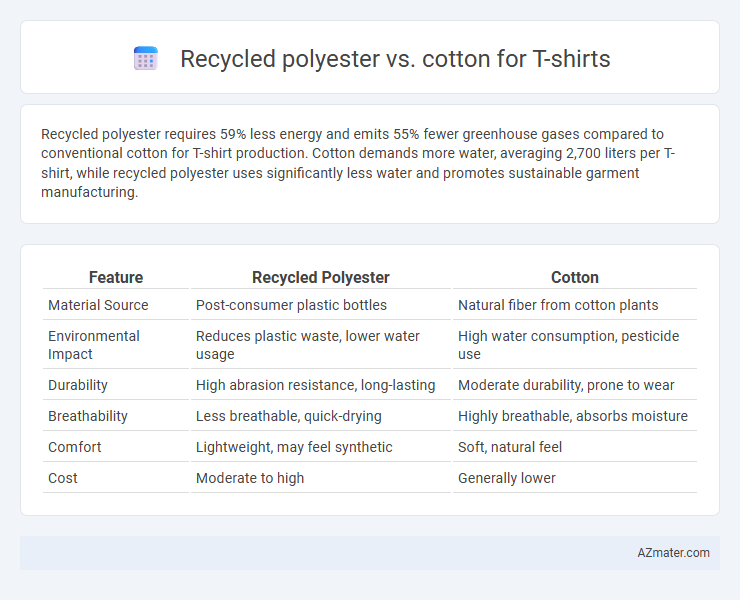
Recycled polyester requires 59% less energy and emits 55% fewer greenhouse gases compared to conventional cotton for T-shirt production. Cotton demands more water, averaging 2,700 liters per T-shirt, while recycled polyester uses significantly less water and promotes sustainable garment manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recycled Polyester | Cotton |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Post-consumer plastic bottles | Natural fiber from cotton plants |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces plastic waste, lower water usage | High water consumption, pesticide use |
| Durability | High abrasion resistance, long-lasting | Moderate durability, prone to wear |
| Breathability | Less breathable, quick-drying | Highly breathable, absorbs moisture |
| Comfort | Lightweight, may feel synthetic | Soft, natural feel |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally lower |
Introduction to Recycled Polyester and Cotton
Recycled polyester is produced from post-consumer plastic bottles and textile waste, reducing environmental impact by lowering reliance on virgin petroleum-based materials. Cotton, a natural fiber derived from the cotton plant, is prized for its breathability and softness but often requires significant water and pesticide use in conventional farming. Choosing between recycled polyester and cotton for T-shirts involves considering factors such as sustainability, comfort, and durability.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Recycled polyester significantly reduces landfill waste and energy consumption by repurposing plastic bottles, emitting approximately 75% fewer greenhouse gases compared to virgin polyester. Cotton cultivation, though biodegradable, requires substantial water use--around 10,000 liters per kilogram--and extensive pesticide application, contributing to soil degradation and water pollution. Choosing recycled polyester over cotton for T-shirts lowers carbon footprint and conserves natural resources, making it a more sustainable option for environmentally conscious consumers.
Production Process Differences
Recycled polyester is made by melting down PET plastic waste, such as soda bottles, and spinning it into fibers through a closed-loop process that significantly reduces water and energy consumption compared to virgin polyester production. Cotton cultivation involves extensive land use, high water consumption, and pesticide application, contributing to environmental degradation and resource depletion. The production of recycled polyester bypasses the agricultural phase and chemical treatments typical in cotton farming, making it a more sustainable choice in terms of production efficiency and environmental impact.
Resource Consumption: Water and Energy Use
Recycled polyester t-shirts significantly reduce water consumption, using up to 90% less water compared to conventional cotton production, which is highly water-intensive due to irrigation needs. Energy use in recycled polyester production is lower than virgin polyester but generally higher than organic cotton cultivation, though the overall environmental impact is mitigated by using post-consumer materials. Cotton farming also requires substantial pesticides and fertilizers, further increasing its resource footprint beyond just water and energy metrics.
Durability and Longevity of Fabrics
Recycled polyester offers superior durability and longevity compared to cotton, resisting wear, shrinking, and fading over extended use. Cotton, while breathable and comfortable, tends to weaken with frequent washing and prolonged exposure to sunlight. Fabrics made from recycled polyester maintain their structural integrity and vibrant appearance longer, making them ideal for long-lasting T-shirts.
Comfort and Wearability
Recycled polyester offers excellent moisture-wicking properties and durability, making it ideal for activewear T-shirts that require quick drying and shape retention. Cotton provides superior breathability and softness, enhancing overall comfort and preventing skin irritation during prolonged wear. Blended fabrics combining recycled polyester and cotton can optimize both comfort and wearability, balancing the benefits of moisture management and natural softness.
Cost and Price Factors
Recycled polyester T-shirts typically cost less to produce than cotton ones due to lower water usage and faster manufacturing processes, which reduces overall expenses. Cotton T-shirts often have higher raw material costs, influenced by agricultural factors such as water consumption, pesticides, and longer cultivation cycles. Pricing for recycled polyester shirts can be more competitive in mass markets, while cotton garments, especially organic varieties, command premium prices driven by consumer demand for natural fibers and sustainability claims.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendliness
Recycled polyester T-shirts significantly reduce plastic waste by reusing PET bottles and other plastics, consuming less water and energy compared to conventional cotton cultivation. Organic cotton requires substantial land and water resources but offers biodegradability and supports soil health without synthetic chemicals. Choosing recycled polyester supports circular economies and decreases reliance on fossil fuels, whereas cotton's natural fibers enhance compostability and reduce microplastic pollution in textile waste.
Consumer Perceptions and Preferences
Consumers increasingly prefer recycled polyester for T-shirts due to its sustainability and durability, valuing eco-friendly production and long-lasting wear. Cotton remains favored for its natural breathability, softness, and comfort, appealing to those prioritizing tactile experience and traditional fabric qualities. Buyer perceptions often balance the environmental benefits of recycled polyester against the familiar comfort of cotton, influencing choices toward blends or specific lifestyle needs.
Which Is Better for T-Shirts?
Recycled polyester offers superior moisture-wicking, durability, and lower environmental impact compared to conventional cotton, making it ideal for activewear T-shirts. Cotton provides exceptional breathability and natural softness but requires significantly more water and pesticides in cultivation, impacting sustainability. For eco-conscious consumers seeking performance and resource efficiency, recycled polyester is often the better choice for T-shirts.
Infographic: Recycled polyester vs Cotton for T-shirt
 azmater.com
azmater.com