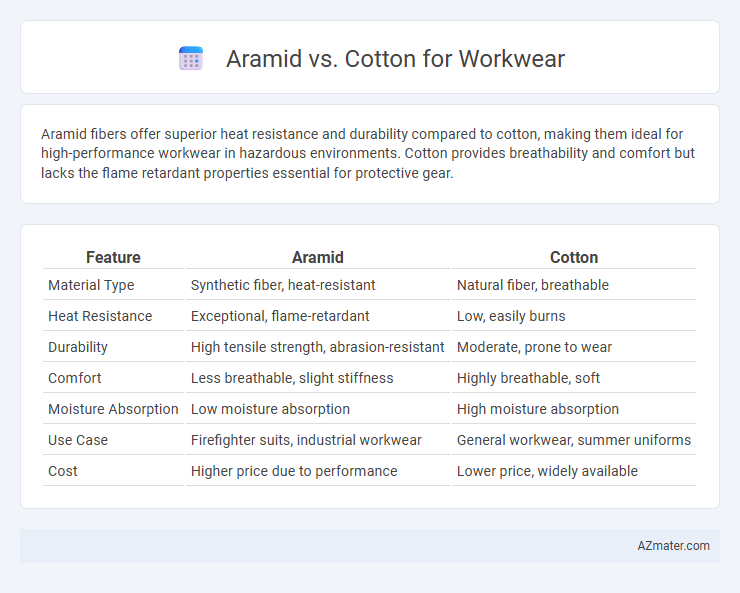
Aramid fibers offer superior heat resistance and durability compared to cotton, making them ideal for high-performance workwear in hazardous environments. Cotton provides breathability and comfort but lacks the flame retardant properties essential for protective gear.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Aramid | Cotton |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic fiber, heat-resistant | Natural fiber, breathable |
| Heat Resistance | Exceptional, flame-retardant | Low, easily burns |
| Durability | High tensile strength, abrasion-resistant | Moderate, prone to wear |
| Comfort | Less breathable, slight stiffness | Highly breathable, soft |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorption | High moisture absorption |
| Use Case | Firefighter suits, industrial workwear | General workwear, summer uniforms |
| Cost | Higher price due to performance | Lower price, widely available |
Introduction to Workwear Materials
Aramid fibers, known for their exceptional heat and flame resistance, are widely used in high-performance workwear for industries like firefighting and electrical utilities. Cotton, valued for its breathability and comfort, remains a popular choice for general workwear but lacks inherent flame-resistant properties unless specially treated. The selection between aramid and cotton depends on the specific safety requirements and working conditions, making material choice critical for protective clothing performance.
Overview of Aramid Fabrics
Aramid fabrics, such as Kevlar and Nomex, are renowned for their exceptional strength, heat resistance, and durability, making them ideal for workwear in hazardous environments. These synthetic fibers offer superior protection against flames, cuts, and abrasions compared to traditional cotton, which lacks inherent flame-retardant properties. Aramid materials maintain lightweight comfort while providing long-lasting safety in industries like firefighting, electrical work, and manufacturing.
Characteristics of Cotton in Workwear
Cotton in workwear offers exceptional breathability and comfort, making it ideal for environments requiring moisture absorption and ventilation. Its natural fibers provide softness and hypoallergenic properties, reducing skin irritation during prolonged wear. Although less resistant to flames and abrasions compared to aramid fibers, cotton remains favored for lightweight tasks where flexibility and ease of movement are essential.
Durability Comparison: Aramid vs Cotton
Aramid fibers offer superior durability for workwear compared to cotton, with high resistance to abrasion, heat, and chemical exposure, making them ideal for hazardous environments. Cotton, while breathable and comfortable, tends to wear out faster under extreme conditions and frequent washing, reducing its lifespan in heavy-duty applications. The enhanced strength and flame retardant properties of aramid fabrics ensure longer-lasting protection and reliability for demanding industrial tasks.
Fire and Heat Resistance Properties
Aramid fibers, such as Nomex and Kevlar, provide superior fire and heat resistance compared to traditional cotton fabrics, making them ideal for high-risk work environments. These synthetic fibers can withstand temperatures up to 370degC (700degF) without melting or igniting, offering enhanced protection for workers exposed to flames or extreme heat. Cotton, while breathable and comfortable, ignites at lower temperatures and burns quickly, limiting its effectiveness in fire-resistant workwear applications.
Comfort and Breathability Factors
Aramid fibers provide superior heat and abrasion resistance, making them ideal for protective workwear but often feel less breathable and less soft compared to cotton. Cotton offers excellent comfort and breathability due to its natural fiber structure, allowing better air circulation and moisture absorption, which helps keep workers cool and dry. Blended fabrics are frequently used to balance the durability of aramid with cotton's comfort, optimizing workwear for both safety and wearability.
Safety Standards and Compliance
Aramid fabrics, such as Nomex and Kevlar, meet stringent safety standards including NFPA 70E and ASTM F1506, providing superior flame resistance and thermal protection compared to cotton. Cotton workwear often requires treatment with flame-retardant chemicals to comply with OSHA regulations but may degrade in protection after repeated washes. Aramid's inherent durability and compliance with industry safety standards make it the preferred choice for high-risk environments requiring reliable flame-resistant workwear.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Aramid workwear, known for its flame-resistant properties, requires specialized cleaning methods such as washing in cold water with mild detergents and avoiding bleach to preserve fabric integrity. Cotton workwear is easier to maintain, as it can withstand high-temperature washing and frequent laundering without special care, but it lacks inherent flame resistance and deteriorates faster under harsh treatment. Proper maintenance of aramid garments extends their durability and safety performance, while cotton offers convenience but demands more frequent replacement.
Cost Analysis and Value for Money
Aramid workwear offers superior durability and flame resistance but usually comes with a higher upfront cost compared to cotton alternatives. Cotton workwear, while cheaper initially, may require more frequent replacement due to lower resilience and protection against hazards. Evaluating long-term value, aramid's investment provides enhanced safety and reduced replacement frequency, often resulting in better overall cost-effectiveness for industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Workplace
Aramid fibers provide superior flame resistance, durability, and abrasion protection compared to cotton, making them ideal for high-risk work environments such as firefighting and electrical work. Cotton, while comfortable and breathable, lacks inherent flame resistance and wears out faster, which may compromise safety in hazardous settings. Selecting aramid workwear ensures compliance with safety standards like NFPA 2112 and enhances worker protection, whereas cotton suits low-risk or indoor tasks requiring comfort and ease of movement.
Infographic: Aramid vs Cotton for Workwear
 azmater.com
azmater.com