Biofabricated textiles offer sustainable, biodegradable alternatives to traditional polyester jackets, reducing environmental impact through renewable resources. Polyester jackets provide durability and water resistance but contribute to microplastic pollution and rely on non-renewable petrochemicals.
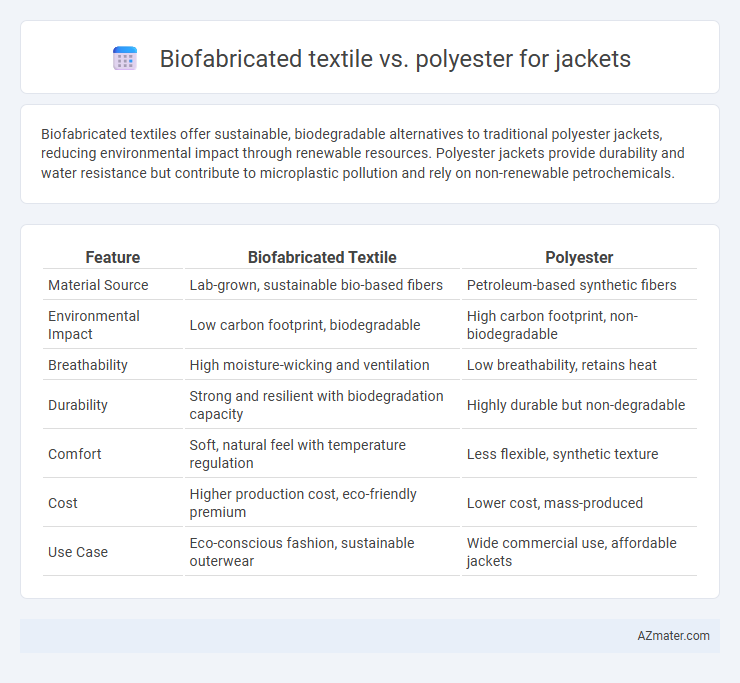
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biofabricated Textile | Polyester |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Lab-grown, sustainable bio-based fibers | Petroleum-based synthetic fibers |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable | High carbon footprint, non-biodegradable |
| Breathability | High moisture-wicking and ventilation | Low breathability, retains heat |
| Durability | Strong and resilient with biodegradation capacity | Highly durable but non-degradable |
| Comfort | Soft, natural feel with temperature regulation | Less flexible, synthetic texture |
| Cost | Higher production cost, eco-friendly premium | Lower cost, mass-produced |
| Use Case | Eco-conscious fashion, sustainable outerwear | Wide commercial use, affordable jackets |
Introduction to Jacket Fabrics: Biofabrication vs Polyester
Biofabricated textiles represent a breakthrough in sustainable jacket fabrics, produced through biological processes that reduce environmental impact by minimizing waste and reliance on fossil fuels. Polyester, a synthetic fabric derived from petroleum, remains popular for its durability, water resistance, and affordability but contributes significantly to microplastic pollution and non-biodegradability issues. Comparing biofabricated textiles to polyester highlights a shift toward eco-friendly alternatives in jacket manufacturing, emphasizing renewable resources and biodegradability.
What Are Biofabricated Textiles?
Biofabricated textiles are innovative materials produced through biological processes using microorganisms, cells, or natural polymers instead of traditional petrochemical methods. These textiles offer sustainable alternatives with reduced environmental impact, often biocompatible and biodegradable, making them ideal for eco-friendly jacket production. Unlike polyester, which is derived from fossil fuels and contributes to microplastic pollution, biofabricated textiles prioritize renewable resources and circular economy principles.
Understanding Polyester: Production and Properties
Polyester is a synthetic polymer derived primarily from petroleum through a polycondensation process involving terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol. Its production results in fibers known for high durability, resistance to wrinkles, and quick-drying capabilities, making it a popular choice for jackets. Key properties such as tensile strength, moisture-wicking, and thermal insulation contribute to polyester's performance but present environmental challenges due to its non-biodegradable nature and high carbon footprint.
Environmental Impact: Biofabrication vs Polyester
Biofabricated textiles significantly reduce environmental impact by utilizing renewable biological resources and producing fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to petroleum-based polyester, which relies heavily on fossil fuels and contributes to microplastic pollution. Polyester production consumes large amounts of energy and releases synthetic microfibers during washing, exacerbating ocean pollution and harming marine ecosystems. Biofabrication processes often promote biodegradability and lower water usage, positioning them as a sustainable alternative for eco-friendly jacket manufacturing.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Biofabricated textiles, made from cultured cells or sustainable bio-based materials, offer promising durability with resistance to wear and environmental degradation, often outperforming traditional fabrics in biodegradability and breathability. Polyester jackets provide high tensile strength, water resistance, and excellent abrasion resistance, making them a durable choice for harsh weather and frequent use. Performance-wise, biofabricated textiles deliver enhanced moisture management and reduced environmental impact, while polyester excels in quick-drying properties and cost-effective mass production.
Comfort, Breathability, and Wearability
Biofabricated textiles offer superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties compared to polyester, enhancing overall comfort for long-term wear. The natural fibers and engineered porous structures in biofabricated fabrics promote better airflow, reducing sweat accumulation and skin irritation often associated with polyester jackets. Enhanced wearability is achieved through the lightweight and flexible nature of biofabricated textiles, making them a preferred choice for active and sustainable outerwear.
Cost Analysis: Biofabricated Textiles vs Polyester
Biofabricated textiles typically incur higher production costs due to advanced biotechnological processes and limited market scale compared to polyester, which benefits from mature manufacturing methods and economies of scale. Polyester jackets are generally more affordable, with prices driven down by widespread synthetic fiber production and lower raw material expenses. When evaluating long-term costs, biofabricated textiles may offer potential savings through sustainability incentives and reduced environmental impact, but current upfront costs remain significantly higher than those of polyester alternatives.
Innovation and Trends in Sustainable Jackets
Biofabricated textiles use lab-grown materials like mycelium or bacterial cellulose, offering a renewable and biodegradable alternative to conventional polyester. These innovative fabrics reduce reliance on fossil fuels and minimize microplastic pollution, aligning with rising consumer demand for eco-friendly jackets. Emerging trends highlight the integration of biofabricated textiles in fashion, driving sustainable jacket production with enhanced durability and performance compared to traditional synthetic fibers.
Consumer Preferences and Market Demand
Biofabricated textiles for jackets appeal to eco-conscious consumers seeking sustainable alternatives to traditional polyester, which dominates the market due to its durability and affordability. Consumer preferences increasingly favor biofabricated materials because of their reduced environmental impact, biodegradability, and innovation appeal, driving niche market growth. Market demand for biofabricated textiles is projected to rise as regulatory pressures mount and brands emphasize circular economy practices, challenging polyester's long-standing market share.
Future Prospects: The Evolution of Jacket Materials
Biofabricated textiles present a sustainable and innovative alternative to traditional polyester in jacket manufacturing, with advancements in microbial fermentation and plant-based leather substitutes driving their development. These materials offer enhanced biodegradability and reduced carbon footprints, aligning with global demands for eco-friendly fashion. Future prospects indicate increased adoption of biofabricated textiles as technologies mature, potentially transforming the jacket industry through circular economy principles and minimizing reliance on petrochemical-based fabrics like polyester.
Infographic: Biofabricated textile vs Polyester for Jacket
 azmater.com
azmater.com