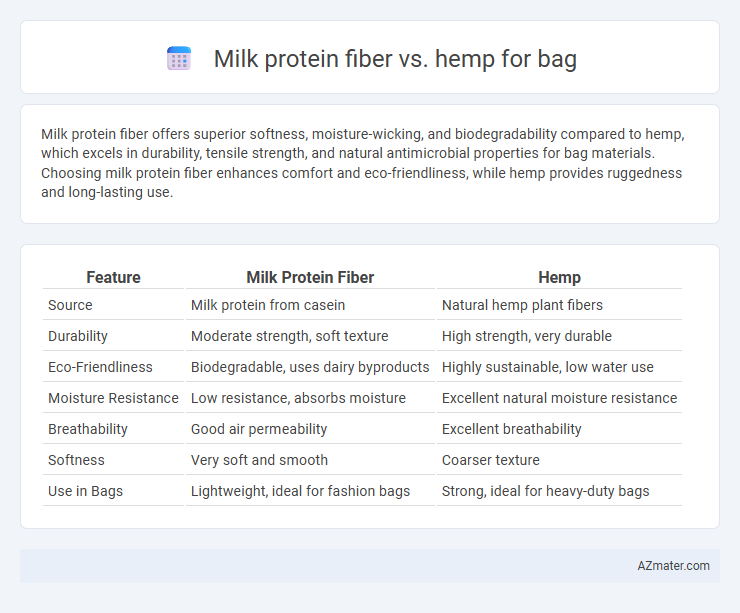
Milk protein fiber offers superior softness, moisture-wicking, and biodegradability compared to hemp, which excels in durability, tensile strength, and natural antimicrobial properties for bag materials. Choosing milk protein fiber enhances comfort and eco-friendliness, while hemp provides ruggedness and long-lasting use.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Milk Protein Fiber | Hemp |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Milk protein from casein | Natural hemp plant fibers |
| Durability | Moderate strength, soft texture | High strength, very durable |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable, uses dairy byproducts | Highly sustainable, low water use |
| Moisture Resistance | Low resistance, absorbs moisture | Excellent natural moisture resistance |
| Breathability | Good air permeability | Excellent breathability |
| Softness | Very soft and smooth | Coarser texture |
| Use in Bags | Lightweight, ideal for fashion bags | Strong, ideal for heavy-duty bags |
Introduction to Sustainable Bag Materials
Milk protein fiber offers a biodegradable and eco-friendly alternative to synthetic textiles, derived from casein protein found in milk, which promotes sustainable fashion by reducing plastic pollution. Hemp fibers are renowned for their durability, fast growth, and minimal water requirements, making them a highly sustainable choice for bag production that supports environmental conservation. Both materials contribute to reducing the carbon footprint of bag manufacturing through renewable resources and lower energy consumption compared to conventional fabrics.
Overview of Milk Protein Fiber
Milk protein fiber, derived from casein in cow's milk, offers a soft, biodegradable, and moisture-absorbent alternative to traditional textile fibers in bag manufacturing. It provides excellent breathability and antibacterial properties, making bags durable and odor-resistant, while maintaining a lightweight and eco-friendly profile. Unlike hemp, which is coarser and more rigid, milk protein fiber delivers a smoother texture and enhanced comfort, appealing to sustainable fashion consumers.
Hemp Fiber: A Classic Eco-Friendly Choice
Hemp fiber remains a classic eco-friendly choice for bag production due to its durability, biodegradability, and minimal environmental impact during cultivation. Unlike milk protein fiber, which requires industrial processing and synthetic additives, hemp grows rapidly with low water and pesticide needs, making it a sustainable natural fiber. This combination of strength, sustainability, and renewable sourcing solidifies hemp's position as a preferred material in eco-conscious fashion.
Production Process: Milk Protein vs. Hemp Fiber
Milk protein fiber production involves extracting casein protein from milk, followed by spinning it into yarn through chemical and mechanical processes, resulting in a soft, biodegradable fabric. Hemp fiber production includes harvesting the hemp stalks, retting to separate fibers, and mechanical processing into strong, durable yarns with minimal chemical use. Compared to hemp, milk protein fiber relies more on chemical extraction whereas hemp fiber utilizes primarily mechanical methods, impacting sustainability and fabric properties.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Milk protein fiber production generates less carbon dioxide and consumes significantly less water compared to conventional hemp cultivation, which requires ample water and land resources. Hemp, however, offers high biodegradability and naturally pest-resistant qualities, reducing the need for harmful pesticides and synthetic fertilizers during growth. Overall, milk protein fiber is more water-efficient, while hemp provides substantial benefits in soil regeneration and lower chemical inputs, making both fibers environmentally advantageous in different contexts.
Durability and Strength in Bags
Milk protein fiber bags exhibit excellent durability due to their fine, smooth texture and strong natural protein bonds that resist wear and tear. Hemp bags are renowned for their superior strength, boasting high tensile resistance and abrasion durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty use. Comparing both, hemp typically outperforms milk protein fiber in overall bag strength, while milk protein fiber offers a softer yet resilient alternative for lightweight, durable bags.
Comfort and Texture Differences
Milk protein fiber offers a smooth, silky texture and excellent moisture-wicking properties, enhancing comfort by keeping the skin dry and cool. Hemp fabric, known for its durability and natural breathability, provides a coarser texture that softens with washing but may feel rougher initially against the skin. Choosing between milk protein fiber and hemp for bags depends on the desired balance between softness and ruggedness in texture and comfort.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Options
Milk protein fiber offers excellent biodegradability, breaking down naturally within weeks under composting conditions, making it an eco-friendly option for bags. Hemp fibers also biodegrade efficiently but tend to take longer, often several months, due to their tougher cellulose content. Both materials support sustainable end-of-life options, with milk protein ideal for quick composting and hemp suitable for industrial composting or recycling into other products.
Cost and Market Availability
Milk protein fiber generally incurs higher production costs compared to hemp fibers due to complex processing techniques and limited scalability, resulting in a niche market with less widespread availability. Hemp fibers benefit from lower cultivation expenses, renewable growth cycles, and established supply chains, making them more cost-effective and readily accessible for bag manufacturing. Market demand trends favor hemp products for their sustainability and affordability, whereas milk protein fiber remains a premium option targeting specialized eco-conscious consumers.
Future Prospects and Consumer Preferences
Milk protein fiber offers sustainable, biodegradable qualities and a soft, silk-like texture that appeals to eco-conscious consumers seeking luxury and comfort in bags. Hemp provides durability, resistance to wear, and natural antimicrobial properties, aligning with the growing demand for robust, eco-friendly materials in fashion accessories. Future prospects indicate rising consumer preferences for milk protein fiber in premium, sustainable products, while hemp maintains strong market presence due to its cost-effectiveness and eco-responsibility.
Infographic: Milk protein fiber vs Hemp for Bag
 azmater.com
azmater.com