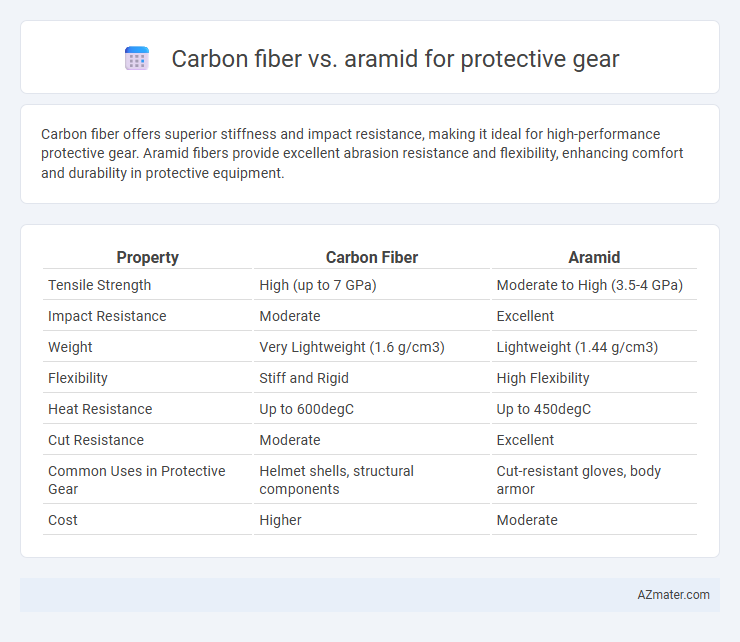
Carbon fiber offers superior stiffness and impact resistance, making it ideal for high-performance protective gear. Aramid fibers provide excellent abrasion resistance and flexibility, enhancing comfort and durability in protective equipment.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Fiber | Aramid |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | High (up to 7 GPa) | Moderate to High (3.5-4 GPa) |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Weight | Very Lightweight (1.6 g/cm3) | Lightweight (1.44 g/cm3) |
| Flexibility | Stiff and Rigid | High Flexibility |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 600degC | Up to 450degC |
| Cut Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Common Uses in Protective Gear | Helmet shells, structural components | Cut-resistant gloves, body armor |
| Cost | Higher | Moderate |
Introduction to Carbon Fiber and Aramid
Carbon fiber is a lightweight, high-strength material composed of thin strands of carbon atoms tightly bonded in a crystalline formation, offering exceptional stiffness and impact resistance ideal for protective gear. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, are synthetic polymers known for their outstanding tensile strength and superior resistance to abrasion, making them highly effective in ballistic and cut-resistant applications. Both materials enhance protective gear performance by combining durability and weight efficiency, with carbon fiber excelling in rigidity and aramid providing enhanced flexibility and energy absorption.
Material Composition and Structure
Carbon fiber consists of tightly woven strands of carbon atoms bonded in a crystalline structure, providing exceptional tensile strength and rigidity ideal for impact resistance in protective gear. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, are synthetic polyamides featuring a highly oriented molecular structure that delivers superior energy absorption and flexibility while maintaining lightweight durability. The distinct molecular arrangements of carbon fiber and aramid influence their performance characteristics, making carbon fiber more suitable for stiffness-demanding applications and aramid optimal for cut resistance and ballistic protection.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Carbon fiber exhibits superior tensile strength, often exceeding 3,500 MPa, making it highly effective for impact resistance in protective gear. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide excellent tensile strength around 3,000 MPa combined with exceptional energy absorption and flexibility, ideal for ballistic and stab protection. In mechanical strength comparison, carbon fiber offers higher stiffness and rigidity, while aramid fibers deliver better toughness and elongation before failure, influencing the choice based on specific protective gear requirements.
Weight and Flexibility Factors
Carbon fiber offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making protective gear lightweight yet highly durable, ideal for impact resistance without adding bulk. Aramid fibers like Kevlar provide superior flexibility and excellent energy absorption, allowing gear to conform comfortably to the body while maintaining strong protection. When prioritizing weight and flexibility, carbon fiber excels in lightweight rigidity, whereas aramid delivers enhanced flexibility with reliable strength for mobility-focused applications.
Impact and Abrasion Resistance
Carbon fiber offers exceptional impact resistance due to its high tensile strength and stiffness, making it ideal for protective gear requiring robust shock absorption. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, excel in abrasion resistance and maintain flexibility, providing superior durability against cuts and wear during high-friction activities. Combining carbon fiber with aramid optimizes protective gear by balancing impact resistance with abrasion durability for comprehensive protection.
Heat and Chemical Resistance
Carbon fiber offers excellent heat resistance, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 1,500degF (815degC), making it ideal for high-heat protective gear. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, exhibit superior chemical resistance and flame retardancy, withstanding exposure to various solvents and acids without degrading. For applications requiring combined heat and chemical resistance, hybrid composites of carbon fiber and aramid provide balanced protection and enhanced durability.
Comfort and Wearability
Carbon fiber offers superior rigidity and lightweight properties, enhancing protective gear comfort by reducing fatigue during extended wear. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide exceptional flexibility and breathability, improving wearability through better movement and heat dissipation. The choice between carbon fiber and aramid depends on the specific balance needed between stiffness and comfort for different protective applications.
Cost and Availability
Carbon fiber protective gear tends to be more expensive due to its complex manufacturing process and higher material costs, often limiting widespread availability. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer a more cost-effective alternative with greater accessibility in mass-produced protective equipment. This economic advantage makes aramid-based gear a preferred choice for budget-conscious consumers and large-scale applications.
Common Applications in Protective Gear
Carbon fiber is extensively used in protective gear for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for helmets, body armor, and motorcycle protective panels where impact resistance and lightweight performance are critical. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, are prevalent in ballistic vests, cut-resistant gloves, and firefighting suits due to their superior thermal resistance, flexibility, and ability to absorb and dissipate energy from impacts and punctures. Both materials are often integrated into composite systems to optimize protection, durability, and wearer comfort in various high-risk environments.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Needs
Carbon fiber offers superior rigidity and impact resistance ideal for lightweight protective gear requiring high structural integrity, while aramid fibers such as Kevlar provide exceptional flexibility and abrasion resistance suited for garments needing enhanced cut and heat protection. Selecting between carbon fiber and aramid depends on balancing factors like weight, durability, flexibility, and specific threat mitigation in applications such as motorcycle armor, ballistic vests, or industrial safety equipment. Optimal protection results from matching material properties with intended use scenarios, emphasizing carbon fiber for stiff, high-impact needs and aramid for flexible, multi-threat environments.
Infographic: Carbon fiber vs Aramid for Protective gear
 azmater.com
azmater.com