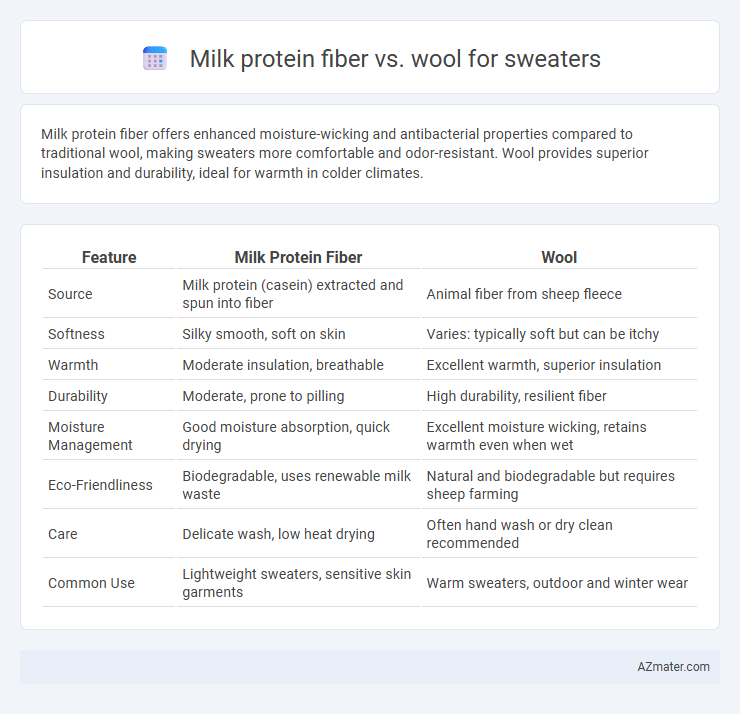
Milk protein fiber offers enhanced moisture-wicking and antibacterial properties compared to traditional wool, making sweaters more comfortable and odor-resistant. Wool provides superior insulation and durability, ideal for warmth in colder climates.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Milk Protein Fiber | Wool |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Milk protein (casein) extracted and spun into fiber | Animal fiber from sheep fleece |
| Softness | Silky smooth, soft on skin | Varies: typically soft but can be itchy |
| Warmth | Moderate insulation, breathable | Excellent warmth, superior insulation |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to pilling | High durability, resilient fiber |
| Moisture Management | Good moisture absorption, quick drying | Excellent moisture wicking, retains warmth even when wet |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable, uses renewable milk waste | Natural and biodegradable but requires sheep farming |
| Care | Delicate wash, low heat drying | Often hand wash or dry clean recommended |
| Common Use | Lightweight sweaters, sensitive skin garments | Warm sweaters, outdoor and winter wear |
Introduction: Comparing Milk Protein Fiber and Wool for Sweaters
Milk protein fiber offers a hypoallergenic and silky-soft alternative to traditional wool, making it suitable for sensitive skin and those prone to allergies. Wool provides superior insulation and moisture-wicking properties, ensuring warmth and breathability in various climates. Both fibers present unique benefits in sweater production, with milk protein fiber excelling in softness and sustainability, while wool remains unmatched in durability and thermal regulation.
Fiber Origins: How Milk Protein Fiber and Wool Are Produced
Milk protein fiber is created through a process where casein protein from milk is extracted, purified, and then spun into fibers, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional animal-based materials. Wool is harvested directly from sheep through shearing, relying on natural animal fiber growth cycles and requiring careful processing to clean and spin the wool into yarn. The production of milk protein fiber emphasizes sustainability by utilizing surplus dairy, while wool production depends on ethical animal farming and seasonal shearing practices.
Texture and Comfort: Feel on the Skin
Milk protein fiber offers a smooth, silky texture that feels exceptionally soft and gentle against the skin, making it ideal for sensitive or allergy-prone individuals. Wool provides natural warmth and breathability but can sometimes be coarse or itchy, especially for those with sensitive skin. The moisture-wicking properties of milk protein fiber enhance comfort by keeping the skin dry, whereas wool excels in temperature regulation but may require blending for optimal softness.
Warmth and Insulation Properties
Milk protein fiber offers excellent moisture-wicking capabilities and thermal regulation, making sweaters warm and breathable, while wool excels in superior insulation due to its natural crimp and lanolin content that traps heat effectively. Wool fibers create insulating air pockets that retain warmth, particularly in cold and damp conditions, whereas milk protein fiber provides a softer feel with moderate insulation, ideal for mild to cooler climates. Both materials deliver warmth, but wool remains the top choice for maximum insulation and cold-weather performance in sweaters.
Moisture Management and Breathability
Milk protein fiber offers superior moisture management and breathability compared to wool, as its natural bioactive properties allow it to absorb and release moisture efficiently, keeping the skin dry and comfortable. Wool, while also breathable and moisture-wicking, retains more moisture within its fibers, which can lead to a heavier feel when wet. The unique structure of milk protein fiber promotes faster drying times and enhanced air circulation, making it an ideal choice for sweaters designed for active wear or warm climates.
Durability and Longevity of Sweaters
Milk protein fiber sweaters offer notable durability due to their resistance to fading, pilling, and shrinking, maintaining shape and softness over time. Wool sweaters, especially those made from high-quality merino or lambswool, provide exceptional longevity with natural elasticity and resilience against wear, but can be prone to felting if not cared for properly. The longevity of milk protein fiber suits those seeking low-maintenance durability, while wool appeals to consumers valuing natural fiber strength combined with traditional insulation properties.
Hypoallergenic and Skin Sensitivity Considerations
Milk protein fiber offers exceptional hypoallergenic properties due to its natural silk-like protein structure, reducing the risk of skin irritation commonly associated with wool fibers. Wool, while breathable and insulating, often contains lanolin and coarse fibers that can trigger allergic reactions or discomfort in individuals with sensitive skin. Choosing milk protein fiber sweaters provides a softer, gentler option for those prone to eczema or dermatitis, ensuring comfort without compromising warmth or durability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Milk protein fiber offers a sustainable alternative to wool by utilizing casein proteins from milk waste, reducing reliance on animal farming and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. Wool production often involves significant land use, methane emissions, and water consumption, while milk protein fiber manufacturing conserves water and reduces environmental degradation. Both fibers biodegrade naturally, but milk protein fiber's innovation in using byproducts enhances circular economy practices compared to traditional wool.
Care, Washing, and Maintenance Tips
Milk protein fiber sweaters require gentle hand washing in cold water with mild detergent to preserve their softness and prevent fiber damage. Wool sweaters benefit from using wool-specific detergents and either hand washing or gentle machine cycles, followed by flat drying to maintain shape and prevent shrinking. For both materials, avoid wringing or twisting and store sweaters folded in a cool, dry place to reduce pilling and maintain fiber integrity.
Price and Availability for Consumers
Milk protein fiber sweaters offer a competitive price point, often lower than traditional wool, making them an attractive option for budget-conscious consumers. They are manufactured through innovative processes that utilize casein protein from milk, which may affect availability depending on regional production capacity. Wool remains widely available worldwide due to established supply chains, but its price tends to fluctuate based on source quality and seasonal demand.
Infographic: Milk protein fiber vs Wool for Sweater
 azmater.com
azmater.com