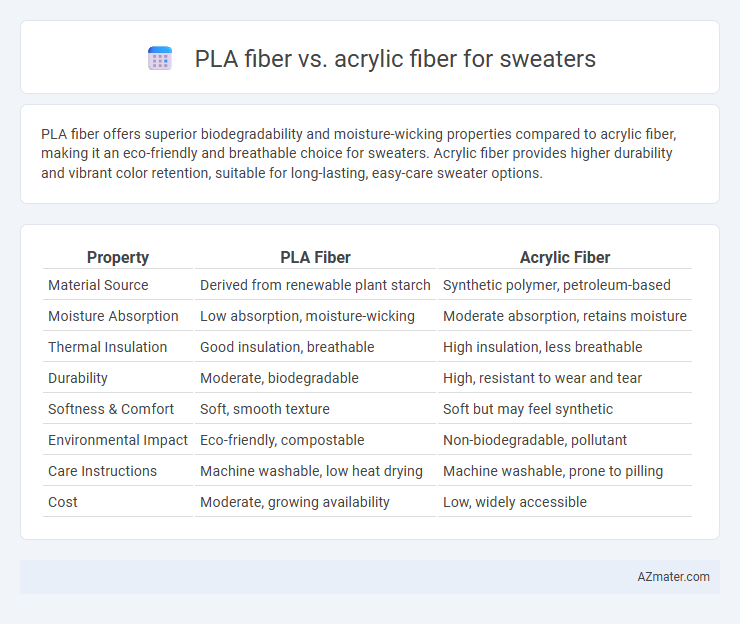
PLA fiber offers superior biodegradability and moisture-wicking properties compared to acrylic fiber, making it an eco-friendly and breathable choice for sweaters. Acrylic fiber provides higher durability and vibrant color retention, suitable for long-lasting, easy-care sweater options.
Table of Comparison
| Property | PLA Fiber | Acrylic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Derived from renewable plant starch | Synthetic polymer, petroleum-based |
| Moisture Absorption | Low absorption, moisture-wicking | Moderate absorption, retains moisture |
| Thermal Insulation | Good insulation, breathable | High insulation, less breathable |
| Durability | Moderate, biodegradable | High, resistant to wear and tear |
| Softness & Comfort | Soft, smooth texture | Soft but may feel synthetic |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, compostable | Non-biodegradable, pollutant |
| Care Instructions | Machine washable, low heat drying | Machine washable, prone to pilling |
| Cost | Moderate, growing availability | Low, widely accessible |
Introduction to PLA and Acrylic Fibers
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers biodegradability and excellent moisture-wicking properties, making it an eco-friendly choice for sweaters. Acrylic fiber, a synthetic polymer primarily made from polyacrylonitrile, is known for its softness, lightweight warmth, and colorfastness in knitwear applications. Both fibers provide distinctive benefits, with PLA focusing on sustainability and breathability, while acrylic excels in durability and vibrant color retention.
Overview of Sweater Fiber Materials
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers biodegradability, moisture-wicking properties, and lightweight comfort for sweaters, making it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional fibers. Acrylic fiber, a synthetic material made from polymer, provides excellent warmth, durability, and resistance to moisture and UV rays, commonly chosen for its affordability and vibrant color retention in sweaters. Both fibers serve distinct purposes, with PLA suited for sustainable and breathable sweaters, while acrylic excels in durability and easy maintenance.
Production Process: PLA vs Acrylic Fiber
PLA fiber production involves fermenting renewable resources like corn starch to produce polylactic acid, which is then spun into fibers, ensuring eco-friendly biodegradability and lower carbon emissions. Acrylic fiber manufacturing relies on polymerization of acrylonitrile, a petroleum-derived chemical, through a solvent or dry-spinning process, resulting in non-biodegradable fibers with higher environmental impact. The production of PLA fibers uses less energy and emits fewer greenhouse gases compared to the energy-intensive and chemically hazardous acrylic fiber process.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers superior biodegradability compared to acrylic fiber, which is petroleum-based and non-biodegradable. PLA fiber production consumes less energy and generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions, supporting a lower carbon footprint in sweater manufacturing. Acrylic fiber's reliance on fossil fuels and its microplastic shedding during washing contribute significantly to environmental pollution and sustainability challenges.
Comfort and Wearability Factors
PLA fiber offers superior moisture-wicking properties and breathability, making sweaters more comfortable for extended wear. Acrylic fiber provides softness and warmth but tends to retain heat and can cause skin irritation in sensitive individuals. Sweaters made from PLA fiber are more suitable for active, temperature-regulated comfort, while acrylic emphasizes cozy insulation.
Thermal Insulation and Warmth
PLA fiber offers superior thermal insulation due to its biopolymer structure that traps heat effectively, ensuring warmth in sweaters without added bulk. Acrylic fiber, while lightweight and soft, provides moderate insulation but tends to lose heat retention compared to PLA in cold conditions. The moisture-wicking properties of PLA enhance thermal comfort by keeping the wearer dry, whereas acrylic fibers may retain moisture, reducing overall warmth.
Durability and Maintenance
PLA fiber offers moderate durability with good resistance to stretching and shrinking, making it suitable for lightweight sweaters, while acrylic fiber provides higher durability, excellent abrasion resistance, and retains shape well under frequent wear. Maintenance of PLA fiber requires gentle washing and careful drying to prevent fiber degradation, whereas acrylic fiber is easier to maintain with machine washability and quick drying properties. Sweaters made from acrylic fibers typically withstand regular laundering and wear better than those made from PLA fibers.
Allergies and Skin Sensitivity
PLA fiber, derived from renewable resources like corn starch, offers a hypoallergenic and breathable option for sweaters, reducing the risk of irritation for sensitive skin. Acrylic fiber, a synthetic material, may cause allergic reactions or discomfort due to its chemical composition and lower moisture-wicking ability. Choosing PLA fiber sweaters can enhance comfort for individuals prone to allergies or skin sensitivity by minimizing exposure to irritants and promoting better skin health.
Cost Comparison of PLA and Acrylic Sweaters
PLA fiber sweaters typically cost more than acrylic fiber sweaters due to the higher production expenses of biodegradable and renewable PLA materials. Acrylic fiber sweaters are generally more affordable, benefiting from large-scale synthetic fiber manufacturing that lowers prices. Consumers seeking budget-friendly options often prefer acrylic, while those prioritizing sustainability might accept the premium cost of PLA sweaters.
Which Fiber is Better for Sweaters?
PLA fiber offers superior moisture-wicking properties and biodegradability, making it an eco-friendly choice for sweaters, while acrylic fiber is known for its durability, vibrant color retention, and affordability. PLA's breathability and natural origin suit lightweight, sustainable sweaters, but acrylic provides greater warmth and resilience in heavier knitwear. Choosing the better fiber depends on prioritizing environmental impact or cost-effectiveness and durability in sweater production.
Infographic: PLA fiber vs Acrylic fiber for Sweater
 azmater.com
azmater.com