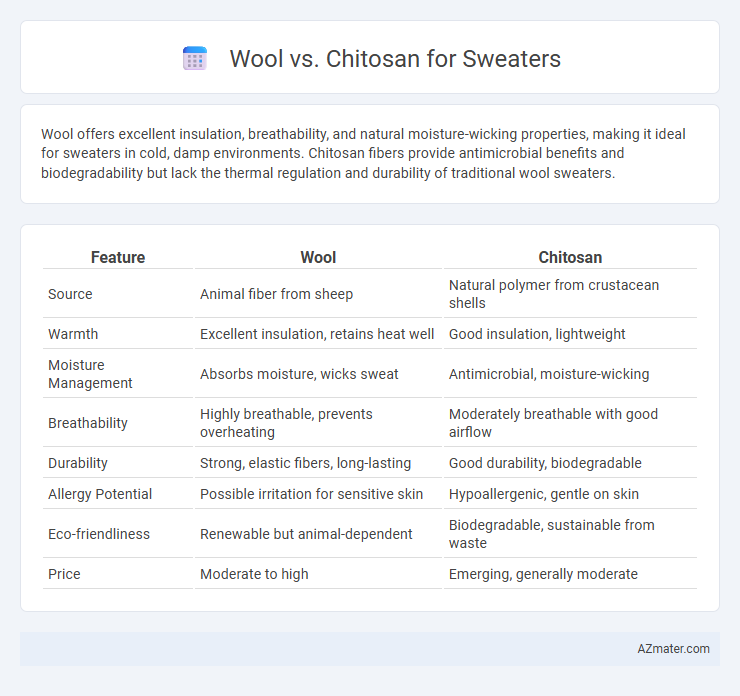
Wool offers excellent insulation, breathability, and natural moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for sweaters in cold, damp environments. Chitosan fibers provide antimicrobial benefits and biodegradability but lack the thermal regulation and durability of traditional wool sweaters.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wool | Chitosan |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Animal fiber from sheep | Natural polymer from crustacean shells |
| Warmth | Excellent insulation, retains heat well | Good insulation, lightweight |
| Moisture Management | Absorbs moisture, wicks sweat | Antimicrobial, moisture-wicking |
| Breathability | Highly breathable, prevents overheating | Moderately breathable with good airflow |
| Durability | Strong, elastic fibers, long-lasting | Good durability, biodegradable |
| Allergy Potential | Possible irritation for sensitive skin | Hypoallergenic, gentle on skin |
| Eco-friendliness | Renewable but animal-dependent | Biodegradable, sustainable from waste |
| Price | Moderate to high | Emerging, generally moderate |
Overview: Wool vs Chitosan Sweaters
Wool sweaters excel in natural insulation, moisture-wicking, and breathability, making them ideal for cold weather and active wear. Chitosan sweaters offer enhanced antibacterial properties, odor resistance, and biodegradability due to their biopolymer composition derived from crustacean shells. Both materials provide sustainability benefits, but wool is renowned for warmth and durability, while chitosan emphasizes antimicrobial performance and eco-friendliness.
Material Origins and Sustainability
Wool, sourced from sheep fleece, is a renewable and biodegradable natural fiber widely praised for its insulation and moisture-wicking properties, but its environmental impact includes issues like land use and methane emissions. Chitosan, derived from the exoskeletons of crustaceans such as shrimp and crabs, is a sustainable biopolymer with antimicrobial qualities and biodegradability, often used as an innovative textile enhancer. Choosing between wool and chitosan-infused sweaters depends on prioritizing traditional natural fibers versus advanced marine-based materials with enhanced ecological benefits.
Production Process Comparison
Wool production involves shearing sheep, cleaning, carding, spinning, and weaving or knitting, relying on animal fiber that requires large amounts of water and land resources. Chitosan production starts with extracting chitin from crustacean shells, followed by deacetylation to convert it into chitosan, emphasizing sustainable waste utilization and lower environmental impact. Chitosan offers a biodegradable and antimicrobial alternative with a chemical-intensive process, whereas wool's natural fiber harvesting is labor-intensive and resource-heavy.
Texture and Comfort Differences
Wool fibers are natural protein-based materials known for their softness, warmth, and excellent moisture-wicking properties, offering a cozy and breathable texture ideal for sweaters. Chitosan, derived from crustacean shells, provides a smooth, lightweight, and slightly firm texture with antimicrobial benefits but lacks the natural elasticity and insulation characteristics of wool. Sweaters made from wool generally provide superior comfort and thermal regulation, while chitosan blends enhance durability and odor resistance without compromising overall softness.
Insulation and Warmth Properties
Wool provides exceptional insulation due to its natural crimped fibers that trap air, maintaining warmth even when wet. Chitosan, derived from chitin, offers antimicrobial benefits and moisture management but has comparatively lower insulation capabilities than wool. Combining chitosan with wool fibers enhances sweater warmth, leveraging wool's thermal regulation and chitosan's odor control for improved comfort.
Moisture-Wicking and Breathability
Wool offers superior moisture-wicking capabilities by naturally absorbing and releasing perspiration, keeping the skin dry during physical activity. Chitosan, derived from crustacean shells, enhances breathability with its porous structure that promotes air circulation and rapid moisture evaporation. Sweaters made from wool provide balanced temperature regulation, while chitosan-infused fabrics excel in antimicrobial properties, contributing to long-lasting freshness.
Allergenicity and Skin Sensitivity
Wool can trigger allergic reactions and skin irritation in sensitive individuals due to lanolin and coarse fibers, leading to redness and itchiness. Chitosan, derived from crustacean shells, is hypoallergenic and possesses antimicrobial properties that reduce skin irritation and improve comfort for sensitive skin. Choosing chitosan-based sweaters benefits those prone to allergies and skin sensitivity by minimizing inflammatory responses.
Durability and Longevity
Wool offers high durability and natural elasticity, allowing sweaters to retain shape and resist wear over time, while chitosan enhances fabric strength by providing antimicrobial properties that reduce fiber degradation. Sweaters infused with chitosan exhibit improved resistance to moisture and odor, which contributes to extended garment lifespan compared to untreated wool. Combining wool with chitosan results in sweaters that maintain durability and longevity through enhanced fiber protection and moisture management.
Environmental Impact and Biodegradability
Wool is a natural fiber derived from sheep, known for its excellent biodegradability and renewable sourcing, making it environmentally friendly when sourced sustainably. Chitosan, a biopolymer extracted from crustacean shells, offers biodegradability and antimicrobial properties, contributing to reduced odor and bacterial growth in sweaters. Both materials minimize landfill waste, but chitosan's use of seafood industry by-products further enhances its sustainability profile by promoting circular resource use.
Cost and Market Availability
Wool sweaters typically have a moderate to high price point due to the natural fiber's durability and insulation properties, making them widely available in fashion and outdoor markets globally. Chitosan-based sweaters, derived from crustacean shells, tend to be more expensive because of limited production scale and specialized manufacturing processes, resulting in lower market availability. Consumers seeking eco-friendly alternatives face higher costs and fewer retail options with chitosan sweaters compared to the more established wool market.
Infographic: Wool vs Chitosan for Sweater
 azmater.com
azmater.com