Biofabricated textiles provide sustainable, cruelty-free alternatives to traditional wool, offering comparable durability and breathability for suits. These innovative materials reduce environmental impact by minimizing water usage and greenhouse gas emissions during production.
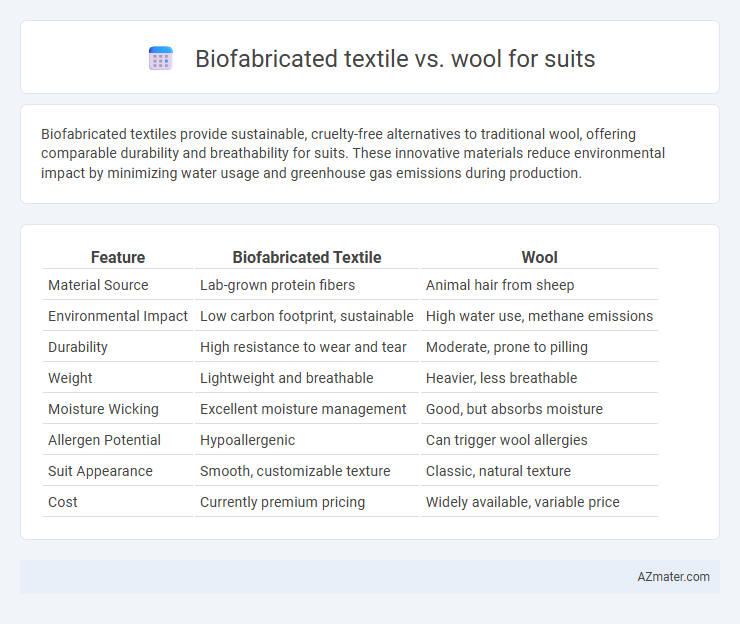
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biofabricated Textile | Wool |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Lab-grown protein fibers | Animal hair from sheep |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, sustainable | High water use, methane emissions |
| Durability | High resistance to wear and tear | Moderate, prone to pilling |
| Weight | Lightweight and breathable | Heavier, less breathable |
| Moisture Wicking | Excellent moisture management | Good, but absorbs moisture |
| Allergen Potential | Hypoallergenic | Can trigger wool allergies |
| Suit Appearance | Smooth, customizable texture | Classic, natural texture |
| Cost | Currently premium pricing | Widely available, variable price |
Introduction to Biofabricated Textiles and Wool
Biofabricated textiles are innovative materials produced through cellular agriculture techniques, using microbial fermentation or cultured cells to create sustainable fabrics with properties similar to natural fibers. Wool, a traditional textile sourced from sheep, offers natural insulation, breathability, and elasticity, widely valued in suit tailoring for its comfort and durability. Comparing biofabricated textiles to wool highlights advancements in eco-friendly production methods and potential performance benefits such as reduced environmental impact and customizable fabric characteristics.
Material Origins: Lab-Grown vs. Natural Fiber
Biofabricated textiles are created using microorganisms or cells in controlled lab environments, offering consistent quality and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional wool. Wool, sourced from sheep, is a natural fiber valued for its breathability, insulation, and biodegradability but involves land use and animal husbandry concerns. Choosing between lab-grown biofabricated textile and natural wool depends on priorities like sustainability, ethics, and performance characteristics in suit materials.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Biofabricated textiles offer a sustainable alternative to traditional wool by utilizing lab-grown proteins or plant-based fibers that require significantly less water, land, and energy during production. Wool farming generates methane emissions and involves intensive land use, contributing to environmental degradation and biodiversity loss. Biofabricated textiles reduce carbon footprint and resource consumption, promoting eco-friendly fashion for suits while minimizing ecological impact.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Biofabricated textiles offer superior moisture-wicking and breathability compared to wool, enhancing comfort in varied climates. Wool excels in natural insulation and wrinkle resistance, providing long-lasting wear with minimal maintenance. In durability, biofabricated textiles often incorporate synthetic fibers that increase tear resistance, while wool remains highly resilient due to its natural elasticity and fiber structure.
Comfort, Breathability, and Wearability
Biofabricated textiles offer superior comfort and breathability compared to traditional wool, utilizing innovative materials that regulate temperature and wick moisture efficiently. These textiles are engineered for enhanced wearability, providing lightweight, stretchable properties that adapt to body movements without compromising durability. Wool suits excel in temperature retention and natural moisture absorption, but biofabricated alternatives often surpass wool by combining eco-friendly production with advanced performance features tailored for modern comfort needs.
Aesthetic Qualities: Texture and Appearance
Biofabricated textiles offer a sleek, consistent texture with customizable surface patterns that provide a modern, innovative appearance for suits. Wool maintains a classic, rich texture with natural crimp and luster, contributing to a timeless, elegant look valued in traditional tailoring. The choice between biofabricated textiles and wool depends on desired aesthetic qualities, with biofabrication enabling avant-garde designs and wool delivering enduring sophistication.
Cost and Accessibility of Materials
Biofabricated textiles for suits are emerging as cost-effective alternatives due to scalable production methods requiring fewer resources than traditional wool farming, which is labor-intensive and dependent on climate conditions. Wool suits often involve higher costs linked to animal care, shearing, and seasonal variability that limits material availability. Biofabricated materials provide enhanced accessibility through consistent manufacturing processes, reducing regional supply chain constraints and price volatility.
Ethical Considerations in Production
Biofabricated textiles for suits offer a sustainable alternative by minimizing animal exploitation and reducing environmental impact through lab-based cultivation processes. Wool production, while natural, often involves concerns like animal welfare issues and significant resource consumption, including water and land use. Ethical considerations in biofabrication prioritize cruelty-free methods and lower carbon emissions, making it a progressive choice for eco-conscious consumers.
Innovations in Suit Design and Technology
Biofabricated textiles for suits introduce cutting-edge innovations by utilizing lab-grown materials that mimic wool's natural properties while enhancing sustainability and durability. These textiles offer precise control over fiber composition and texture, enabling customizable breathability and wrinkle resistance not typically achievable with traditional wool. Advanced manufacturing techniques in biofabrication reduce environmental impact, positioning these textiles as a breakthrough in eco-friendly and high-performance suit design technology.
Future Trends and Market Adoption
Biofabricated textiles for suits are gaining traction due to their sustainability, scalability, and ability to replicate wool's natural properties without environmental drawbacks. Advances in biotechnology and material science are driving innovation, enabling biofabricated fabrics to offer improved durability, breathability, and customization compared to traditional wool. Market adoption is accelerating as luxury brands and eco-conscious consumers increasingly prefer biofabricated suits, reflecting a broader shift towards circular fashion and reduced carbon footprints in the apparel industry.
Infographic: Biofabricated textile vs Wool for Suit
 azmater.com
azmater.com