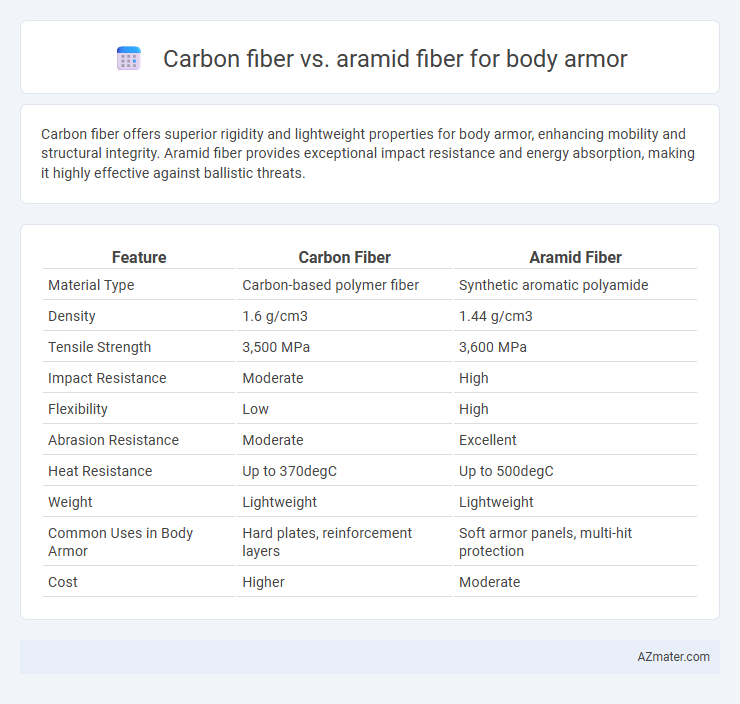
Carbon fiber offers superior rigidity and lightweight properties for body armor, enhancing mobility and structural integrity. Aramid fiber provides exceptional impact resistance and energy absorption, making it highly effective against ballistic threats.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Carbon Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Carbon-based polymer fiber | Synthetic aromatic polyamide |
| Density | 1.6 g/cm3 | 1.44 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 3,500 MPa | 3,600 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate | High |
| Flexibility | Low | High |
| Abrasion Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 370degC | Up to 500degC |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight |
| Common Uses in Body Armor | Hard plates, reinforcement layers | Soft armor panels, multi-hit protection |
| Cost | Higher | Moderate |
Introduction: Understanding Body Armor Materials
Carbon fiber and aramid fiber are prominent materials used in body armor due to their high strength-to-weight ratios and durability. Carbon fiber offers exceptional stiffness and impact resistance, making it ideal for rigid armor panels, while aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, provides superior flexibility and tensile strength crucial for soft body armor applications. Understanding the distinct mechanical properties and energy absorption capabilities of these fibers is essential for optimizing protective performance and comfort in body armor design.
Carbon Fiber: Properties and Performance
Carbon fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and high stiffness, making it ideal for body armor requiring lightweight yet durable materials. Its superior resistance to impact and fatigue enhances protective performance while maintaining flexibility and comfort for prolonged wear. Compared to aramid fiber, carbon fiber provides better structural integrity under high-stress conditions, ensuring reliable ballistic protection.
Aramid Fiber (Kevlar): Characteristics and Advantages
Aramid fiber, particularly Kevlar, is widely favored in body armor for its exceptional tensile strength, lightweight nature, and high resistance to impact and abrasion. Its molecular structure provides superior energy absorption, enabling effective ballistic protection against bullets and shrapnel while maintaining flexibility for mobility. Kevlar's resistance to heat and chemical degradation enhances durability, making it a reliable choice over carbon fiber, which lacks comparable impact-resistant qualities essential for personal body armor.
Weight and Comfort Comparison
Carbon fiber body armor offers superior lightweight properties with a density of approximately 1.6 g/cm3 compared to aramid fiber's density of about 1.44 g/cm3, making aramid fiber slightly lighter in weight. Despite carbon fiber's rigidity, aramid fibers like Kevlar provide enhanced flexibility and comfort due to their woven structure, allowing better movement and breathability during extended wear. Aramid fiber armor typically offers better comfort for long-term use, while carbon fiber excels in weight reduction but may compromise ease of movement.
Ballistic Protection Capabilities
Carbon fiber offers high tensile strength and lightweight properties but has limited energy absorption and fragmentation resistance, making it less suitable for ballistic protection in body armor. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, provide superior ballistic protection due to their excellent energy dispersion, high tensile strength, and resistance to penetration and impact from projectiles. The inherent flexibility and multi-layered weave of aramid fibers enable enhanced stopping power and durability compared to carbon fiber, which is primarily designed for structural reinforcement rather than ballistic resistance.
Durability and Resistance to Wear
Carbon fiber exhibits exceptional durability and high tensile strength, making it resistant to impact and deformation under stress, but it can be brittle and prone to cracking under sharp or repeated flexing. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, offers superior resistance to wear, abrasion, and cuts, maintaining flexibility and structural integrity even under repeated stress or bending. For body armor applications, aramid fibers provide better durability against wear and long-term use, while carbon fiber contributes enhanced rigidity but may require additional layering or composites to improve impact resistance and durability.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Carbon fiber offers higher strength-to-weight ratio but comes at a significantly higher cost compared to Aramid fiber, which provides effective ballistic resistance at a more affordable price point. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, are widely produced and readily available, making them a cost-efficient choice for mass-produced body armor. Supply chain factors and manufacturing complexity contribute to carbon fiber's limited availability and elevated price in the protective gear market.
Environmental and Chemical Resistance
Carbon fiber exhibits excellent chemical resistance, withstanding acids, alkalis, and solvents without degradation, making it highly suitable for body armor exposed to harsh environments. Aramid fiber also offers strong chemical resistance but is vulnerable to prolonged exposure to UV light, moisture, and certain acids, which can reduce its durability. Both materials provide environmental resilience, though carbon fiber's superior resistance to corrosion and environmental factors often ensures longer-lasting performance in body armor applications.
Applications in Military and Law Enforcement
Carbon fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and lightweight properties, making it ideal for rigid ballistic plates used in military and law enforcement body armor. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, provides superior impact resistance and flexibility, often utilized in soft armor vests for enhanced mobility and multi-hit protection. Combining carbon fiber's structural rigidity with aramid's energy-absorbing capabilities results in advanced hybrid armor systems optimized for tactical operations.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fiber for Body Armor
Carbon fiber offers exceptional stiffness and impact resistance, making it ideal for lightweight body armor components requiring high structural integrity. Aramid fiber, such as Kevlar, excels in energy absorption and multi-hit protection due to its superior tensile strength and flexibility. Selecting the right fiber depends on balancing protection level, weight considerations, and mission-specific mobility requirements to optimize body armor performance.
Infographic: Carbon fiber vs Aramid fiber for Body armor
 azmater.com
azmater.com