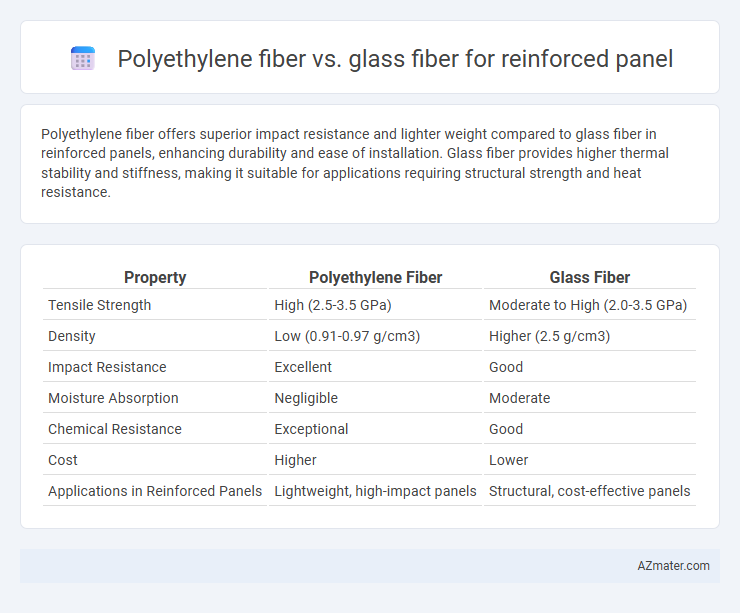
Polyethylene fiber offers superior impact resistance and lighter weight compared to glass fiber in reinforced panels, enhancing durability and ease of installation. Glass fiber provides higher thermal stability and stiffness, making it suitable for applications requiring structural strength and heat resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyethylene Fiber | Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | High (2.5-3.5 GPa) | Moderate to High (2.0-3.5 GPa) |
| Density | Low (0.91-0.97 g/cm3) | Higher (2.5 g/cm3) |
| Impact Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Moisture Absorption | Negligible | Moderate |
| Chemical Resistance | Exceptional | Good |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Applications in Reinforced Panels | Lightweight, high-impact panels | Structural, cost-effective panels |
Introduction: Polyethylene Fiber and Glass Fiber in Reinforced Panels
Polyethylene fiber and glass fiber are two commonly used materials for reinforced panels, each offering distinct benefits in strength and durability. Polyethylene fiber provides high impact resistance, excellent flexibility, and low weight, making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced toughness and corrosion resistance. Glass fiber, on the other hand, excels in tensile strength, stiffness, and thermal stability, often favored for structural reinforcement where rigidity and load-bearing capacity are critical.
Material Properties Overview
Polyethylene fiber exhibits high tensile strength, excellent impact resistance, and low density, making it ideal for lightweight reinforced panels requiring durability and flexibility. Glass fiber offers superior stiffness, excellent thermal stability, and higher compressive strength but is heavier and more brittle compared to polyethylene fiber. Material selection depends on specific performance criteria such as weight constraints, mechanical load, and environmental resistance in reinforced panel applications.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polyethylene fiber exhibits high tensile strength and impact resistance, making it suitable for lightweight reinforced panels requiring flexibility and durability. Glass fiber offers superior compressive strength and stiffness, providing enhanced rigidity and load-bearing capacity in reinforced panels. Mechanical strength comparison reveals glass fiber panels outperform polyethylene fiber panels in stiffness and hardness, while polyethylene fiber panels excel in toughness and resistance to crack propagation.
Weight and Density Considerations
Polyethylene fiber offers a significantly lower density, approximately 0.97 g/cm3, compared to glass fiber's density around 2.5 g/cm3, resulting in lighter reinforced panels. This weight advantage makes polyethylene fiber ideal for applications requiring high strength-to-weight ratios and improved handling ease. The reduced density also contributes to enhanced performance in weight-sensitive industries such as aerospace and automotive manufacturing.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Polyethylene fiber offers exceptional durability and superior resistance to moisture, chemicals, and UV radiation compared to glass fiber, making it highly suitable for reinforced panels exposed to harsh environments. Glass fiber, while providing high tensile strength and stiffness, is more susceptible to degradation from prolonged exposure to moisture and alkalis, which can compromise its long-term performance. The enhanced environmental resistance of polyethylene fiber panels contributes to lower maintenance costs and extended service life in applications requiring resilience against weathering and chemical exposure.
Flexibility and Impact Resistance
Polyethylene fiber offers superior flexibility and impact resistance compared to glass fiber in reinforced panels, making it ideal for applications requiring high toughness and durability. Glass fiber, while providing excellent stiffness and strength, tends to be more brittle and less flexible, which can result in cracking under sudden impacts or bending stresses. The inherent elasticity of polyethylene fibers allows reinforced panels to absorb and dissipate energy more effectively, enhancing overall performance in dynamic and high-impact environments.
Cost Analysis and Commercial Availability
Polyethylene fiber offers a cost-effective solution with lower raw material and production expenses compared to glass fiber in reinforced panels, making it attractive for budget-sensitive projects. Glass fiber panels, while generally more expensive due to higher material costs and energy-intensive manufacturing, provide superior strength and durability that can justify the investment in high-performance applications. Commercial availability of glass fiber is widespread globally, supported by extensive supply chains, whereas polyethylene fiber, though increasingly accessible, may have limited availability in some markets, influencing procurement decisions.
Applications in Various Industries
Polyethylene fiber reinforced panels excel in maritime, automotive, and sports equipment industries due to their high impact resistance, corrosion resistance, and lightweight properties. Glass fiber reinforced panels are widely used in construction, aerospace, and electronics sectors, offering superior stiffness, thermal resistance, and electrical insulation. Each fiber type enhances panel performance tailored to specific industrial demands such as durability, weight reduction, and environmental resistance.
Sustainability and Recycling Aspects
Polyethylene fiber offers superior sustainability due to its lightweight nature and lower energy consumption during production compared to glass fiber. Recycling polyethylene fiber reinforced panels is more efficient since the thermoplastic matrix enables easier material recovery and reuse, contrasting with the energy-intensive recycling process required for glass fiber composites. Glass fiber panels, while durable, pose greater environmental challenges due to their non-biodegradable nature and limited recyclability, leading to higher landfill accumulation.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Fiber for Reinforced Panels
Polyethylene fiber offers superior impact resistance and lightweight properties, making it ideal for applications requiring high toughness and flexibility in reinforced panels. Glass fiber provides excellent stiffness, thermal stability, and cost-effectiveness, suited for panels where structural rigidity and durability under heat are critical. Selecting the optimal fiber depends on balancing the specific mechanical and environmental demands of the application, with polyethylene favored for impact-heavy uses and glass fiber preferred for strength and thermal performance.
Infographic: Polyethylene fiber vs Glass fiber for Reinforced panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com