Biofabricated textiles offer sustainable, biodegradable alternatives with superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties compared to traditional flannel, which is typically made from cotton or wool and provides warmth but can retain moisture. Choosing biofabricated materials for pajamas enhances comfort and environmental responsibility by reducing resource consumption and chemical use.
Table of Comparison
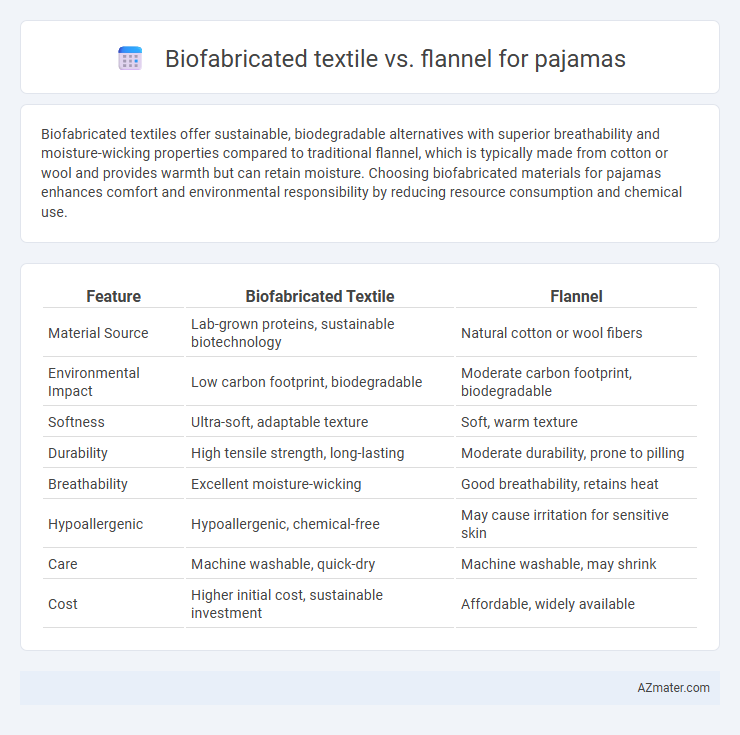
| Feature | Biofabricated Textile | Flannel |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Lab-grown proteins, sustainable biotechnology | Natural cotton or wool fibers |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable | Moderate carbon footprint, biodegradable |
| Softness | Ultra-soft, adaptable texture | Soft, warm texture |
| Durability | High tensile strength, long-lasting | Moderate durability, prone to pilling |
| Breathability | Excellent moisture-wicking | Good breathability, retains heat |
| Hypoallergenic | Hypoallergenic, chemical-free | May cause irritation for sensitive skin |
| Care | Machine washable, quick-dry | Machine washable, may shrink |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, sustainable investment | Affordable, widely available |
Introduction to Pajama Fabrics: Biofabricated Textile vs Flannel
Biofabricated textiles are engineered from sustainable biological materials, offering innovative properties like enhanced breathability and moisture-wicking perfect for pajama comfort. Flannel, a traditional fabric made from cotton or wool, is prized for its softness and warmth, making it a popular choice for cozy sleepwear. Comparing these fabrics highlights biofabricated textiles' eco-friendly advantages against flannel's established comfort and insulating qualities.
What Are Biofabricated Textiles?
Biofabricated textiles are innovative fabrics created through biological processes involving microorganisms or cells, reducing reliance on traditional petrochemical materials and minimizing environmental impact. Unlike flannel, which is typically woven from cotton or wool fibers for softness and warmth, biofabricated textiles offer customizable properties such as enhanced breathability, durability, and biodegradability. These textiles represent a sustainable alternative in pajama manufacturing by harnessing lab-grown materials that promote eco-friendly production and reduce waste.
Understanding Flannel: Material and Characteristics
Flannel is a soft, woven fabric primarily made from cotton, wool, or synthetic fibers, known for its warmth and breathability, making it ideal for pajamas. Its brushed surface enhances insulation and provides a cozy, comfortable feel against the skin. Unlike biofabricated textiles, flannel relies on traditional weaving and natural fiber properties rather than innovative, lab-grown materials.
Comfort and Softness: A Comparative Analysis
Biofabricated textiles offer superior softness and breathability compared to traditional flannel, making them ideal for pajamas that require both comfort and moisture-wicking properties. Unlike flannel, which can feel heavier and retain heat, biofabricated materials provide lightweight warmth with enhanced thermal regulation for a cozy sleep experience. The innovative fiber structure in biofabricated textiles promotes skin-friendly softness and durability, setting a new standard for pajama comfort over conventional cotton flannel.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Biofabricated textiles offer superior breathability and moisture management compared to flannel, utilizing advanced materials engineered for enhanced airflow and rapid moisture wicking. These textiles maintain a comfortable body temperature by efficiently dispersing sweat and preventing fabric saturation, making them ideal for pajama wear. Flannel, while soft and warm, tends to retain moisture and lacks the same level of ventilation, potentially causing discomfort during extended wear.
Durability and Longevity in Pajama Use
Biofabricated textiles offer superior durability compared to traditional flannel, maintaining structural integrity through repeated washes and prolonged wear. Flannel, typically made from cotton or wool, tends to wear thin over time, leading to pilling and reduced softness after extensive use. The advanced material engineering of biofabricated textiles enhances longevity, making them a sustainable and long-lasting choice for pajamas.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Biofabricated textiles for pajamas reduce environmental impact by utilizing lab-grown materials that minimize water consumption, chemical use, and land depletion compared to traditional flannel production. Flannel, typically made from cotton or wool, involves intensive resource usage such as high water demand and pesticide application, contributing to soil degradation and greenhouse gas emissions. Choosing biofabricated textiles supports sustainability goals by lowering carbon footprints and promoting circular manufacturing processes.
Skin Sensitivity and Hypoallergenic Properties
Biofabricated textiles offer superior hypoallergenic properties compared to traditional flannel, making them ideal for sensitive skin by minimizing irritation and allergic reactions. Unlike flannel, which can harbor allergens and cause discomfort due to its natural fibers, biofabricated fabrics are engineered to be breathable, moisture-wicking, and free from harmful chemicals. Their skin-friendly composition provides enhanced comfort and reduces the risk of inflammation for individuals prone to skin sensitivities.
Care, Maintenance, and Shrink Resistance
Biofabricated textiles for pajamas offer superior shrink resistance and require minimal care compared to traditional flannel, which tends to shrink after washing and demands gentle handling. These innovative textiles often feature antimicrobial properties, reducing the need for frequent washing and enhancing durability. Flannel requires careful maintenance, such as cold water washing and low-heat drying, to preserve softness and avoid pilling, whereas biofabricated fabrics maintain structural integrity and softness with standard laundering.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Biofabricated textiles for pajamas typically have a higher upfront cost due to advanced manufacturing processes and limited production scale, whereas flannel remains an affordable and widely accessible option thanks to its traditional, mass-produced nature. Market availability of biofabricated textiles is currently niche and primarily found through specialty sustainable brands, while flannel enjoys broad distribution across global retail channels. As biofabricated textile technology matures, costs are expected to decrease, potentially improving market penetration and consumer adoption rates.
Infographic: Biofabricated textile vs Flannel for Pajama
 azmater.com
azmater.com