Spider silk outperforms cotton in strength, elasticity, and biodegradability, making it an exceptional material for advanced textiles. Its natural protein structure provides superior durability and lightweight comfort compared to traditional cotton fibers.
Table of Comparison
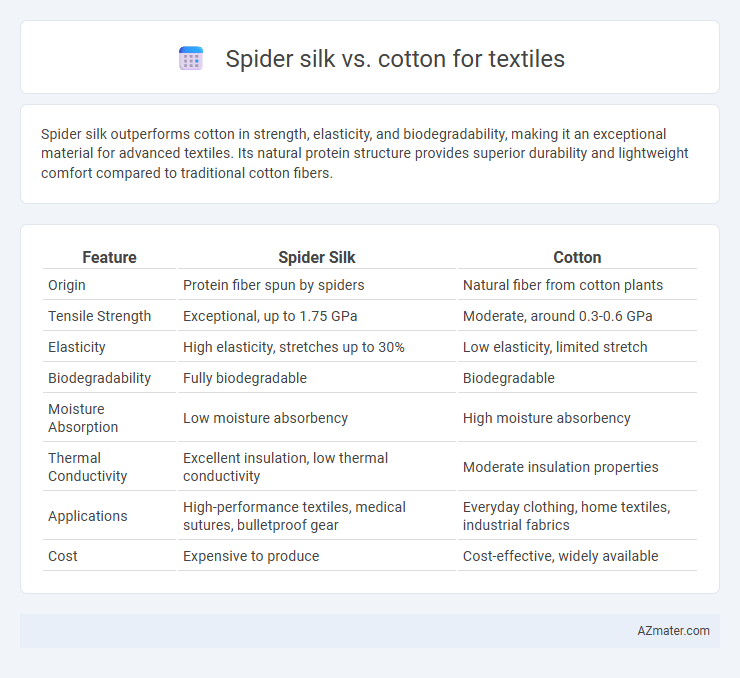
| Feature | Spider Silk | Cotton |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Protein fiber spun by spiders | Natural fiber from cotton plants |
| Tensile Strength | Exceptional, up to 1.75 GPa | Moderate, around 0.3-0.6 GPa |
| Elasticity | High elasticity, stretches up to 30% | Low elasticity, limited stretch |
| Biodegradability | Fully biodegradable | Biodegradable |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorbency | High moisture absorbency |
| Thermal Conductivity | Excellent insulation, low thermal conductivity | Moderate insulation properties |
| Applications | High-performance textiles, medical sutures, bulletproof gear | Everyday clothing, home textiles, industrial fabrics |
| Cost | Expensive to produce | Cost-effective, widely available |
Introduction: Spider Silk and Cotton in Textile Industry
Spider silk exhibits exceptional tensile strength, elasticity, and biodegradability, making it a highly sought-after material for advanced textile applications. Cotton, a widely cultivated natural fiber, dominates the global textile industry due to its breathability, softness, and versatility in fabric production. Comparing spider silk to cotton reveals significant differences in mechanical properties, sustainability, and potential for innovation within the textile sector.
Origins and Production Methods
Spider silk, a natural protein fiber produced by spiders through specialized silk glands, is harvested primarily via bioengineering techniques due to the impracticality of direct spider farming. Cotton fibers originate from the seed hairs of the Gossypium plant and are cultivated through large-scale agricultural farming involving planting, irrigation, and mechanical harvesting. While cotton production relies on cellulose extraction from plant fibers utilizing ginning and spinning processes, spider silk production emphasizes recombinant protein synthesis and spinning in controlled bioreactor environments to replicate the silk's unique molecular structure.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Durability
Spider silk exhibits exceptional mechanical properties with tensile strength reaching up to 1.3 GPa, surpassing cotton's average strength of 0.3 GPa, making spider silk more resistant to breaking under stress. Its high toughness and elasticity allow it to stretch up to 35% of its length without losing durability, whereas cotton fibers tend to be less elastic and degrade faster under repeated wear. These attributes position spider silk as a superior material for durable, lightweight textiles requiring high mechanical performance.
Softness and Texture Comparison
Spider silk demonstrates exceptional softness and a smooth, silk-like texture that surpasses traditional cotton fibers, which tend to feel coarser and less refined. The molecular structure of spider silk allows for a fine, lightweight fabric with natural elasticity and sheen, offering superior comfort against the skin compared to cotton's more absorbent and fibrous texture. Innovations in biomimetic engineering have enabled spider silk textiles to maintain durability while enhancing softness, making them a premium alternative for luxurious and sensitive fabric applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Spider silk offers exceptional biodegradability and requires significantly less water and pesticides compared to cotton, reducing environmental strain in textile production. Cotton cultivation is water-intensive and often involves extensive pesticide use, contributing to soil degradation and pollution. Sustainable spider silk production leverages bioengineering techniques to replicate silk proteins, minimizing ecological footprints while providing a renewable alternative to traditional cotton fibers.
Moisture Management and Breathability
Spider silk exhibits superior moisture management compared to cotton, effectively wicking sweat away from the skin and promoting rapid evaporation. Its protein-based fibers create a breathable fabric with natural temperature regulation, enhancing comfort in both hot and humid conditions. Cotton, while breathable and moisture-absorbent, tends to retain moisture longer, which can lead to discomfort and slower drying times.
Biocompatibility and Hypoallergenic Qualities
Spider silk exhibits superior biocompatibility compared to cotton, making it ideal for sensitive skin and medical textiles. Its natural protein structure minimizes allergic reactions, while cotton often retains allergens and irritants. This hypoallergenic quality positions spider silk as a premium alternative for advanced textile applications requiring skin-friendly materials.
Cost and Commercial Availability
Spider silk offers exceptional strength and elasticity but remains prohibitively expensive and limited in commercial availability due to challenges in large-scale farming and production. Cotton, by contrast, is widely cultivated, cost-effective, and extensively used in the textile industry, providing affordability and ease of access for mass manufacturing. The high production costs and scalability issues restrict spider silk's use mainly to niche or luxury textile markets rather than everyday apparel.
Current Applications in Fashion and Industry
Spider silk exhibits remarkable tensile strength and elasticity, making it a revolutionary material for high-performance fashion and industrial textiles. Its lightweight, biodegradable nature is increasingly utilized in luxury apparel, athletic wear, and medical sutures, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional cotton fabrics. Cotton remains dominant in mass-produced clothing due to cost-effectiveness and versatility, yet spider silk's superior durability and moisture-wicking properties are driving innovation in eco-friendly fabric technologies.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Spider silk offers exceptional tensile strength, elasticity, and biodegradability compared to traditional cotton textiles, making it a prime candidate for sustainable fabric innovations. Advancements in bioengineering and synthetic biology are enabling scalable production of spider silk proteins, potentially revolutionizing textile manufacturing with eco-friendly, high-performance materials. Emerging applications in wearable technology, medical textiles, and lightweight protective gear highlight the future prospects of spider silk as a transformative alternative to conventional cotton fabrics.
Infographic: Spider silk vs Cotton for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com