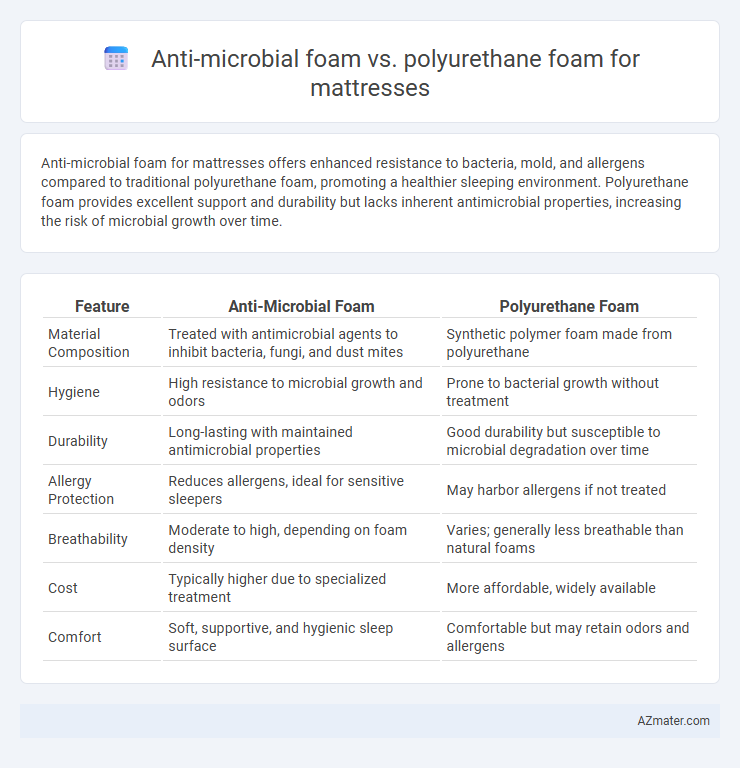
Anti-microbial foam for mattresses offers enhanced resistance to bacteria, mold, and allergens compared to traditional polyurethane foam, promoting a healthier sleeping environment. Polyurethane foam provides excellent support and durability but lacks inherent antimicrobial properties, increasing the risk of microbial growth over time.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Anti-Microbial Foam | Polyurethane Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Treated with antimicrobial agents to inhibit bacteria, fungi, and dust mites | Synthetic polymer foam made from polyurethane |
| Hygiene | High resistance to microbial growth and odors | Prone to bacterial growth without treatment |
| Durability | Long-lasting with maintained antimicrobial properties | Good durability but susceptible to microbial degradation over time |
| Allergy Protection | Reduces allergens, ideal for sensitive sleepers | May harbor allergens if not treated |
| Breathability | Moderate to high, depending on foam density | Varies; generally less breathable than natural foams |
| Cost | Typically higher due to specialized treatment | More affordable, widely available |
| Comfort | Soft, supportive, and hygienic sleep surface | Comfortable but may retain odors and allergens |
Introduction to Mattress Foam Technologies
Anti-microbial foam incorporates specialized agents to inhibit the growth of bacteria, mold, and allergens, enhancing mattress hygiene and longevity. Polyurethane foam, a versatile and widely used material, offers customizable firmness and support through varying density and cushioning properties. Both technologies play crucial roles in mattress innovation by improving comfort, durability, and sleep quality.
What is Anti-Microbial Foam?
Anti-microbial foam is a type of mattress foam treated with antimicrobial agents designed to inhibit the growth of bacteria, mold, and mildew, enhancing hygiene and durability. Unlike standard polyurethane foam, which primarily offers comfort and support, anti-microbial foam actively contributes to a healthier sleep environment by reducing allergens and preventing odor-causing microbes. This foam is especially beneficial for individuals with allergies or sensitive skin, providing long-lasting protection against microbial buildup in mattresses.
Understanding Polyurethane Foam
Polyurethane foam, a versatile and widely used material in mattresses, offers excellent support and pressure relief while maintaining breathability and durability. Unlike anti-microbial foam, polyurethane foam does not inherently resist bacteria or allergens but can be treated with antimicrobial agents to enhance hygiene and prolong mattress lifespan. Its open-cell structure promotes airflow, making it a popular choice for combination comfort and temperature regulation in bedding.
Key Differences Between Anti-Microbial and Polyurethane Foam
Anti-microbial foam contains additives that inhibit the growth of bacteria, fungi, and dust mites, enhancing hygiene and reducing allergens in mattresses. Polyurethane foam, commonly used for cushioning, lacks inherent antimicrobial properties but offers durability and pressure relief through its flexible and supportive structure. The primary difference lies in anti-microbial foam's targeted health benefits versus polyurethane foam's emphasis on comfort and resilience.
Health and Hygiene Benefits: A Comparative Analysis
Anti-microbial foam mattresses offer superior protection against bacteria, mold, and dust mites compared to traditional polyurethane foam, significantly reducing allergic reactions and respiratory issues. The embedded antimicrobial agents inhibit microbial growth, enhancing hygiene and extending mattress lifespan. Polyurethane foam lacks these inherent properties, making it more susceptible to microbial contamination and requiring more frequent cleaning to maintain health standards.
Durability and Longevity of Mattress Foams
Anti-microbial foam offers enhanced resistance to bacteria, mold, and mildew, significantly extending the durability of mattresses compared to standard polyurethane foam, which is more prone to microbial degradation over time. Polyurethane foam tends to compress and lose its structural integrity faster, leading to a shorter lifespan, whereas anti-microbial foam maintains consistent support and hygiene for a longer period. Choosing anti-microbial foam improves mattress longevity by preserving foam density and preventing odor-causing microbial buildup.
Comfort and Support: Which Foam Performs Better?
Anti-microbial foam offers enhanced comfort by resisting bacterial growth, maintaining hygiene and freshness for prolonged use, making it ideal for sensitive skin and allergy sufferers. Polyurethane foam typically provides firmer support and durability due to its dense structure, effectively contouring to body shapes and offering consistent spinal alignment. When prioritizing comfort, anti-microbial foam excels in breathability and softness, whereas polyurethane foam outperforms in long-lasting support and resilience.
Allergen Resistance and Sleep Quality
Anti-microbial foam in mattresses provides superior allergen resistance by inhibiting the growth of bacteria, mold, and dust mites, significantly reducing allergen exposure for sensitive sleepers. Polyurethane foam, while offering good support and comfort, lacks inherent antimicrobial properties, making it more prone to harboring allergens that can disrupt sleep quality. Enhanced allergen resistance in anti-microbial foam contributes to a cleaner sleep environment, promoting uninterrupted rest and improved overall sleep quality.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability Considerations
Anti-microbial foam is often produced with specialized treatments that can introduce chemicals impacting biodegradability, whereas polyurethane foam typically relies on petrochemical bases with a higher carbon footprint due to energy-intensive manufacturing. Sustainable alternatives like plant-based polyurethane foams reduce reliance on fossil fuels and improve environmental profiles compared to conventional foams. Both foams pose recycling challenges, but advances in foam recycling technologies and biodegradable additives are progressively enhancing their sustainability.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Mattress Needs
Anti-microbial foam offers enhanced resistance to bacteria, mold, and allergens, making it ideal for individuals with allergies or respiratory sensitivities. Polyurethane foam provides excellent support and durability at a generally lower cost but may lack inherent antimicrobial properties unless treated. Choosing the right foam depends on prioritizing health benefits versus budget and support requirements for optimal mattress performance.
Infographic: Anti-microbial foam vs Polyurethane foam for Mattress
 azmater.com
azmater.com