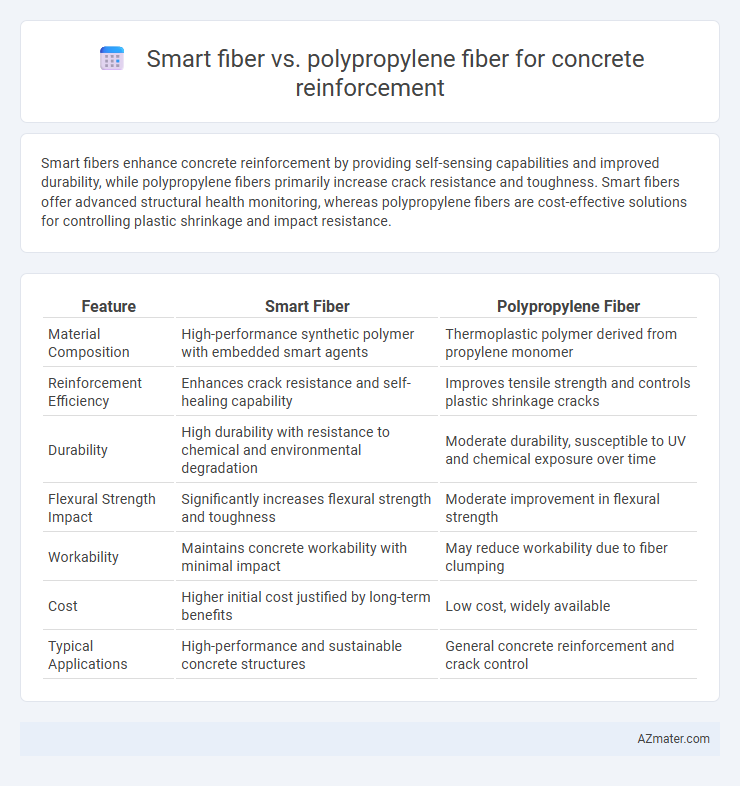
Smart fibers enhance concrete reinforcement by providing self-sensing capabilities and improved durability, while polypropylene fibers primarily increase crack resistance and toughness. Smart fibers offer advanced structural health monitoring, whereas polypropylene fibers are cost-effective solutions for controlling plastic shrinkage and impact resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Smart Fiber | Polypropylene Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | High-performance synthetic polymer with embedded smart agents | Thermoplastic polymer derived from propylene monomer |
| Reinforcement Efficiency | Enhances crack resistance and self-healing capability | Improves tensile strength and controls plastic shrinkage cracks |
| Durability | High durability with resistance to chemical and environmental degradation | Moderate durability, susceptible to UV and chemical exposure over time |
| Flexural Strength Impact | Significantly increases flexural strength and toughness | Moderate improvement in flexural strength |
| Workability | Maintains concrete workability with minimal impact | May reduce workability due to fiber clumping |
| Cost | Higher initial cost justified by long-term benefits | Low cost, widely available |
| Typical Applications | High-performance and sustainable concrete structures | General concrete reinforcement and crack control |
Introduction to Concrete Reinforcement
Concrete reinforcement enhances structural integrity and durability by improving tensile strength and crack resistance. Smart fibers, embedded with advanced sensors, provide real-time monitoring of strain and stress, while polypropylene fibers primarily focus on reducing shrinkage-induced cracking and improving impact resistance. Both fiber types contribute to reinforced concrete's performance, with smart fibers offering additional intelligence for structural health monitoring.
Overview of Smart Fibers
Smart fibers for concrete reinforcement consist of advanced materials such as shape memory alloys, carbon nanotubes, or synthetic fibers embedded with sensors that provide real-time monitoring of structural health and crack control. Unlike polypropylene fibers that primarily improve toughness and reduce shrinkage cracking, smart fibers offer adaptive responses to stress and damage, enhancing durability and extending the lifespan of reinforced concrete structures. Their integration supports predictive maintenance by detecting changes in strain and temperature, making them ideal for high-performance, intelligent infrastructure applications.
Understanding Polypropylene Fibers
Polypropylene fibers are widely used in concrete reinforcement due to their excellent tensile strength, chemical resistance, and ability to control plastic shrinkage cracks, enhancing the durability and longevity of concrete structures. These synthetic fibers improve impact resistance and reduce micro-cracking, making them a cost-effective solution for various construction applications. Unlike smart fibers, polypropylene fibers do not provide self-sensing or adaptive capabilities but remain a reliable choice for improving concrete performance under mechanical stress.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Smart fiber demonstrates superior tensile strength and elongation capacity compared to polypropylene fiber, enhancing crack resistance and durability in concrete reinforcement. Polypropylene fiber offers notable impact resistance and chemical inertness but falls short in load-bearing performance under tensile stress. The enhanced modulus of elasticity and bond strength of smart fiber contribute to improved mechanical integration within concrete matrices, leading to increased structural integrity and long-term performance.
Durability and Longevity
Smart fiber enhances concrete durability through superior crack resistance, reducing micro-cracking and improving structural integrity over time. Polypropylene fiber provides moderate durability by controlling plastic shrinkage cracks but may degrade under UV exposure and chemical attack, affecting longevity. Smart fiber's advanced composition offers extended lifespan and better performance in harsh environments compared to conventional polypropylene fiber.
Impact on Concrete Workability
Smart fiber enhances concrete workability by improving dispersion and reducing water demand, resulting in a smoother mix and easier placement compared to polypropylene fiber. Polypropylene fiber tends to increase the viscosity of the concrete mix, leading to potential challenges in flow and compaction. Optimizing fiber type and dosage is critical to maintaining desired workability while achieving effective reinforcement.
Crack Resistance Performance
Smart fiber offers superior crack resistance performance compared to polypropylene fiber due to its advanced material composition and high tensile strength, which effectively control micro-crack propagation and enhance the structural integrity of concrete. Polypropylene fibers provide adequate shrinkage crack control but have lower stiffness and bonding capacity, resulting in less efficient crack bridging under tensile stresses. Concrete reinforced with smart fiber demonstrates improved durability and reduced maintenance costs by minimizing crack widths and preventing crack development under dynamic loading conditions.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Smart fiber offers enhanced durability and crack resistance in concrete reinforcement but comes with a higher initial cost compared to polypropylene fiber. Polypropylene fiber, widely used for its affordability and ease of mixing, delivers effective microcrack control at a lower price point. When evaluating cost-effectiveness, polypropylene fibers provide a budget-friendly solution for large-scale projects, while smart fibers, despite higher upfront costs, may reduce long-term repair expenses and improve structural lifespan.
Applications in Modern Construction
Smart fiber enhances concrete reinforcement by providing superior crack control and self-sensing capabilities, making it ideal for advanced infrastructure like smart buildings and bridges. Polypropylene fiber is widely used for general applications due to its cost-effectiveness and excellent resistance to shrinkage cracking in precast panels, slabs, and industrial floors. Modern construction increasingly favors smart fibers for their durability and performance in high-stress environments, while polypropylene fibers remain popular for improving toughness and reducing plastic shrinkage in mass concrete pours.
Future Trends in Concrete Fiber Technology
Smart fiber technology in concrete reinforcement is advancing with self-sensing capabilities and enhanced durability, offering improved structural health monitoring and longevity compared to traditional polypropylene fibers. Polypropylene fibers remain popular for their cost-effectiveness and crack control but lack the adaptive properties found in smart fibers. Future trends emphasize integrating nanomaterials and AI-driven analytics to optimize fiber performance, enabling smarter, more resilient concrete infrastructures.
Infographic: Smart fiber vs Polypropylene fiber for Concrete reinforcement
 azmater.com
azmater.com