Viscose scarves offer a soft, breathable texture with excellent drape and moisture absorption, making them ideal for comfort and elegance. Nylon scarves provide superior durability, wrinkle resistance, and vibrant color retention, ensuring long-lasting wear and easy maintenance.
Table of Comparison
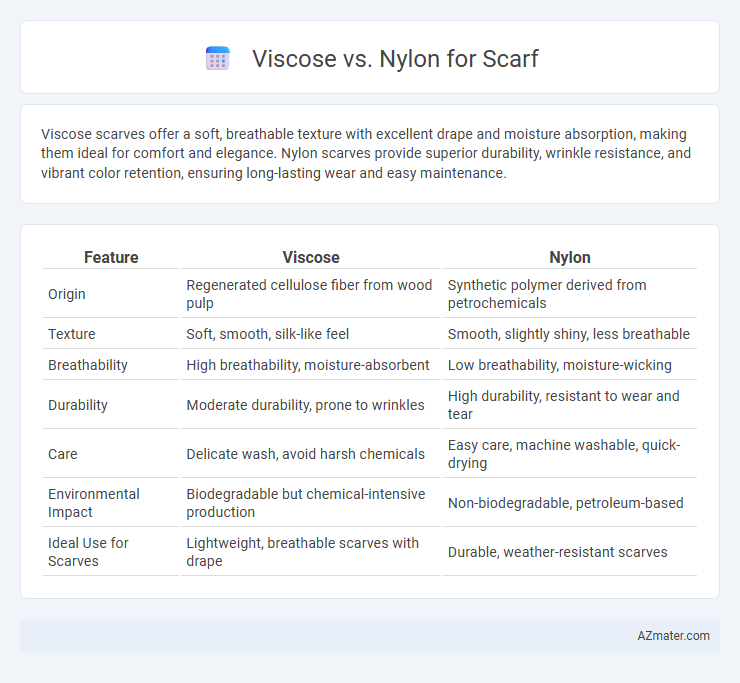
| Feature | Viscose | Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Regenerated cellulose fiber from wood pulp | Synthetic polymer derived from petrochemicals |
| Texture | Soft, smooth, silk-like feel | Smooth, slightly shiny, less breathable |
| Breathability | High breathability, moisture-absorbent | Low breathability, moisture-wicking |
| Durability | Moderate durability, prone to wrinkles | High durability, resistant to wear and tear |
| Care | Delicate wash, avoid harsh chemicals | Easy care, machine washable, quick-drying |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable but chemical-intensive production | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based |
| Ideal Use for Scarves | Lightweight, breathable scarves with drape | Durable, weather-resistant scarves |
Overview of Viscose and Nylon Fabrics
Viscose, a semi-synthetic fiber derived from cellulose, offers a soft, breathable, and lightweight texture ideal for scarves, providing a natural drape and vibrant color retention. Nylon, a fully synthetic polymer, is known for its exceptional strength, elasticity, and resistance to moisture, making it durable and wrinkle-resistant for everyday scarf use. Both fabrics serve distinct purposes: viscose emphasizes comfort and natural feel, while nylon prioritizes durability and stretch.
Key Differences Between Viscose and Nylon
Viscose is a semi-synthetic fiber made from cellulose, offering breathability and a soft, silky texture ideal for scarves, while nylon is a fully synthetic polymer known for its durability, elasticity, and moisture-wicking properties. Viscose scarves provide excellent drape and comfort but may be less resistant to wear and moisture compared to nylon, which excels in strength and quick-drying functionality. Choosing between viscose and nylon scarves depends on preferences for natural feel and breathability versus enhanced durability and performance in various conditions.
Softness and Comfort Comparison
Viscose scarves offer exceptional softness and a smooth texture, making them highly comfortable for sensitive skin and prolonged wear. Nylon scarves, while durable and lightweight, tend to have a slightly synthetic feel that may not match the natural comfort of viscose. For maximum softness and breathable comfort in scarf materials, viscose remains the preferred choice over nylon.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Viscose offers superior breathability for scarves due to its natural cellulose fibers that allow better air circulation, making it ideal for warmer climates. Nylon, a synthetic fiber, tends to trap heat and moisture, resulting in less effective moisture management and reduced comfort during prolonged wear. Scarves made from viscose wick moisture away efficiently, keeping the skin dry, while nylon scarves may retain sweat and lead to discomfort.
Durability: Which Lasts Longer?
Nylon scarves typically outperform viscose in durability due to nylon's high resistance to wear, stretching, and abrasion. Viscose, made from regenerated cellulose fibers, is more prone to weakening over time and developing pilling or tears with frequent use. For long-lasting scarves, nylon offers superior strength and resilience, making it the preferred choice for durability-focused consumers.
Color Vibrancy and Pattern Retention
Viscose scarves offer rich color vibrancy due to their excellent dye absorption, resulting in bright, eye-catching hues that enhance intricate patterns. Nylon, while durable, often displays less intense colors and may fade faster under frequent washing or exposure to sunlight. Viscose maintains pattern clarity over time, making it a preferred choice for scarves where color and design longevity are important.
Eco-Friendliness and Sustainability
Viscose scarves are generally more eco-friendly than nylon due to their plant-based origins, typically derived from cellulose in wood pulp, which can be sustainably sourced and biodegradable under proper conditions. Nylon, a synthetic polymer made from petroleum, poses environmental concerns related to fossil fuel consumption and slow biodegradability, contributing to microplastic pollution. Choosing viscose over nylon supports sustainability efforts by reducing reliance on non-renewable resources and improving end-of-life ecological impact.
Maintenance and Care Instructions
Viscose scarves require gentle hand washing with cold water and mild detergent to prevent shrinking and fabric damage, while avoiding wringing or twisting the material. Nylon scarves are more durable, allowing machine washing on a delicate cycle with cold water, and they dry quickly without losing shape or color. Proper storage for both fabrics involves keeping them in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight to preserve fiber quality and extend the scarf's lifespan.
Price and Affordability Factors
Viscose scarves generally offer a more budget-friendly option compared to nylon, making them attractive for cost-conscious shoppers seeking soft, breathable fabrics. Nylon scarves, while often priced higher, provide enhanced durability and moisture-wicking properties, which can justify the investment for users prioritizing longevity and performance. Price variations depend on brand, fabric blend, and production quality, but viscose remains the more affordable choice for everyday fashion scarves.
Which Fabric is Best for Scarves?
Viscose offers a soft, breathable texture ideal for lightweight, comfortable scarves, while nylon provides superior durability and moisture resistance, making it suitable for active or weather-exposed use. Viscose's natural fiber qualities ensure excellent dye absorption and vibrant colors, perfect for fashion scarves with intricate patterns. Nylon's strength and elasticity make it less prone to wrinkles and wear, offering long-lasting scarves that maintain shape and vibrancy over time.
Infographic: Viscose vs Nylon for Scarf
 azmater.com
azmater.com