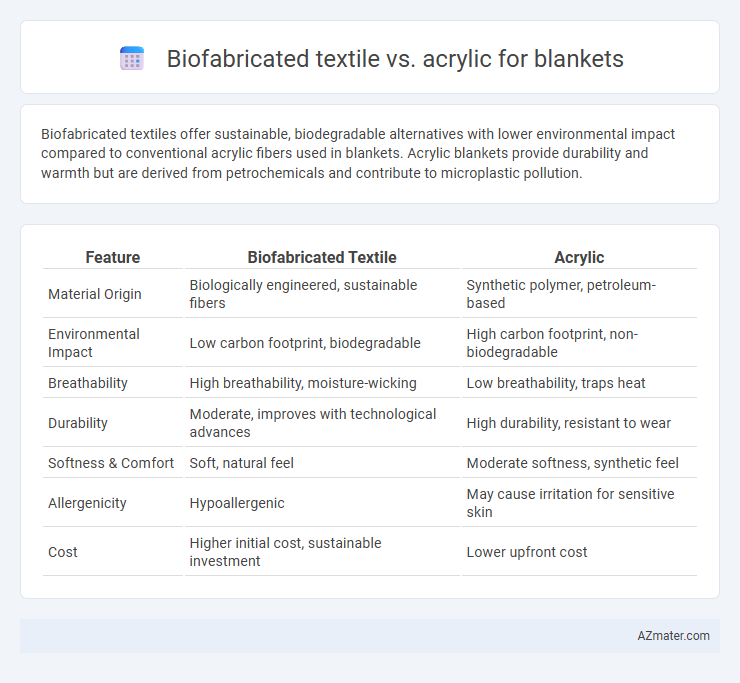
Biofabricated textiles offer sustainable, biodegradable alternatives with lower environmental impact compared to conventional acrylic fibers used in blankets. Acrylic blankets provide durability and warmth but are derived from petrochemicals and contribute to microplastic pollution.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biofabricated Textile | Acrylic |
|---|---|---|
| Material Origin | Biologically engineered, sustainable fibers | Synthetic polymer, petroleum-based |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable | High carbon footprint, non-biodegradable |
| Breathability | High breathability, moisture-wicking | Low breathability, traps heat |
| Durability | Moderate, improves with technological advances | High durability, resistant to wear |
| Softness & Comfort | Soft, natural feel | Moderate softness, synthetic feel |
| Allergenicity | Hypoallergenic | May cause irritation for sensitive skin |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, sustainable investment | Lower upfront cost |
Introduction to Biofabricated Textiles and Acrylic Blankets
Biofabricated textiles are produced through sustainable processes using living cells to create fibers that mimic natural materials, offering eco-friendly alternatives to traditional fabrics. Acrylic blankets, made from synthetic polymers, provide warmth and durability but rely heavily on petroleum-based resources, raising environmental concerns. The shift toward biofabricated textiles highlights advancements in sustainability and innovation within the blanket industry.
Material Composition: Biofabricated Textiles vs Acrylic
Biofabricated textiles are created using sustainable, lab-grown materials derived from natural proteins or plant fibers, offering biodegradable and environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional fabrics. Acrylic blankets are made from synthetic polymers derived from petrochemicals, resulting in non-biodegradable fibers with lower moisture-wicking properties. The material composition of biofabricated textiles enhances breathability and comfort, while acrylic's chemical structure provides durability and easy care but lacks eco-friendly benefits.
Production Process and Environmental Impact
Biofabricated textiles are produced using biological processes such as microbial fermentation, which significantly reduces reliance on petrochemicals and minimizes carbon emissions compared to acrylic production. Acrylic fibers are synthesized from acrylonitrile, a fossil fuel-derived chemical, through energy-intensive polymerization methods that generate substantial greenhouse gases and non-biodegradable waste. The biofabrication process promotes sustainability by utilizing renewable resources and enabling biodegradability, whereas acrylic blankets contribute to microplastic pollution and have a larger ecological footprint throughout their lifecycle.
Softness and Comfort Comparison
Biofabricated textiles offer superior softness and breathability compared to acrylic fibers, providing a more natural and gentle feel against the skin for blankets. Acrylic blankets tend to be less breathable and can sometimes cause skin irritation or discomfort due to their synthetic nature. The enhanced moisture-wicking and hypoallergenic properties of biofabricated textiles make them a more comfortable choice for prolonged use.
Durability and Longevity of Each Material
Biofabricated textiles exhibit enhanced durability due to their engineered molecular structure, offering resistance to wear, tear, and environmental degradation compared to traditional materials. Acrylic blankets, while affordable and relatively durable, tend to pill and degrade faster under prolonged exposure to heat and friction, reducing their longevity. Biofabricated materials provide a sustainable, long-lasting alternative with superior resilience in maintaining texture and strength over time.
Thermal Insulation and Warmth
Biofabricated textiles offer superior thermal insulation compared to acrylic blankets due to their natural fiber composition and enhanced breathability, which effectively traps body heat while allowing moisture to escape. Unlike acrylic, which tends to retain moisture and lose insulating properties when damp, biofabricated textiles maintain consistent warmth in varying conditions. This makes biofabricated blankets more efficient at providing sustained warmth with less bulk, ideal for cold-weather use.
Health, Safety, and Hypoallergenic Properties
Biofabricated textiles exhibit superior hypoallergenic properties and enhanced breathability compared to acrylic, reducing risks of skin irritation and allergic reactions in sensitive individuals. Their natural origin minimizes exposure to harmful chemicals and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), promoting safer indoor air quality and overall health during prolonged use. Acrylic blankets, often treated with synthetic chemicals, may emit toxins and retain allergens, posing greater concerns for respiratory health and skin sensitivities.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Biofabricated textiles require gentle washing with mild detergents and air drying to preserve their structural integrity and sustainability benefits, whereas acrylic blankets offer more straightforward machine washability and quick drying. Biofabricated fabrics are more sensitive to high heat and harsh chemicals, demanding low-temperature laundering conditions to avoid damage. Acrylic blankets typically handle regular washing cycles and higher temperatures but may be prone to pilling and static buildup over time.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Biofabricated textiles generally exhibit higher production costs compared to acrylic blankets due to advanced biotechnology processes and limited manufacturing scale. Acrylic blankets benefit from widespread market availability and lower price points driven by established synthetic fiber production, making them more accessible to consumers. While biofabricated textiles offer sustainable innovation, their current market penetration and cost competitiveness remain constrained compared to the prevalent acrylic alternatives.
Future Trends and Innovations in Blanket Materials
Biofabricated textiles are emerging as sustainable alternatives to acrylic in blanket production, utilizing lab-grown fibers derived from natural proteins and cellulose to reduce environmental impact. Innovations in biofabricated blankets include enhanced biodegradability, improved thermal regulation, and customizable softness through genetic and process engineering. Future trends indicate increasing adoption of these eco-friendly materials driven by consumer demand for sustainable, high-performance textiles and advancements in scalable, cost-effective biofabrication technologies.
Infographic: Biofabricated textile vs Acrylic for Blanket
 azmater.com
azmater.com