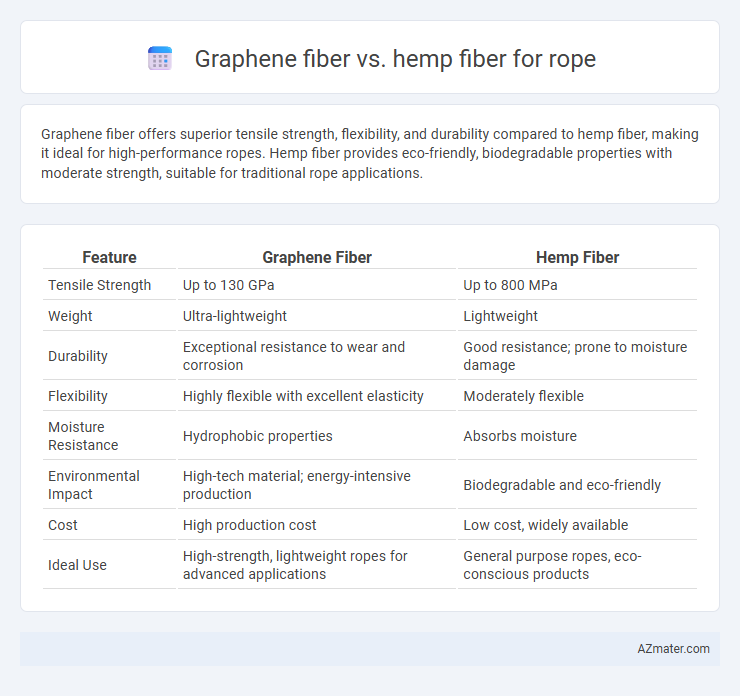
Graphene fiber offers superior tensile strength, flexibility, and durability compared to hemp fiber, making it ideal for high-performance ropes. Hemp fiber provides eco-friendly, biodegradable properties with moderate strength, suitable for traditional rope applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Graphene Fiber | Hemp Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | Up to 130 GPa | Up to 800 MPa |
| Weight | Ultra-lightweight | Lightweight |
| Durability | Exceptional resistance to wear and corrosion | Good resistance; prone to moisture damage |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible with excellent elasticity | Moderately flexible |
| Moisture Resistance | Hydrophobic properties | Absorbs moisture |
| Environmental Impact | High-tech material; energy-intensive production | Biodegradable and eco-friendly |
| Cost | High production cost | Low cost, widely available |
| Ideal Use | High-strength, lightweight ropes for advanced applications | General purpose ropes, eco-conscious products |
Introduction to Graphene and Hemp Fibers
Graphene fiber, derived from a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, exhibits extraordinary strength, flexibility, and electrical conductivity, making it a revolutionary material for advanced rope applications. Hemp fiber, a natural cellulose-based material harvested from the stalks of the hemp plant, is known for its durability, biodegradability, and resistance to rot, historically favored in traditional rope making. While graphene fibers offer unparalleled tensile strength and lightweight properties, hemp fibers provide sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives with natural resilience for various industrial uses.
Origins and Production Methods
Graphene fiber originates from graphene oxide sheets reduced and spun into fibers using chemical vapor deposition or wet spinning techniques, ensuring high tensile strength and conductivity. Hemp fiber derives from the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant, extracted through retting and mechanical processing to obtain long, durable bast fibers ideal for natural rope production. Manufacturing graphene fiber involves advanced nanomaterial synthesis, whereas hemp fiber relies on traditional agricultural and mechanical methods, highlighting a contrast between high-tech and eco-friendly production approaches.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Graphene fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength, often exceeding 130 GPa, which is significantly higher than hemp fiber's tensile strength that typically ranges between 200-900 MPa. The outstanding mechanical strength of graphene fiber results in superior durability and load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for high-performance rope applications. In contrast, hemp fiber offers moderate strength with benefits like biodegradability and cost-effectiveness but falls short in withstanding extreme mechanical stress compared to graphene-based fibers.
Flexibility and Durability
Graphene fiber exhibits exceptional flexibility and durability, offering high tensile strength and resistance to wear, making it ideal for ropes that endure heavy loads and frequent bending. Hemp fiber provides moderate flexibility and good durability, with natural resistance to abrasion and environmental factors, but it tends to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to moisture and UV light. Graphene fiber ropes outperform hemp counterparts in maintaining structural integrity and flexibility over extended use in demanding conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Graphene fiber, derived from carbon atoms arranged in a two-dimensional lattice, offers exceptional strength and durability with minimal environmental footprint due to its lightweight nature, reducing the need for frequent replacements in rope applications. Hemp fiber is biodegradable, renewable, and requires less water and pesticides compared to conventional crops, making it a sustainable option with a low carbon footprint for rope production. Choosing hemp fiber promotes organic farming and soil health, while graphene fiber's production currently involves high energy consumption, highlighting a trade-off between advanced performance and ecological sustainability.
Weight and Density Differences
Graphene fiber exhibits significantly lower density compared to hemp fiber, resulting in a lighter rope with enhanced tensile strength and flexibility. Hemp fiber, with a density around 1.48 g/cm3, is heavier and less durable, making it less ideal for high-performance applications where weight reduction is critical. The superior strength-to-weight ratio of graphene fiber enables the production of ropes that are both lightweight and exceptionally strong, outperforming traditional hemp alternatives in various industrial uses.
Cost and Economic Viability
Graphene fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and durability compared to hemp fiber but comes at a significantly higher production cost, limiting its widespread economic viability for rope manufacturing. Hemp fiber remains a cost-effective and renewable resource with established supply chains, making it a more economically viable choice for large-scale rope production. The high price of graphene fiber currently restricts its use to specialized applications where performance justifies the expense.
Applications in Rope Manufacturing
Graphene fiber offers exceptional tensile strength, lightweight properties, and excellent durability, making it ideal for high-performance ropes used in aerospace, military, and rescue operations where reliability is critical. Hemp fiber provides natural biodegradability, resistance to UV degradation, and cost-effectiveness, favoring applications in eco-friendly marine ropes, agricultural twines, and general-purpose utility cords. Combining graphene fiber with hemp can enhance the mechanical properties of ropes while maintaining sustainability benefits for diverse manufacturing needs.
Safety and Biodegradability
Graphene fiber offers superior tensile strength and chemical resistance, enhancing rope safety by reducing the risk of breakage under extreme stress and exposure to harsh environments. Hemp fiber is highly biodegradable, decomposing naturally within months, which makes it an eco-friendly option for disposable or short-term rope applications. While hemp ropes provide adequate safety for general use, graphene fibers excel in durability, though they currently lack biodegradability, posing environmental concerns for long-term disposal.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Graphene fiber offers exceptional tensile strength, lightweight properties, and electrical conductivity, positioning it as a revolutionary material for advanced rope applications in aerospace, military, and smart textiles. Hemp fiber, valued for its sustainability, biodegradability, and cost-effectiveness, continues to attract innovations through blending with synthetic fibers and treatments enhancing durability and moisture resistance. Future prospects involve hybrid fibers combining graphene and hemp, enabling ropes with superior strength, environmental benefits, and multifunctional capabilities such as sensor integration.
Infographic: Graphene fiber vs Hemp fiber for Rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com