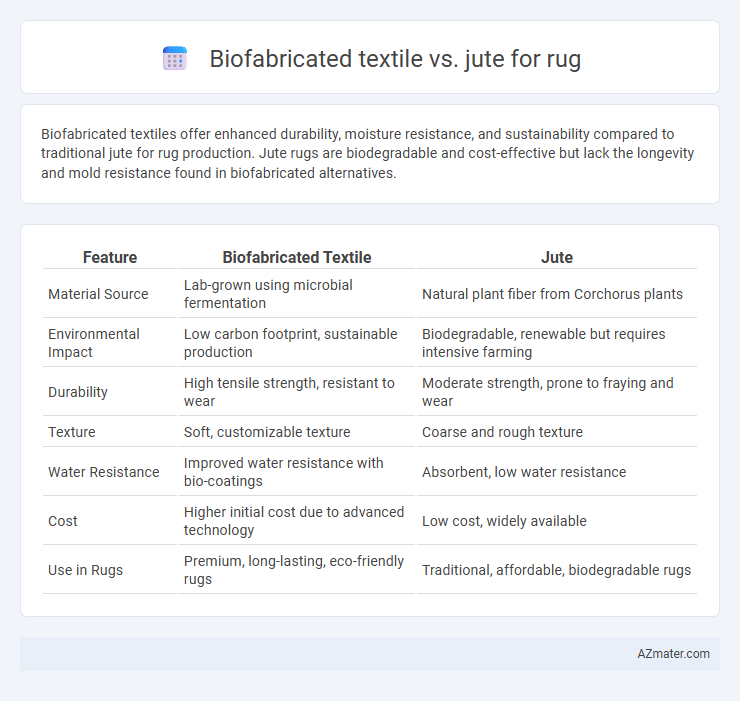
Biofabricated textiles offer enhanced durability, moisture resistance, and sustainability compared to traditional jute for rug production. Jute rugs are biodegradable and cost-effective but lack the longevity and mold resistance found in biofabricated alternatives.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biofabricated Textile | Jute |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Lab-grown using microbial fermentation | Natural plant fiber from Corchorus plants |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, sustainable production | Biodegradable, renewable but requires intensive farming |
| Durability | High tensile strength, resistant to wear | Moderate strength, prone to fraying and wear |
| Texture | Soft, customizable texture | Coarse and rough texture |
| Water Resistance | Improved water resistance with bio-coatings | Absorbent, low water resistance |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to advanced technology | Low cost, widely available |
| Use in Rugs | Premium, long-lasting, eco-friendly rugs | Traditional, affordable, biodegradable rugs |
Introduction: The Evolution of Sustainable Rugs
Biofabricated textiles represent a groundbreaking advancement in sustainable rug materials, offering biodegradable and low-impact production methods compared to traditional jute fibers. Jute, a natural fiber prized for its durability and affordability, has been a staple in eco-friendly rug manufacturing but faces challenges related to water usage and chemical treatments. The evolution from jute to biofabricated textiles signifies a shift towards innovative, renewable sources that minimize environmental footprints while maintaining functional and aesthetic qualities.
What Are Biofabricated Textiles?
Biofabricated textiles are innovative materials created through biological processes such as microbial fermentation or cell culture, offering sustainable alternatives to traditional fabrics. Unlike jute, a natural fiber derived from the jute plant known for its durability and biodegradability, biofabricated textiles can be engineered for specific properties like enhanced strength, softness, or moisture resistance. These textiles minimize environmental impact by reducing reliance on agriculture and chemical treatments, making them a promising option for eco-friendly rug production.
Jute: The Traditional Natural Fiber
Jute, a traditional natural fiber, has long been prized for its strength, biodegradability, and eco-friendly cultivation, making it an excellent choice for rugs that prioritize sustainability. Compared to biofabricated textiles, jute offers a renewable and low-impact material sourced from the Corchorus plant, thriving in tropical regions with minimal chemical inputs. Its coarse texture and durability create rustic, resilient rugs ideal for high-traffic areas, anchoring interior designs with a natural, earthy aesthetic.
Production Processes: Biofabrication vs. Jute Weaving
Biofabricated textiles for rugs are produced through microbial fermentation processes that cultivate cellulose or protein-based fibers in controlled environments, enabling precise customization of material properties and reducing environmental impact. In contrast, jute rugs are crafted using traditional weaving techniques that involve harvesting, retting, and manually processing jute fibers derived from the Corchorus plant, which demands extensive water and labor resources. The biofabrication method offers scalability and consistency, while jute weaving relies on artisanal skills and sustainable crop cultivation.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Biofabricated textiles significantly reduce environmental impact compared to jute rugs by minimizing water usage and eliminating harmful pesticides often required in jute cultivation. The production of biofabricated textiles involves renewable biological processes that lower carbon emissions and reduce soil degradation. Conversely, jute farming contributes to deforestation and soil nutrient depletion, making biofabricated textiles a more sustainable choice for eco-conscious rug manufacturing.
Durability and Longevity: Which Rug Lasts Longer?
Biofabricated textiles exhibit superior durability and longevity compared to traditional jute rugs due to their engineered resistance to wear, tear, and environmental factors. Jute rugs, while natural and biodegradable, tend to degrade faster under heavy foot traffic and moisture exposure, limiting their lifespan. Advanced biofabricated materials offer enhanced strength and longer-lasting performance, making them a more durable choice for high-traffic areas.
Aesthetic Qualities and Design Flexibility
Biofabricated textiles for rugs offer a modern aesthetic characterized by smooth textures and customizable colors, enabling intricate patterns and contemporary designs that enhance interior decor. Jute, known for its natural, coarse texture and earthy tones, provides a rustic and organic appearance, ideal for traditional or eco-friendly interiors. Design flexibility in biofabricated textiles surpasses jute due to their ability to be engineered at the molecular level, allowing varied thicknesses, weaves, and finishes that jute's natural fiber constraints cannot match.
Cost Efficiency and Market Accessibility
Biofabricated textiles offer innovative cost efficiency through scalable production methods and reduced reliance on traditional agriculture, lowering long-term expenses compared to jute, which depends heavily on seasonal farming and labor-intensive processing. Market accessibility for biofabricated textiles is expanding rapidly due to growing investment in sustainable materials and advanced manufacturing infrastructure, while jute maintains established demand primarily in regions with strong agricultural ties but faces limitations in global distribution and product consistency. The combination of lower production volatility and broader adoption potential positions biofabricated textiles as a cost-effective and accessible alternative to jute for rug manufacturing.
Consumer Preferences and Eco-Conscious Choices
Consumers increasingly prefer biofabricated textiles over traditional jute rugs due to their enhanced durability, unique textures, and sustainability credentials derived from lab-grown materials that minimize resource use. Eco-conscious buyers value biofabricated rugs for their reduced carbon footprint and biodegradability, aligning with zero-waste principles, while jute remains favored for its natural appeal and affordability. Market trends indicate a growing demand for innovative, environmentally responsible biofabricated options that meet aesthetic and functional needs without compromising ecological impact.
Future Prospects: The Next Generation of Sustainable Rugs
Biofabricated textiles, engineered from microbial proteins and cellulose, offer promising advantages over traditional jute in rug production by providing enhanced durability, biodegradability, and customization potential. Advances in biofabrication technologies are driving scalable, eco-friendly manufacturing processes that significantly reduce the environmental impact compared to conventional jute cultivation, which involves intensive land and water use. The future of sustainable rugs lies in integrating these next-generation biofabricated materials with smart design innovations to create high-performance, circular economy solutions in the home decor industry.
Infographic: Biofabricated textile vs Jute for Rug
 azmater.com
azmater.com