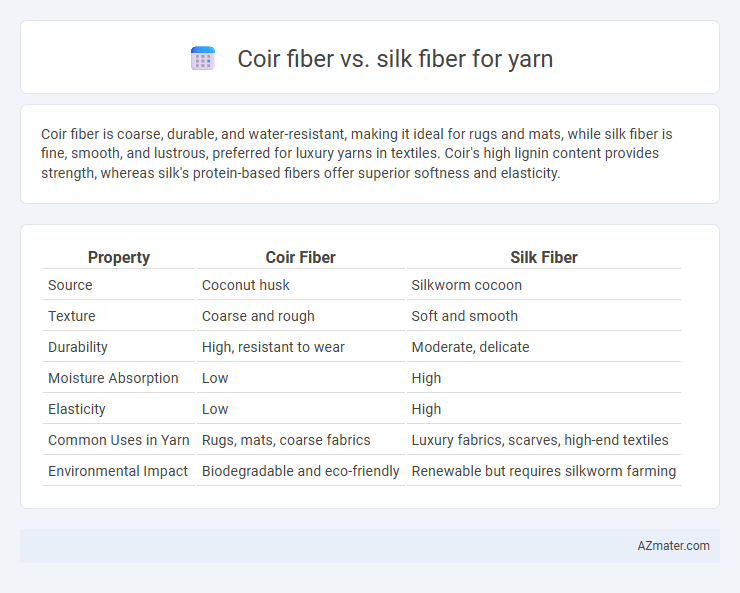
Coir fiber is coarse, durable, and water-resistant, making it ideal for rugs and mats, while silk fiber is fine, smooth, and lustrous, preferred for luxury yarns in textiles. Coir's high lignin content provides strength, whereas silk's protein-based fibers offer superior softness and elasticity.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Coir Fiber | Silk Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Coconut husk | Silkworm cocoon |
| Texture | Coarse and rough | Soft and smooth |
| Durability | High, resistant to wear | Moderate, delicate |
| Moisture Absorption | Low | High |
| Elasticity | Low | High |
| Common Uses in Yarn | Rugs, mats, coarse fabrics | Luxury fabrics, scarves, high-end textiles |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable and eco-friendly | Renewable but requires silkworm farming |
Introduction to Coir and Silk Fibers
Coir fiber, derived from the outer husk of coconut shells, is a coarse and durable natural fiber widely used in yarn production for its strength and water resistance. Silk fiber, produced by silkworms, is prized for its smooth texture, lustrous appearance, and excellent elasticity, making it ideal for fine and luxurious yarns. The distinct structural properties of coir and silk fibers influence their respective applications in textiles, with coir favored for rugged, eco-friendly products and silk for high-end, soft fabrics.
Source and Extraction Methods
Coir fiber is derived from the outer husk of coconut shells, extracted through a process of retting and fiber separation by mechanical or manual methods, resulting in coarse and durable yarn. Silk fiber originates from the cocoons of silkworms, obtained by carefully boiling or steaming to unwind the fine protein filaments, yielding smooth and lustrous yarn. The fundamental source difference lies in plant-based coir from coconut husks versus animal-based silk from silkworm secretions, with extraction methods tailored to their unique biological structures.
Physical Properties Comparison
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, is coarse, stiff, and has high tensile strength, making it more durable but less flexible than silk fiber. Silk fiber, produced by silkworms, exhibits a smooth texture, lustrous appearance, and excellent elasticity, offering superior softness and sheen for fine yarns. While coir resists moisture and abrasion effectively, silk provides better thermal regulation and moisture absorption, influencing their suitability for different textile applications.
Durability and Strength
Coir fiber exhibits exceptional durability with a high tensile strength of approximately 15-25 MPa, making it resistant to wear and ideal for coarse yarn applications. Silk fiber, while known for its luxurious texture, offers a tensile strength around 300-500 MPa, providing superior strength and elasticity suitable for fine, delicate yarns. The natural toughness of coir lends itself to long-lasting, rough-textured products, whereas silk's strength combined with flexibility ensures durability in soft, high-end fabrics.
Texture and Comfort in Yarns
Coir fiber yarns are coarse and rough with low elasticity, making them ideal for durable, sturdy textiles but less comfortable against the skin. Silk fiber yarns offer a smooth, soft texture with high elasticity, providing exceptional comfort and breathability in garments. The natural sheen and fine fibers of silk result in luxurious, lightweight yarns preferred for soft, high-end apparel, whereas coir's rigidity suits textured, rustic fabric applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, is highly sustainable due to its biodegradable nature and low environmental impact, as it utilizes agricultural waste and requires minimal processing chemicals. Silk fiber production involves sericulture, which has higher water usage and energy consumption, though it is biodegradable and renewable. Coir yarn offers a more eco-friendly option compared to silk yarn, especially in terms of resource efficiency and waste reduction.
Dyeability and Color Retention
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, exhibits limited dyeability due to its coarse texture and low moisture absorption, resulting in muted colors and poor color retention over time. In contrast, silk fiber, a natural protein fiber from silkworms, possesses excellent dye affinity and vibrant color retention owing to its smooth surface and high porosity. Silk yarn maintains brightness and luster longer, making it superior for applications requiring rich, enduring hues.
Cost and Market Availability
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, offers a low-cost alternative to silk fiber due to its abundant availability in tropical regions, making it a preferred choice for budget-conscious yarn production. Silk fiber commands a higher price owing to its labor-intensive harvesting process and limited production areas, primarily in countries like China and India, resulting in less market availability compared to coir. The cost-effectiveness and wide distribution of coir fiber contribute to a larger market presence, whereas silk yarn remains a niche product favored for luxury textiles.
Best Applications for Each Fiber
Coir fiber, derived from coconut husks, is highly durable, coarse, and water-resistant, making it ideal for products like mats, brushes, and upholstery fabric where strength and moisture resistance are essential. Silk fiber, known for its smooth texture, sheen, and elasticity, excels in luxury textiles, high-end fashion garments, and delicate upholstery due to its softness and natural luster. Each fiber's unique properties dictate its best applications, with coir favored for utility and durability, while silk is preferred for comfort and elegance.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Yarn
Coir fiber offers exceptional durability and natural resistance to moisture, making it ideal for sturdy, eco-friendly yarn applications such as mats and ropes. Silk fiber provides unmatched softness, sheen, and elasticity, perfect for luxury textiles and fine garments. Selecting the right fiber depends on prioritizing either coir's robustness and sustainability or silk's elegance and comfort for the intended yarn use.
Infographic: Coir fiber vs Silk fiber for Yarn
 azmater.com
azmater.com