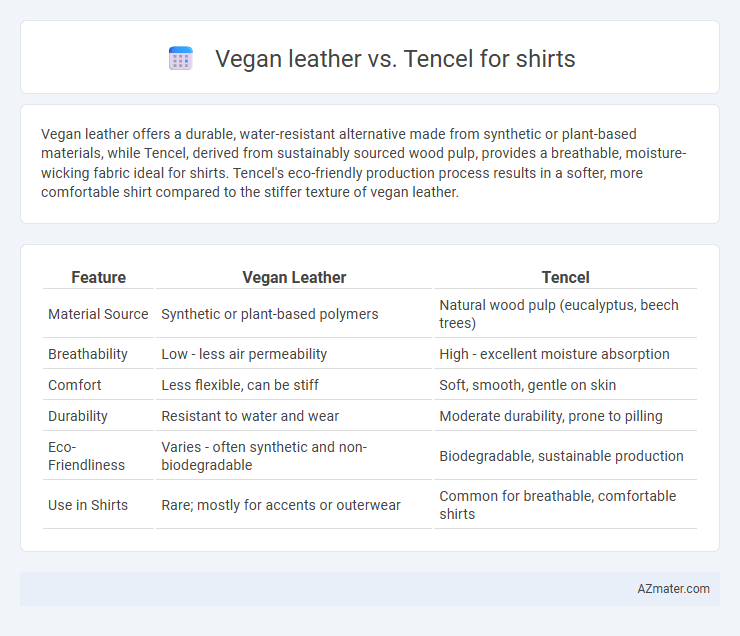
Vegan leather offers a durable, water-resistant alternative made from synthetic or plant-based materials, while Tencel, derived from sustainably sourced wood pulp, provides a breathable, moisture-wicking fabric ideal for shirts. Tencel's eco-friendly production process results in a softer, more comfortable shirt compared to the stiffer texture of vegan leather.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vegan Leather | Tencel |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Synthetic or plant-based polymers | Natural wood pulp (eucalyptus, beech trees) |
| Breathability | Low - less air permeability | High - excellent moisture absorption |
| Comfort | Less flexible, can be stiff | Soft, smooth, gentle on skin |
| Durability | Resistant to water and wear | Moderate durability, prone to pilling |
| Eco-Friendliness | Varies - often synthetic and non-biodegradable | Biodegradable, sustainable production |
| Use in Shirts | Rare; mostly for accents or outerwear | Common for breathable, comfortable shirts |
Introduction to Vegan Leather and Tencel
Vegan leather, a synthetic or plant-based material designed to mimic traditional leather, offers durability and water resistance while avoiding animal products. Tencel, derived from sustainably sourced wood pulp, is a breathable and moisture-wicking fiber known for its softness and environmental benefits. Both materials provide eco-friendly alternatives for shirts, with vegan leather emphasizing animal-free durability and Tencel highlighting comfort and sustainability.
Material Origins and Production Processes
Vegan leather, typically made from synthetic materials like polyurethane or natural sources such as pineapple leaves, mimics traditional leather's texture without animal products. Tencel, derived from sustainably sourced eucalyptus wood pulp, undergoes a closed-loop production process that recycles water and solvents, minimizing environmental impact. Comparing both, vegan leather often involves petrochemical-based production, whereas Tencel emphasizes renewable raw materials and eco-friendly manufacturing.
Environmental Impact: Vegan Leather vs Tencel
Tencel, derived from sustainably sourced wood pulp, boasts a lower environmental impact compared to vegan leather, which often involves synthetic materials like polyurethane with petrochemical origins. Tencel production utilizes closed-loop processes that recycle water and solvents, minimizing waste and energy consumption. In contrast, vegan leather manufacturing typically generates higher greenhouse gas emissions and non-biodegradable waste, making Tencel a more eco-friendly choice for shirts.
Texture, Feel, and Comfort Comparison
Vegan leather offers a smooth, durable texture with a slightly stiffer feel, often resulting in less breathability and reduced comfort in shirts compared to Tencel. Tencel is known for its exceptionally soft, lightweight, and breathable fibers, providing superior comfort and a natural drape ideal for shirts. The moisture-wicking and hypoallergenic properties of Tencel further enhance its comfort, making it a preferred choice for all-day wear over the synthetic feel of vegan leather.
Durability and Longevity in Shirts
Vegan leather, often made from polyurethane or plant-based materials, offers moderate durability but tends to wear out faster with frequent washing and abrasion compared to Tencel, which is known for its strength and resistance to stretching and shrinking. Tencel, derived from sustainably sourced wood pulp, provides exceptional longevity in shirts due to its robust fiber structure and moisture-wicking properties that help maintain fabric integrity over time. Shirts crafted from Tencel maintain their shape and color longer, making them a more durable and environmentally friendly option for everyday wear.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Tencel shirts offer superior breathability and moisture management compared to vegan leather, as Tencel fibers naturally wick away sweat and allow air circulation, keeping the wearer cool and dry. Vegan leather, typically made from polyurethane or plant-based materials, lacks the porous structure of natural fibers, leading to reduced breathability and potential heat retention. For active or warm environments, Tencel is a more comfortable choice due to its eco-friendly fabrication and enhanced moisture control properties.
Ethical Considerations and Sustainability
Vegan leather, often made from polyurethane or plant-based materials like pineapple or mushroom fibers, offers an animal-free alternative but can vary in environmental impact depending on production methods and chemical use. Tencel, derived from sustainably harvested eucalyptus wood through a closed-loop process, is biodegradable and requires less water and energy, making it a more eco-friendly option for shirts. Ethical considerations favor Tencel for its renewable sourcing and minimal pollution, whereas vegan leather's sustainability depends heavily on the source material and manufacturing transparency.
Style Versatility and Design Possibilities
Vegan leather offers bold, edgy aesthetics ideal for structured, statement shirts with a sleek, modern finish, while Tencel provides soft, flowing drapes perfect for casual to elegant designs emphasizing comfort and breathability. The durability and rigidity of vegan leather support intricate, sculptural detailing, whereas Tencel's lightweight, smooth texture enhances color vibrancy and fluid movement, expanding creative possibilities. Both materials cater to diverse style preferences, with vegan leather excelling in avant-garde fashion and Tencel suited for versatile, eco-friendly wardrobe staples.
Care, Maintenance, and Ease of Use
Vegan leather requires gentle cleaning with a damp cloth and mild soap to prevent cracking, making it less breathable and prone to retaining heat during wear. Tencel shirts offer superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties, requiring simple machine washing without losing shape or softness. The ease of maintaining Tencel fabric surpasses vegan leather due to its durability and resistance to wrinkles and stains.
Cost, Availability, and Market Trends
Vegan leather for shirts generally carries a higher production cost and limited availability compared to Tencel, which is known for its cost-effectiveness and widespread accessibility due to sustainable wood pulp sourcing. Market trends show a growing preference for Tencel in apparel because of its eco-friendly reputation, breathability, and comfort, driving increased demand in mainstream and luxury segments. Despite rising interest in vegan leather alternatives, Tencel's scalability and lower environmental impact position it more favorably for mass-market shirt production.
Infographic: Vegan leather vs Tencel for Shirt
 azmater.com
azmater.com