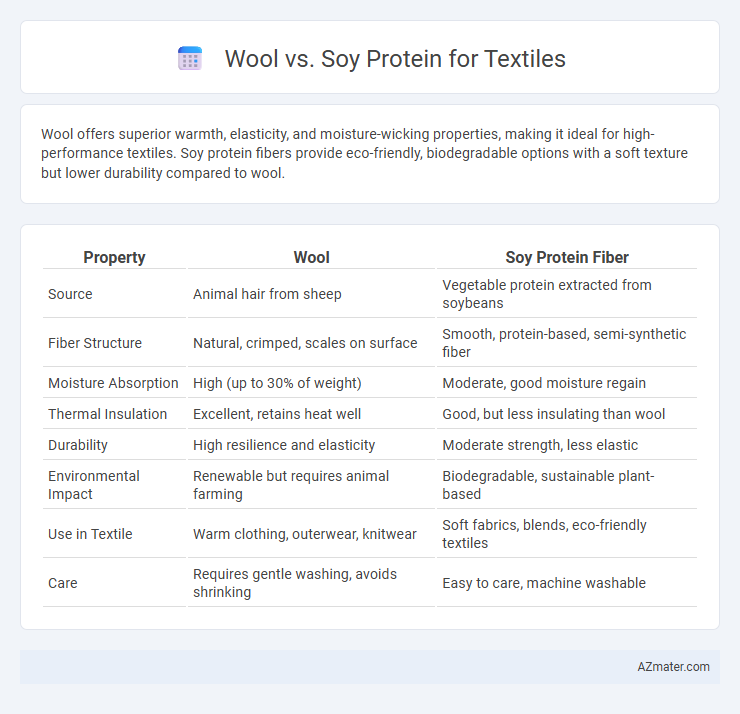
Wool offers superior warmth, elasticity, and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for high-performance textiles. Soy protein fibers provide eco-friendly, biodegradable options with a soft texture but lower durability compared to wool.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Wool | Soy Protein Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Animal hair from sheep | Vegetable protein extracted from soybeans |
| Fiber Structure | Natural, crimped, scales on surface | Smooth, protein-based, semi-synthetic fiber |
| Moisture Absorption | High (up to 30% of weight) | Moderate, good moisture regain |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent, retains heat well | Good, but less insulating than wool |
| Durability | High resilience and elasticity | Moderate strength, less elastic |
| Environmental Impact | Renewable but requires animal farming | Biodegradable, sustainable plant-based |
| Use in Textile | Warm clothing, outerwear, knitwear | Soft fabrics, blends, eco-friendly textiles |
| Care | Requires gentle washing, avoids shrinking | Easy to care, machine washable |
Introduction to Wool and Soy Protein in Textiles
Wool, a natural fiber derived from sheep, is prized in textile production for its excellent insulation, moisture-wicking properties, and durability, making it ideal for apparel and upholstery. Soy protein fiber, produced from regenerated soybeans, offers a sustainable alternative with a soft, silk-like texture, high biodegradability, and antimicrobial qualities beneficial for eco-friendly fashion. Both fibers emphasize renewable resources but differ in origin; wool is animal-based while soy protein is plant-based, influencing their applications and environmental impacts in the textile industry.
Origin and Processing of Wool vs Soy Protein
Wool originates from the fleece of sheep and undergoes processes such as shearing, scouring, carding, and spinning to transform raw fiber into yarn suitable for textiles. Soy protein fiber, derived from soybean protein isolate, involves chemical extraction, wet spinning, and drying to create a soft, biodegradable textile fiber. The natural animal-based origin of wool contrasts with the plant-based, sustainable origin of soy protein fibers, influencing their environmental footprints and functional properties in textile applications.
Fiber Structure and Composition Comparison
Wool fibers consist primarily of keratin proteins with a complex, scaly surface that provides excellent insulation and elasticity, while soy protein fibers are made from regenerated soy protein polymers with a smoother surface and higher moisture retention. Wool's natural crimp enhances loft and resilience, whereas soy fibers offer a softer, silk-like texture due to their protein-based structure and amino acid composition. The differences in fiber morphology and protein composition directly influence the durability, comfort, and biodegradability of wool and soy protein textiles.
Environmental Impact: Wool vs Soy Protein
Wool production generates higher greenhouse gas emissions and consumes more water compared to soy protein fibers, which are derived from renewable plant sources with a lower carbon footprint. Soy protein textiles offer enhanced biodegradability and require fewer pesticides and fertilizers than conventional wool farming, reducing soil and water pollution. However, wool is naturally durable and biodegradable, making it a sustainable choice when sourced from responsibly managed sheep farms.
Comfort and Wearability: Which Feels Better?
Wool fibers provide exceptional warmth, breathability, and moisture-wicking properties, resulting in high comfort and natural elasticity that enhances wearability in cold conditions. Soy protein fibers, derived from renewable sources, offer a soft, smooth texture with excellent moisture absorption and hypoallergenic qualities, making garments gentle on sensitive skin and comfortable for extended wear. When comparing comfort, wool excels in thermal regulation and durability, while soy protein ensures a silkier feel and lightweight softness, appealing to those prioritizing gentle touch and skin sensitivity.
Durability and Performance in Fabric Production
Wool fibers exhibit exceptional durability due to their natural crimp and elasticity, which enhance fabric resilience and longevity in textile production. Soy protein fibers, derived from renewable sources, offer good softness and moisture absorption but generally fall short in tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to wool. For high-performance fabric applications requiring robust durability, wool remains the superior choice, while soy protein contributes sustainable and comfortable alternatives in less demanding uses.
Dyeing, Printing, and Color Fastness
Wool fiber exhibits superior dye affinity and color fastness due to its natural protein structure, enabling deep dye penetration and vibrant hues in textile applications. Soy protein fibers offer a softer hand and eco-friendly alternative but generally demonstrate lower dye uptake and color fastness compared to wool, requiring specialized dyeing techniques to enhance performance. In printing processes, wool maintains sharper patterns with less bleeding, whereas soy protein may need chemical treatments to improve print clarity and durability.
Sustainability and Biodegradability Factors
Wool is a natural fiber derived from sheep, prized for its biodegradability and renewable nature, decomposing efficiently without releasing harmful residues. Soy protein fibers, produced from soy waste, offer a sustainable alternative with lower environmental impact due to reduced water use and carbon emissions during production. Both fibers support circular textile economies, but wool's long-standing biodegradability and durability provide advantages in natural decomposition compared to soy-based textiles.
Cost Analysis: Wool vs Soy Protein Textiles
Wool textiles generally incur higher production costs due to labor-intensive shearing, cleaning, and processing, while soy protein textiles benefit from lower raw material costs and more sustainable extraction methods. Soy protein fibers offer competitive pricing compared to wool, especially in large-scale manufacturing, making them an economical alternative in the textile industry. The cost differential is influenced by factors such as fiber yield, durability, and market demand, with soy proteins gaining traction for eco-friendly and cost-efficient fabric production.
Future Trends in Wool and Soy Protein Fabrics
Future trends in wool and soy protein fabrics emphasize sustainable innovation and eco-friendly production technologies. Wool advancements focus on enhanced fiber durability, improved moisture management, and biodegradability, while soy protein textiles gain attention for their softness, biodegradability, and use of renewable resources. Increasing consumer demand for natural, biodegradable, and high-performance textiles drives research into blending wool with soy protein fibers to achieve versatility and environmental benefits.
Infographic: Wool vs Soy protein for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com