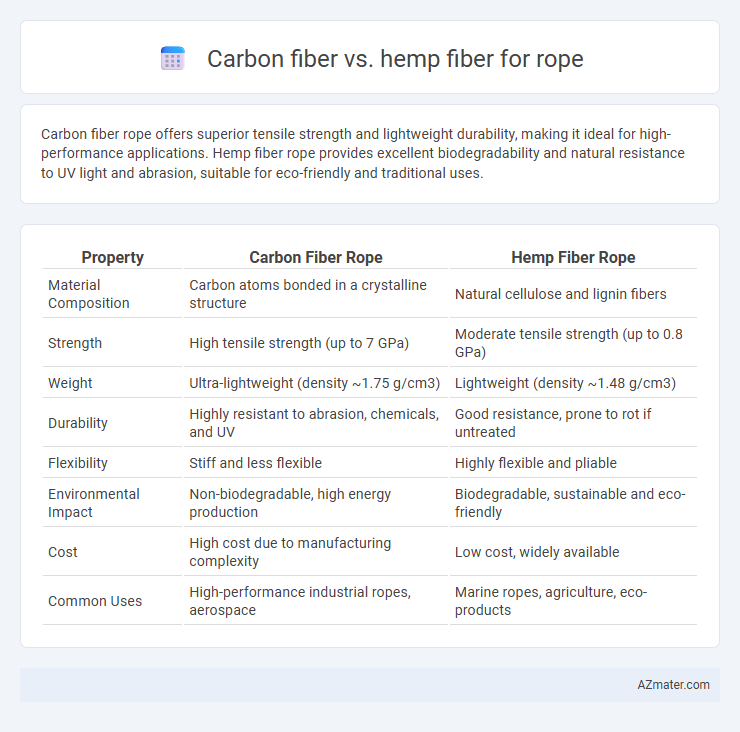
Carbon fiber rope offers superior tensile strength and lightweight durability, making it ideal for high-performance applications. Hemp fiber rope provides excellent biodegradability and natural resistance to UV light and abrasion, suitable for eco-friendly and traditional uses.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Fiber Rope | Hemp Fiber Rope |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Carbon atoms bonded in a crystalline structure | Natural cellulose and lignin fibers |
| Strength | High tensile strength (up to 7 GPa) | Moderate tensile strength (up to 0.8 GPa) |
| Weight | Ultra-lightweight (density ~1.75 g/cm3) | Lightweight (density ~1.48 g/cm3) |
| Durability | Highly resistant to abrasion, chemicals, and UV | Good resistance, prone to rot if untreated |
| Flexibility | Stiff and less flexible | Highly flexible and pliable |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, high energy production | Biodegradable, sustainable and eco-friendly |
| Cost | High cost due to manufacturing complexity | Low cost, widely available |
| Common Uses | High-performance industrial ropes, aerospace | Marine ropes, agriculture, eco-products |
Introduction to Carbon Fiber and Hemp Fiber Ropes
Carbon fiber ropes are composed of tightly woven carbon filaments known for their exceptional tensile strength, lightweight nature, and resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for high-performance applications such as aerospace and marine industries. Hemp fiber ropes, derived from the bast fibers of the Cannabis sativa plant, offer natural biodegradability, excellent grip, and resistance to ultraviolet light, commonly used in agriculture, outdoor activities, and eco-friendly packaging. Both materials provide unique benefits, with carbon fiber emphasizing strength and durability, while hemp fiber focuses on sustainability and traditional versatility.
Material Composition and Origin
Carbon fiber rope consists of tightly woven strands of carbon filaments derived from polyacrylonitrile (PAN) or petroleum pitch, known for its exceptional tensile strength and lightweight properties. Hemp fiber rope is made from natural bast fibers extracted from the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant, offering biodegradability and moderate strength with high abrasion resistance. While carbon fiber originates from synthetic processes involving high-temperature carbonization, hemp fiber is a renewable resource harvested through agricultural cultivation.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Carbon fiber ropes exhibit significantly higher tensile strength, often exceeding 500 ksi, making them ideal for applications requiring extreme load-bearing capacity and resistance to stretching. Hemp fiber ropes, while naturally strong with tensile strength around 50-150 MPa, offer superior biodegradability and moderate durability but are more susceptible to abrasion and environmental degradation. Carbon fiber's enhanced durability against corrosion and UV exposure provides longer service life compared to hemp fiber, which is prone to moisture retention and microbial attack under harsh conditions.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Carbon fiber ropes are significantly lighter than hemp fiber ropes, offering high strength-to-weight ratios ideal for applications requiring minimal weight. Hemp fiber ropes, while heavier, provide superior natural flexibility and abrasion resistance, making them well-suited for traditional uses where more elasticity is beneficial. The weight advantage of carbon fiber supports enhanced performance in aerospace and marine industries, whereas hemp's flexibility benefits usage in outdoor and agricultural environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbon fiber rope offers exceptional strength and durability but has a high environmental impact due to energy-intensive production and limited recyclability, contributing to carbon emissions and landfill waste. Hemp fiber rope provides a sustainable alternative, being biodegradable, renewable, and requiring fewer resources and chemicals in cultivation and processing, thus reducing its ecological footprint. Choosing hemp fiber rope supports eco-friendly practices while maintaining adequate tensile strength for many applications.
Cost Analysis: Carbon Fiber vs Hemp Fiber
Hemp fiber offers a significantly lower cost compared to carbon fiber, making it a budget-friendly option for rope production with prices often ranging between $1 to $3 per pound. Carbon fiber, by contrast, is priced substantially higher, typically between $20 to $50 per pound due to its advanced manufacturing processes and superior strength-to-weight ratio. When evaluating cost-effectiveness for rope, hemp fiber provides an economical solution with adequate durability, while carbon fiber justifies its higher price through exceptional tensile strength and longevity in specialized applications.
Performance in Various Applications
Carbon fiber rope offers superior tensile strength and exceptional resistance to stretching, making it ideal for high-performance applications such as aerospace, marine, and climbing where durability and lightweight properties are critical. Hemp fiber rope provides excellent biodegradability and natural resistance to abrasion and UV exposure, suitable for eco-friendly uses in agriculture, landscaping, and traditional crafting. While carbon fiber excels in extreme strength and longevity, hemp fiber is preferred for sustainable, versatile performance in less demanding environments.
Resistance to Weather and Chemicals
Carbon fiber ropes exhibit exceptional resistance to weathering, UV exposure, and chemical corrosion, maintaining strength and durability in harsh environments. Hemp fiber ropes are naturally resistant to some chemicals and moisture but degrade faster under prolonged exposure to sunlight, moisture, and certain chemicals, leading to reduced longevity. The superior weather and chemical resistance of carbon fiber make it the preferred choice for industrial and marine applications requiring long-term durability.
Ease of Manufacturing and Processing
Carbon fiber ropes are manufactured through a complex, energy-intensive process involving precursor materials such as polyacrylonitrile, requiring specialized high-temperature carbonization and stretching techniques to achieve high tensile strength. Hemp fiber ropes, derived from natural cellulose fibers, undergo simpler mechanical and chemical retting and processing methods that allow for eco-friendly and cost-effective production with less specialized equipment. The ease of manufacturing hemp fiber ropes makes them more accessible for artisanal and small-scale applications, while carbon fiber ropes demand advanced industrial facilities for optimal performance.
Future Trends and Innovations in Rope Materials
Emerging trends in rope materials emphasize sustainable and high-performance solutions, with hemp fiber gaining attention for its biodegradability and renewable sourcing compared to carbon fiber's superior strength-to-weight ratio but higher environmental footprint. Innovations in hybrid ropes combining carbon fiber's durability with hemp's eco-friendliness aim to optimize performance while reducing ecological impact. Advances in bio-based resin matrices and nanotechnology are poised to enhance hemp fiber's mechanical properties, potentially rivaling carbon fiber in future rope applications.
Infographic: Carbon fiber vs Hemp fiber for Rope
 azmater.com
azmater.com