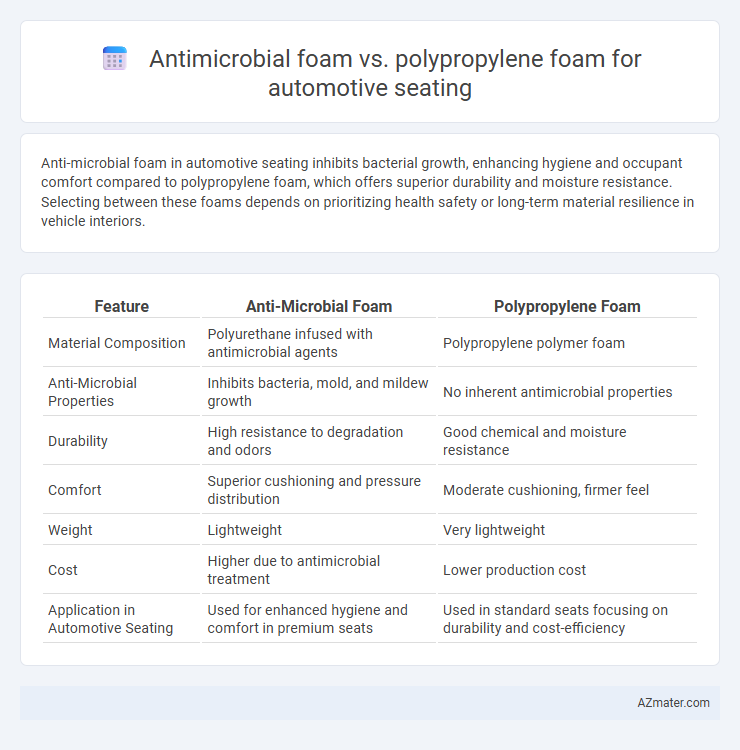
Anti-microbial foam in automotive seating inhibits bacterial growth, enhancing hygiene and occupant comfort compared to polypropylene foam, which offers superior durability and moisture resistance. Selecting between these foams depends on prioritizing health safety or long-term material resilience in vehicle interiors.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Anti-Microbial Foam | Polypropylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polyurethane infused with antimicrobial agents | Polypropylene polymer foam |
| Anti-Microbial Properties | Inhibits bacteria, mold, and mildew growth | No inherent antimicrobial properties |
| Durability | High resistance to degradation and odors | Good chemical and moisture resistance |
| Comfort | Superior cushioning and pressure distribution | Moderate cushioning, firmer feel |
| Weight | Lightweight | Very lightweight |
| Cost | Higher due to antimicrobial treatment | Lower production cost |
| Application in Automotive Seating | Used for enhanced hygiene and comfort in premium seats | Used in standard seats focusing on durability and cost-efficiency |
Introduction to Automotive Seating Materials
Automotive seating materials require a balance of comfort, durability, and hygiene, with anti-microbial foam and polypropylene foam serving distinct roles in this domain. Anti-microbial foam incorporates agents that inhibit bacterial growth, enhancing seat hygiene and reducing odors, making it ideal for vehicles with high passenger turnover or extended use. Polypropylene foam offers superior lightweight cushioning and excellent resistance to moisture and chemicals, contributing to increased seat longevity and vehicle fuel efficiency through weight reduction.
Overview of Anti-Microbial Foam
Anti-microbial foam used in automotive seating incorporates biocidal agents that inhibit the growth of bacteria, mold, and mildew, enhancing passenger hygiene and extending seat durability. This foam type supports improved air quality inside vehicles by reducing microbial proliferation, which is critical in high-traffic environments and shared transportation. Compared to polypropylene foam, anti-microbial foam provides superior protection against odors and degradation caused by microorganisms, contributing to healthier and longer-lasting automotive interiors.
Key Features of Polypropylene Foam
Polypropylene foam offers exceptional durability and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for automotive seating applications that require long-lasting performance and comfort. Its lightweight structure enhances fuel efficiency by reducing overall vehicle weight while maintaining excellent cushioning and impact absorption. Polypropylene foam also provides superior chemical resistance and thermal insulation, ensuring seat integrity in varying environmental conditions.
Comparative Durability in Seating Applications
Anti-microbial foam incorporates antimicrobial agents that inhibit bacterial growth, enhancing hygiene and extending seat longevity against microbial degradation, while polypropylene foam offers superior mechanical durability, resisting compression and deformation under prolonged load. In automotive seating applications, polypropylene foam demonstrates greater resilience to wear and maintains structural integrity under dynamic stresses, whereas anti-microbial foam provides added protection against odor and contamination without compromising moderately on durability. Selecting between the two depends on prioritizing infection control versus long-term mechanical performance in vehicle seating environments.
Anti-Microbial Properties: Benefits and Limitations
Anti-microbial foam used in automotive seating offers superior protection against bacteria, mold, and fungi compared to standard polypropylene foam, enhancing hygiene and reducing odors in vehicle interiors. These foams integrate antimicrobial agents within their cellular structure, providing long-lasting defense that is particularly beneficial in high-use or humid environments. However, anti-microbial foams can incur higher costs and may have limitations in terms of durability and chemical resistance when exposed to certain automotive cleaning products.
Comfort and Ergonomics Considerations
Anti-microbial foam enhances automotive seating comfort by preventing bacterial growth, maintaining freshness, and reducing odors, which contributes to a healthier in-cabin environment over time. Polypropylene foam offers superior ergonomic support due to its high resilience and structural stability, ensuring consistent cushioning and spinal alignment during long drives. Combining anti-microbial properties with polypropylene foam technology maximizes both hygiene and ergonomic benefits for automotive seat comfort.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Anti-microbial foam used in automotive seating offers enhanced hygiene by inhibiting bacterial growth, but often relies on chemical treatments that may raise environmental concerns during production and disposal. Polypropylene foam is noted for its recyclability and lower carbon footprint due to its lightweight nature and energy-efficient manufacturing processes, contributing positively to sustainability goals. Selecting polypropylene foam supports automotive industry efforts to reduce environmental impact through material circularity and reduced waste generation.
Cost-Effectiveness of Each Foam
Polypropylene foam offers a lower initial cost compared to anti-microbial foam, making it a more budget-friendly option for large-scale automotive seating production. Anti-microbial foam, although typically more expensive upfront, reduces long-term maintenance costs by inhibiting bacterial growth and odors, extending seat lifespan and enhancing passenger hygiene. Evaluating total cost-effectiveness involves balancing polypropylene foam's affordability with the health and durability benefits delivered by anti-microbial foam in automotive interiors.
Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Anti-microbial foam for automotive seating offers enhanced protection against bacteria, mold, and allergens, contributing to improved occupant health and meeting stringent hygiene standards set by regulatory bodies like FMVSS and ECE R118. Polypropylene foam, while lightweight and impact-absorbing, lacks inherent antimicrobial properties, potentially increasing risks of microbial contamination and complicating compliance with evolving safety regulations focused on passenger wellbeing. Choosing anti-microbial foam aligns with industry trends prioritizing both passenger safety and regulatory adherence, ensuring automotive seats meet international hygiene and fire-retardant standards.
Future Trends in Automotive Foam Seating
Future trends in automotive seating highlight the growing adoption of anti-microbial foam due to its superior resistance to bacteria, fungi, and odors, enhancing passenger hygiene and comfort. Polypropylene foam remains valued for its lightweight, cost-effective, and recyclable properties, contributing to overall vehicle efficiency and sustainability goals. Innovations in foam materials increasingly emphasize eco-friendly manufacturing, enhanced durability, and integration with smart textile technologies for improved occupant health monitoring.
Infographic: Anti-microbial foam vs Polypropylene foam for Automotive Seating
 azmater.com
azmater.com