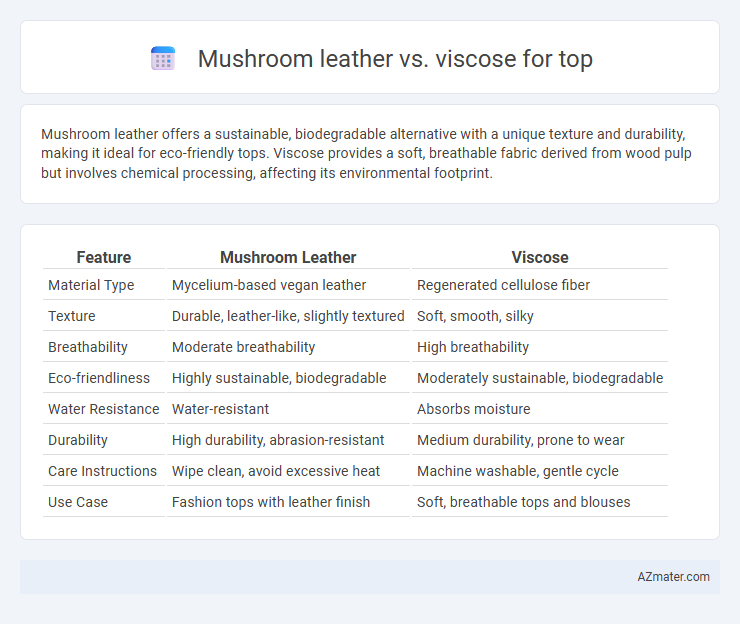
Mushroom leather offers a sustainable, biodegradable alternative with a unique texture and durability, making it ideal for eco-friendly tops. Viscose provides a soft, breathable fabric derived from wood pulp but involves chemical processing, affecting its environmental footprint.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mushroom Leather | Viscose |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Mycelium-based vegan leather | Regenerated cellulose fiber |
| Texture | Durable, leather-like, slightly textured | Soft, smooth, silky |
| Breathability | Moderate breathability | High breathability |
| Eco-friendliness | Highly sustainable, biodegradable | Moderately sustainable, biodegradable |
| Water Resistance | Water-resistant | Absorbs moisture |
| Durability | High durability, abrasion-resistant | Medium durability, prone to wear |
| Care Instructions | Wipe clean, avoid excessive heat | Machine washable, gentle cycle |
| Use Case | Fashion tops with leather finish | Soft, breathable tops and blouses |
Introduction to Mushroom Leather and Viscose
Mushroom leather, crafted from mycelium, offers a sustainable and biodegradable alternative to traditional fabrics with a natural texture and durability ideal for eco-conscious fashion. Viscose, a semi-synthetic fiber derived from cellulose, provides a soft, breathable fabric known for its silk-like feel and versatility in clothing, but relies on chemical processing and resource-intensive production. Comparing mushroom leather and viscose highlights the trade-offs between innovative bio-based materials and established cellulose fibers in terms of environmental impact and performance in textile applications.
What is Mushroom Leather?
Mushroom leather, also known as mycelium leather, is a sustainable, biodegradable material made from the root structure of mushrooms, offering an eco-friendly alternative to conventional leather. It features a unique texture and durability suitable for fashion tops, combining natural fungal fibers with innovative tanning processes to mimic animal leather's strength and flexibility. Compared to viscose, which is a semi-synthetic fabric derived from wood pulp, mushroom leather provides superior environmental benefits by reducing chemical use, water consumption, and carbon footprint during production.
What is Viscose?
Viscose is a semi-synthetic fiber derived from cellulose, primarily sourced from wood pulp, offering a soft and breathable texture commonly used in tops and garments. Unlike mushroom leather, which is a sustainable alternative made from mycelium, viscose undergoes chemical processing that impacts its environmental footprint. Viscose's smooth drape and moisture absorption make it popular for comfortable, lightweight tops.
Production Processes: Mushroom Leather vs Viscose
Mushroom leather is produced using mycelium, which involves growing and harvesting fungal root structures in controlled environments, requiring significantly less water and chemicals compared to viscose production. Viscose is derived from cellulose fibers, primarily sourced from wood pulp, and undergoes extensive chemical treatments including carbon disulfide and caustic soda, which generate environmental pollutants. The production process of mushroom leather emphasizes sustainability and biodegradability, whereas viscose manufacturing often faces criticism for deforestation and toxic waste concerns.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Mushroom leather, derived from mycelium, offers a sustainable alternative to viscose by utilizing fast-growing fungi that require minimal water, no pesticides, and produce negligible waste, significantly reducing environmental impact. Viscose, although biodegradable, relies on intensive chemical processes and deforestation of bamboo or wood pulp, leading to higher carbon emissions and water pollution. Mushroom leather's renewable sourcing and eco-friendly production methods position it as a more environmentally responsible choice compared to viscose fabric in the fashion industry.
Durability and Performance Comparison
Mushroom leather offers superior durability compared to viscose, featuring enhanced resistance to wear, moisture, and temperature variations, making it ideal for long-lasting tops. Viscose, while soft and breathable, tends to degrade faster under stress and repeated washing, compromising its performance over time. The sustainable and resilient properties of mushroom leather also ensure better shape retention and reduced pilling, outperforming viscose in overall longevity and wear resistance.
Aesthetic and Texture Differences
Mushroom leather showcases a unique, natural grain with a slightly matte finish, offering an organic and earthy aesthetic, while viscose typically presents a smooth, silky appearance with a slight sheen. The texture of mushroom leather is firm yet pliable, providing a tactile, textured feel that mimics traditional leather alternatives, whereas viscose fabrics are soft, lightweight, and drape fluidly against the skin. Mushroom leather's texture promotes durability and structure in tops, contrasting with viscose's breathable, airy quality ideal for flowing, delicate garments.
Cost and Accessibility
Mushroom leather, derived from mycelium, is generally more expensive than viscose due to its innovative production process and sustainability benefits. Viscose offers greater accessibility with widespread availability and lower manufacturing costs, making it a budget-friendly choice for tops. Consumers often weigh the eco-friendly appeal of mushroom leather against the affordability and ease of acquisition presented by viscose.
Applications in Fashion and Apparel
Mushroom leather offers a sustainable, biodegradable alternative to traditional materials, making it ideal for eco-conscious fashion brands designing jackets, shoes, and handbags. Viscose, derived from cellulose fibers, provides a soft, breathable fabric widely used in tops, dresses, and blouses for its silky texture and drape. Fashion designers seeking innovative, environmentally friendly options increasingly favor mushroom leather for outerwear, while viscose remains popular for lightweight, comfortable apparel.
Future Trends: Mushroom Leather vs Viscose
Mushroom leather, an innovative sustainable material made from mycelium, is rapidly gaining traction in the fashion industry due to its eco-friendly production and biodegradability, contrasting with viscose which involves chemical-intensive processes despite being plant-based. Future trends indicate mushroom leather's potential to revolutionize tops by offering durability, breathability, and a lower carbon footprint, aligning with increasing consumer demand for vegan and cruelty-free alternatives. Advances in fungal biotechnology and scalable manufacturing are expected to enhance mushroom leather's affordability and texture variety, positioning it as a viable replacement for viscose in sustainable fashion collections.
Infographic: Mushroom leather vs Viscose for Top
 azmater.com
azmater.com