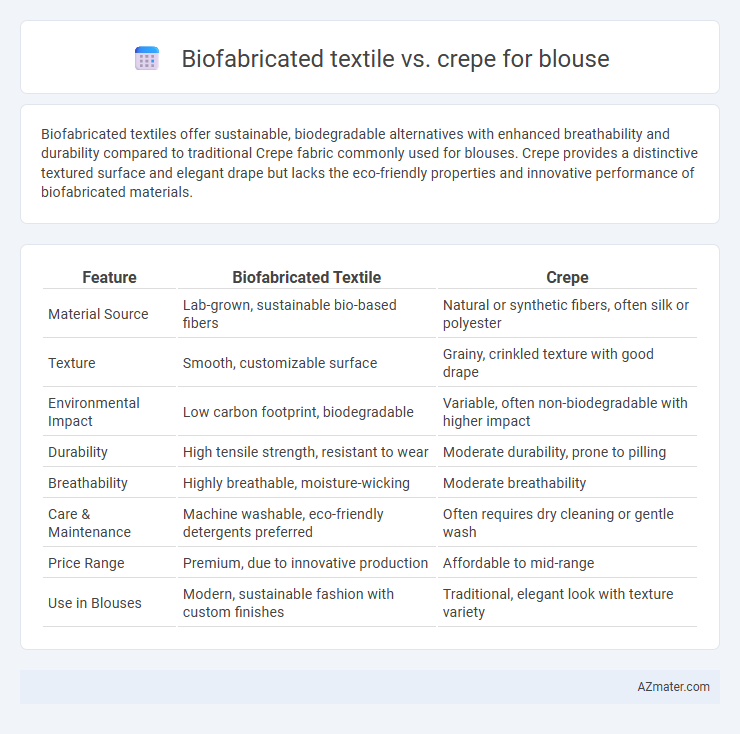
Biofabricated textiles offer sustainable, biodegradable alternatives with enhanced breathability and durability compared to traditional Crepe fabric commonly used for blouses. Crepe provides a distinctive textured surface and elegant drape but lacks the eco-friendly properties and innovative performance of biofabricated materials.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biofabricated Textile | Crepe |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Lab-grown, sustainable bio-based fibers | Natural or synthetic fibers, often silk or polyester |
| Texture | Smooth, customizable surface | Grainy, crinkled texture with good drape |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable | Variable, often non-biodegradable with higher impact |
| Durability | High tensile strength, resistant to wear | Moderate durability, prone to pilling |
| Breathability | Highly breathable, moisture-wicking | Moderate breathability |
| Care & Maintenance | Machine washable, eco-friendly detergents preferred | Often requires dry cleaning or gentle wash |
| Price Range | Premium, due to innovative production | Affordable to mid-range |
| Use in Blouses | Modern, sustainable fashion with custom finishes | Traditional, elegant look with texture variety |
Introduction to Biofabricated Textiles and Crepe
Biofabricated textiles, created through biotechnological processes using living cells or microorganisms, offer sustainable and innovative alternatives to traditional fabrics like crepe. Crepe, a classic fabric characterized by its crinkled texture and fluid drape, is commonly made from silk, wool, or synthetic fibers, renowned for its elegance and versatility in blouse design. The comparison highlights the eco-friendly potential and novel properties of biofabricated textiles against the established texture, durability, and aesthetic appeal of crepe in fashion applications.
What Are Biofabricated Textiles?
Biofabricated textiles are innovative materials created through biological processes, using microorganisms or cell cultures to produce fibers without traditional farming or synthetic methods. Unlike crepe fabrics, which are woven or knitted from natural or synthetic fibers and known for their textured, crinkled surface ideal for blouses, biofabricated textiles offer sustainable alternatives with reduced environmental impact. These textiles enable customization at the molecular level, resulting in unique properties such as enhanced breathability, biodegradability, and strength tailored for fashion applications.
The Origins and Characteristics of Crepe Fabric
Crepe fabric, originating from the French word "crepe," is known for its distinctive crinkled or pebbled texture created through a unique weaving or twisting technique. This fabric is typically made from silk, wool, or synthetic fibers, offering lightweight, breathable qualities with excellent drape, making it ideal for blouses. In contrast, biofabricated textiles are innovative materials engineered through biological processes, emphasizing sustainability and environmental impact reduction, which differs fundamentally from the traditional production and texture of crepe fabric.
Sustainability: Biofabricated Textiles vs Crepe
Biofabricated textiles offer a sustainable alternative to traditional crepe by utilizing lab-grown materials that significantly reduce water usage and carbon emissions in production. Unlike crepe, which often relies on non-renewable resources and chemical-intensive processes, biofabricated fabrics promote biodegradability and minimize environmental impact. Emphasizing circular economy principles, biofabricated textiles support a greener fashion industry by decreasing reliance on harmful dyes and synthetic fibers common in crepe manufacturing.
Comfort and Breathability Comparison
Biofabricated textiles offer superior comfort and breathability compared to traditional crepe fabrics, as their engineered fibers enhance moisture wicking and air circulation. Crepe, made from natural or synthetic fibers, provides moderate breathability but can feel heavier and less flexible during extended wear. The advanced structure of biofabricated textiles ensures a lightweight, soft touch ideal for blouses in warm climates.
Durability and Maintenance Factors
Biofabricated textiles offer enhanced durability compared to traditional crepe fabric, with increased resistance to wear and tear due to innovative fiber engineering. These textiles often require less intensive maintenance, as they are less prone to wrinkling and shrinking, reducing the need for frequent ironing and specialized laundering. Crepe, while lightweight and textured, tends to be more delicate and may require gentle handling and dry cleaning to maintain its appearance and structural integrity over time.
Aesthetic Appeal and Versatility
Biofabricated textiles offer a futuristic aesthetic appeal with unique textures and sustainable origins, enhancing blouse designs with an avant-garde edge. Crepe fabric, known for its elegant drape and subtle crinkled texture, provides classic versatility suitable for both formal and casual blouses. The adaptability of crepe accommodates diverse styles and body types, while biofabricated textiles introduce innovative visual interest and eco-conscious fashion choices.
Cost and Market Availability
Biofabricated textiles generally have higher production costs compared to traditional materials like crepe due to advanced manufacturing processes and limited scale. Crepe fabric remains widely available and cost-effective in the market, making it a popular choice for blouses among mass manufacturers and consumers. The niche market for biofabricated textiles is expanding, but current price points and limited distribution restrict their accessibility compared to crepe.
Best Applications for Blouse Designs
Biofabricated textiles offer sustainable, breathable, and lightweight properties ideal for eco-conscious blouse designs requiring softness and durability. Crepe fabric provides excellent drape, wrinkle resistance, and texture, making it suitable for elegant, structured blouses with a refined finish. Blouse designs aiming for modern sustainability trends benefit from biofabricated textiles, while classic, formal styles excel with crepe's luxurious feel and silhouette-enhancing qualities.
Future Trends in Blouse Fabrics: Biofabrication vs Traditional Crepe
Biofabricated textiles offer sustainable and innovative alternatives to traditional crepe fabrics, featuring enhanced breathability, durability, and eco-friendly production methods. Advanced biofabrication leverages microbial cellulose and plant-based fibers, reducing environmental impact while maintaining the luxurious texture and drape characteristic of crepe. Future blouse designs are expected to integrate these biofabricated materials, meeting consumer demand for ethical fashion without sacrificing style or comfort.
Infographic: Biofabricated textile vs Crepe for Blouse
 azmater.com
azmater.com