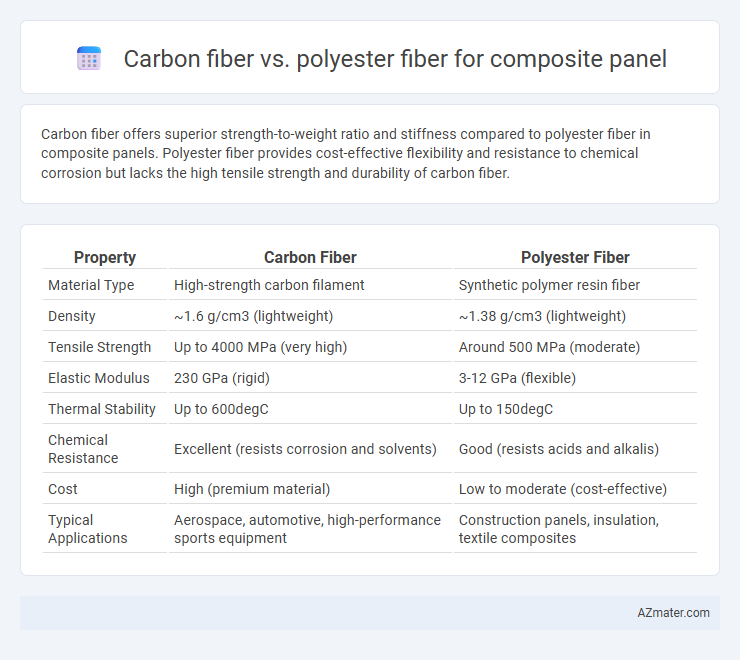
Carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness compared to polyester fiber in composite panels. Polyester fiber provides cost-effective flexibility and resistance to chemical corrosion but lacks the high tensile strength and durability of carbon fiber.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Fiber | Polyester Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-strength carbon filament | Synthetic polymer resin fiber |
| Density | ~1.6 g/cm3 (lightweight) | ~1.38 g/cm3 (lightweight) |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 4000 MPa (very high) | Around 500 MPa (moderate) |
| Elastic Modulus | 230 GPa (rigid) | 3-12 GPa (flexible) |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 600degC | Up to 150degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (resists corrosion and solvents) | Good (resists acids and alkalis) |
| Cost | High (premium material) | Low to moderate (cost-effective) |
| Typical Applications | Aerospace, automotive, high-performance sports equipment | Construction panels, insulation, textile composites |
Introduction to Composite Panels
Composite panels combine fibers and resins to create materials with enhanced strength-to-weight ratios ideal for aerospace, automotive, and construction applications. Carbon fiber offers superior tensile strength, stiffness, and lightweight properties compared to polyester fiber, which provides cost-effective flexibility and chemical resistance. Selecting carbon fiber for composite panels results in higher performance and durability, while polyester fiber suits less demanding, budget-conscious projects.
Overview of Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber offers superior tensile strength and stiffness compared to polyester fiber, making it ideal for high-performance composite panels used in aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods. Its lightweight properties contribute to enhanced fuel efficiency and structural integrity, while carbon fiber's resistance to environmental degradation ensures long-term durability. Although more costly, carbon fiber's exceptional mechanical properties provide significant advantages in applications demanding strength-to-weight optimization.
Overview of Polyester Fiber
Polyester fiber is widely used in composite panels due to its cost-effectiveness, good chemical resistance, and thermal stability. Its moderate mechanical properties, such as tensile strength and flexibility, make it suitable for applications where lightweight and durability are essential but extreme performance is not critical. Polyester fiber composites offer ease of fabrication and excellent resistance to moisture, making them a reliable choice for various industrial and construction applications.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Carbon fiber composites exhibit significantly higher mechanical strength compared to polyester fiber composites, with tensile strength often exceeding 3,500 MPa versus approximately 50-100 MPa for polyester fibers. The high stiffness-to-weight ratio of carbon fiber ensures superior mechanical performance, making it ideal for applications requiring maximum structural integrity. Polyester fiber composites, while more cost-effective, demonstrate lower modulus of elasticity and reduced resistance to fatigue and impact loading.
Weight and Density Differences
Carbon fiber composite panels exhibit significantly lower density, typically around 1.6 g/cm3, compared to polyester fiber panels, which range between 1.3 to 1.4 g/cm3 but require higher volume to achieve similar strength, resulting in greater overall weight. Due to its superior stiffness-to-weight ratio, carbon fiber panels offer enhanced structural performance in lightweight applications such as aerospace and automotive components. Polyester fiber panels tend to be heavier and less rigid, making them more suitable for cost-sensitive or less demanding environments where weight savings are less critical.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Carbon fiber composite panels exhibit superior durability and environmental resistance compared to polyester fiber panels, offering high tensile strength and excellent resistance to UV radiation, chemicals, and moisture. Carbon fiber's inherent stiffness and fatigue resistance ensure prolonged performance in harsh conditions, making it ideal for aerospace and automotive applications. Polyester fiber panels, while more cost-effective, generally show lower mechanical strength and susceptibility to environmental degradation, limiting their use in demanding structural applications.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Carbon fiber composite panels offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and enhanced durability but come at significantly higher material and manufacturing costs compared to polyester fiber panels. Polyester fiber composites provide a more economical alternative with lower raw material expenses and simpler processing, making them suitable for cost-sensitive applications. Evaluating the total lifecycle cost, including maintenance and longevity, is crucial for determining the best economic value between these two composite materials.
Applications in Industry
Carbon fiber composite panels dominate aerospace, automotive, and high-performance sports industries due to their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness. Polyester fiber composites find widespread use in marine, construction, and electrical industries, offering cost-effective durability and corrosion resistance. The choice between carbon and polyester fibers depends on balancing mechanical performance requirements with budget constraints in industrial applications.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Carbon fiber offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio but involves high energy consumption and limited recyclability, impacting its overall environmental footprint. Polyester fiber composites generally exhibit lower energy requirements in production and can incorporate recycled content, enhancing sustainability aspects. The choice between these fibers depends on balancing performance needs with lifecycle environmental impacts, emphasizing the importance of sustainable material innovation in composite panel manufacturing.
Summary: Choosing the Right Fiber for Composite Panels
Carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and stiffness, making it ideal for high-performance composite panels where durability and lightweight are critical. Polyester fiber provides cost-effective, moderate mechanical properties suited for less demanding applications and offers good chemical resistance. Selecting the right fiber depends on balancing performance requirements, budget constraints, and environmental conditions for the intended composite panel use.
Infographic: Carbon fiber vs Polyester fiber for Composite panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com