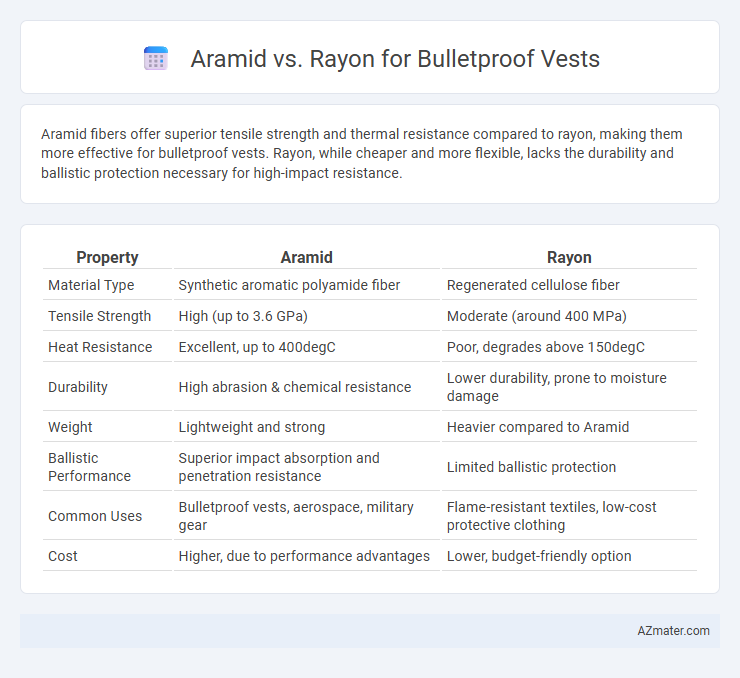
Aramid fibers offer superior tensile strength and thermal resistance compared to rayon, making them more effective for bulletproof vests. Rayon, while cheaper and more flexible, lacks the durability and ballistic protection necessary for high-impact resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aramid | Rayon |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic aromatic polyamide fiber | Regenerated cellulose fiber |
| Tensile Strength | High (up to 3.6 GPa) | Moderate (around 400 MPa) |
| Heat Resistance | Excellent, up to 400degC | Poor, degrades above 150degC |
| Durability | High abrasion & chemical resistance | Lower durability, prone to moisture damage |
| Weight | Lightweight and strong | Heavier compared to Aramid |
| Ballistic Performance | Superior impact absorption and penetration resistance | Limited ballistic protection |
| Common Uses | Bulletproof vests, aerospace, military gear | Flame-resistant textiles, low-cost protective clothing |
| Cost | Higher, due to performance advantages | Lower, budget-friendly option |
Introduction to Bulletproof Vest Materials
Bulletproof vests primarily use aramid fibers and rayon as core materials due to their distinct ballistic properties. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer exceptional tensile strength and heat resistance, making them ideal for high-performance protective gear. Rayon provides cost-effective cut resistance but lacks the durability and impact absorption necessary for advanced ballistic protection.
What is Aramid? Key Properties
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Twaron, are synthetic fibers known for their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for bulletproof vests. These fibers exhibit high tensile strength, excellent heat resistance, and superior impact absorption, which enhances ballistic protection. Aramid's durability and lightweight nature provide enhanced mobility and comfort compared to other materials like rayon.
What is Rayon? Key Properties
Rayon is a semi-synthetic fiber made from regenerated cellulose derived from wood pulp, often used in textiles for its softness and breathability. Key properties include high moisture absorbency, excellent drape, and good tensile strength, but it lacks the high tensile strength, flame resistance, and durability required for bulletproof vest materials. Unlike aramid fibers such as Kevlar, rayon is not suitable for ballistic protection due to its lower resistance to impact and heat.
Aramid: Strengths and Weaknesses
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, are renowned for their exceptional tensile strength and heat resistance, making them ideal for bulletproof vests that require high impact protection and durability. Their lightweight nature and flexibility enhance wearer comfort and mobility, while their resistance to abrasion and chemicals ensures long-lasting performance in various environments. However, Aramid fibers can degrade when exposed to prolonged UV light and moisture, and they often come at a higher cost compared to Rayon-based alternatives, which may limit their use in budget-sensitive applications.
Rayon: Strengths and Weaknesses
Rayon fibers offer excellent comfort and flexibility in bulletproof vests, making them lightweight and breathable compared to aramid fibers. However, rayon lacks the high tensile strength and thermal resistance found in aramid materials such as Kevlar, reducing its effectiveness in stopping high-velocity projectiles. Moisture absorption and lower durability under extreme conditions further limit rayon's suitability for ballistic protection.
Ballistic Performance Comparison
Aramid fibers such as Kevlar deliver superior ballistic performance compared to rayon due to their exceptional tensile strength and energy absorption capabilities, making them ideal for bulletproof vests. Rayon lacks the molecular structure necessary to dissipate high-velocity impacts effectively, resulting in lower resistance to penetration and trauma. The advanced cross-linked polymer chains in aramid fibers provide enhanced durability and multi-hit protection, critical factors in ballistic resistance.
Weight and Comfort Analysis
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, are significantly lighter than rayon, offering superior strength-to-weight ratio essential for bulletproof vests where mobility is critical. Rayon, while softer and more breathable than aramid, lacks the tensile strength required for ballistic protection, resulting in bulkier and heavier vests when layered to meet safety standards. The high durability and lightweight nature of aramid materials enhance wearer comfort by reducing fatigue during extended use compared to rayon-based alternatives.
Durability and Longevity
Aramid fibers such as Kevlar offer superior durability and longevity for bulletproof vests compared to Rayon due to their high tensile strength and resistance to heat and abrasion. Aramid materials maintain structural integrity under extreme stress and environmental exposure, ensuring reliable ballistic protection over extended periods. Rayon, being less resistant to wear and degradation, lacks the long-term durability required for effective body armor performance.
Cost and Availability
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer superior ballistic protection but come with a higher price point due to complex manufacturing processes and limited raw materials. Rayon, while more affordable and easier to source, typically lacks the durability and strength required for effective bulletproof vests. The widespread commercial availability of aramid makes it the preferred choice despite cost, whereas rayon's lower cost is balanced by its reduced protective performance and less frequent use in high-performance ballistic applications.
Choosing the Best Material for Bulletproof Vests
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide superior strength-to-weight ratio, exceptional ballistic resistance, and durability, making them the preferred choice for bulletproof vests in high-risk situations. Rayon, while lighter and more affordable, lacks the tensile strength and impact resistance necessary for effective ballistic protection. Selecting aramid materials enhances the vest's stop power and longevity, ensuring optimal safety for law enforcement and military personnel.
Infographic: Aramid vs Rayon for Bulletproof Vest
 azmater.com
azmater.com