC nitrile foam, while cost-effective and versatile, generally provides moderate insulation performance due to higher thermal conductivity and denser cellular structure.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits superior mechanical strength due to its high tensile strength and resistance to deformation, outperforming PVC nitrile foam which tends to degrade under mechanical stress. The durability of carbon nanostructure foam is enhanced by its resistance to thermal cycling and chemical exposure, maintaining structural integrity over prolonged use. PVC nitrile foam, while cost-effective, shows faster wear and tear in harsh environments, making carbon nanostructure foam a more robust choice for long-term thermal insulation applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbon nanostructure foam offers superior thermal insulation with significantly lower environmental impact due to its high durability, recyclability, and reduced need for frequent replacement compared to PVC nitrile foam. PVC nitrile foam, while effective as an insulator, relies on petroleum-based materials and emits toxic substances during production and disposal, contributing to environmental pollution and challenging waste management. The sustainability of carbon nanostructure foam is further enhanced by its potential for energy-efficient manufacturing processes and minimal off-gassing, supporting eco-friendly building practices and reducing carbon footprint.
Moisture Resistance and Longevity
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits superior moisture resistance compared to PVC nitrile foam due to its hydrophobic surface and dense nanostructured matrix, which reduces water absorption and prevents degradation. PVC nitrile foam tends to absorb moisture over time, leading to diminished thermal insulation performance and potential material breakdown. Consequently, carbon nanostructure foam offers enhanced longevity and sustained thermal insulation efficiency in humid or wet environments.
Fire Safety and Chemical Stability
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits superior fire safety compared to PVC nitrile foam due to its inherent non-combustible nature and higher thermal stability, significantly reducing fire hazards in insulation applications. Chemical stability in carbon nanostructure foam remains robust under harsh environments, resisting oxidation and corrosion better than PVC nitrile foam, which can degrade and release toxic fumes when exposed to heat or chemicals. These properties make carbon nanostructure foam a more reliable and safer choice for thermal insulation in fire-sensitive and chemically aggressive conditions.
Cost-effectiveness and Practical Applications
Carbon nanostructure foam offers superior thermal insulation with high thermal stability and low thermal conductivity, making it cost-effective for advanced industrial applications despite higher initial material costs. PVC nitrile foam provides a more affordable solution with decent insulation properties, widely used in building construction, automotive, and HVAC systems due to its flexibility and moisture resistance. Practical applications favor PVC nitrile foam for budget-conscious projects, whereas carbon nanostructure foam suits specialized environments requiring enhanced performance and durability.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Insulation Material
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits superior thermal insulation properties compared to PVC nitrile foam, offering higher thermal resistance and durability under extreme temperatures. Its lightweight nature and enhanced mechanical strength make it ideal for advanced applications demanding efficiency and longevity. Selecting carbon nanostructure foam ensures optimal thermal management, energy savings, and long-term performance in insulation systems.
Infographic: Carbon nanostructure foam vs PVC nitrile foam for Thermal insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com