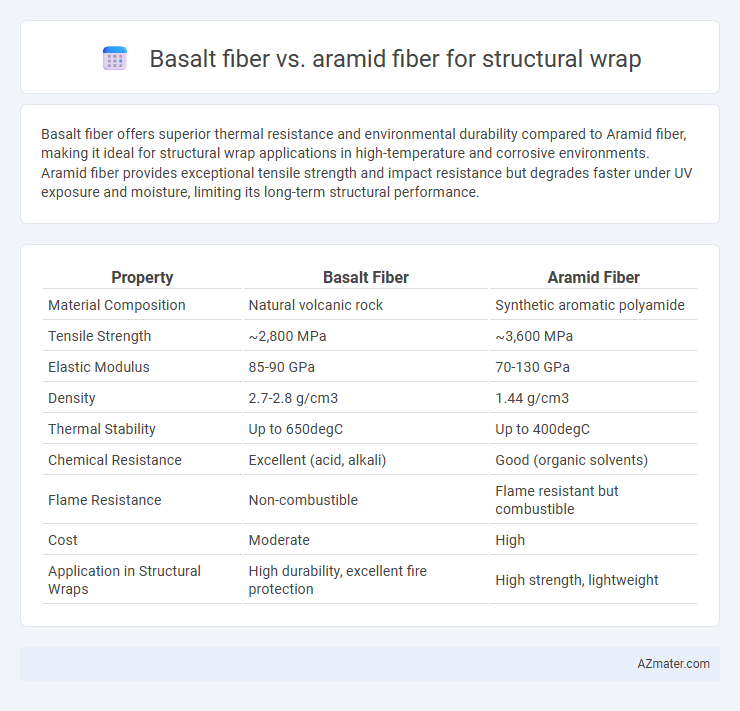
Basalt fiber offers superior thermal resistance and environmental durability compared to Aramid fiber, making it ideal for structural wrap applications in high-temperature and corrosive environments. Aramid fiber provides exceptional tensile strength and impact resistance but degrades faster under UV exposure and moisture, limiting its long-term structural performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Basalt Fiber | Aramid Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural volcanic rock | Synthetic aromatic polyamide |
| Tensile Strength | ~2,800 MPa | ~3,600 MPa |
| Elastic Modulus | 85-90 GPa | 70-130 GPa |
| Density | 2.7-2.8 g/cm3 | 1.44 g/cm3 |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 650degC | Up to 400degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (acid, alkali) | Good (organic solvents) |
| Flame Resistance | Non-combustible | Flame resistant but combustible |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
| Application in Structural Wraps | High durability, excellent fire protection | High strength, lightweight |
Introduction to Structural Fiber Wraps
Structural fiber wraps enhance the durability and strength of infrastructure by reinforcing concrete, masonry, and steel components. Basalt fiber offers exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and high tensile strength, making it ideal for environments exposed to extreme temperatures and corrosive agents. Aramid fiber, known for its superior impact resistance and lightweight properties, excels in applications requiring high energy absorption and flexibility for structural rehabilitation.
Overview of Basalt Fiber Properties
Basalt fiber exhibits excellent thermal stability, high tensile strength averaging 2,800 MPa, and superior chemical resistance, making it ideal for structural wrap applications exposed to harsh environments. Its density is approximately 2.6 g/cm3, which is lower than steel but higher than aramid fiber, offering a durable yet lightweight reinforcement option. The inherent fire resistance and eco-friendly production process of basalt fiber enhance its performance and sustainability compared to synthetic aramid fibers.
Overview of Aramid Fiber Properties
Aramid fibers exhibit exceptional tensile strength, high modulus, and outstanding resistance to impact and abrasion, making them ideal for structural wrap applications requiring durability and performance. Their thermal stability allows them to maintain integrity in temperatures up to 500degF (260degC), while chemical resistance ensures longevity in harsh environments. Compared to basalt fibers, aramid fibers offer superior toughness and flexibility, which enhances their effectiveness in reinforcing concrete and masonry structures.
Mechanical Performance Comparison
Basalt fiber exhibits higher tensile strength and better thermal stability compared to Aramid fiber, making it suitable for high-temperature structural wrap applications. Aramid fiber offers superior impact resistance and excellent elongation at break, providing enhanced flexibility and durability under dynamic loads. The mechanical performance balance between Basalt and Aramid fibers depends on the specific structural requirements, with Basalt favored for strength and heat resistance, while Aramid excels in toughness and vibration absorption.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Basalt fiber offers superior durability due to its high resistance to alkaline environments, UV radiation, and moisture, making it ideal for long-term structural wrap applications in harsh conditions. Aramid fiber provides excellent tensile strength but exhibits lower resistance to UV exposure and moisture degradation, potentially reducing its lifespan in outdoor environments. For structural wraps requiring high environmental resistance and prolonged durability, basalt fiber is often preferred over aramid fiber.
Fire Resistance and Thermal Stability
Basalt fiber exhibits superior fire resistance and thermal stability compared to aramid fiber, withstanding temperatures up to 800degC without significant degradation, while aramid fiber typically resists fire only up to 370degC. The mineral composition of basalt fiber provides enhanced thermal insulation and non-combustible properties essential for structural wrap applications in high-temperature environments. Aramid fiber, though strong and lightweight, tends to degrade under prolonged heat exposure, limiting its effectiveness in fire-critical structural reinforcement scenarios.
Installation and Workability
Basalt fiber offers superior ease of handling and cutting compared to aramid fiber, making installation faster and less labor-intensive for structural wrap applications. Its resistance to moisture and chemicals enhances workability during on-site application, reducing the need for specialized protective gear. Aramid fiber, while strong, tends to be more abrasive and requires careful handling to prevent damage during installation, potentially increasing labor costs.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Basalt fiber offers a cost advantage over aramid fiber, with prices typically 20-40% lower, making it a more economical choice for large-scale structural wrap projects. While aramid fibers like Kevlar provide high tensile strength and excellent impact resistance, their higher production costs lead to increased overall project expenses. Evaluating long-term maintenance and durability, basalt fiber combines cost-effectiveness with corrosion resistance, reducing life-cycle costs in infrastructure reinforcement applications.
Typical Applications in Civil Engineering
Basalt fiber is commonly used in structural wraps for reinforcing concrete, masonry, and steel structures, providing excellent resistance to high temperatures and chemical corrosion in civil engineering applications. Aramid fiber, known for its superior tensile strength and impact resistance, is frequently employed in seismic retrofitting, bridge rehabilitation, and strengthening of load-bearing elements. Both fibers enhance structural durability, but basalt fiber is preferred for environments with harsh chemical exposure while aramid fiber excels in dynamic load and vibration mitigation scenarios.
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Fiber for Structural Wraps
Basalt fiber offers superior thermal resistance and environmental durability compared to aramid fiber, making it ideal for structures exposed to high temperatures and harsh conditions. Aramid fiber provides exceptional tensile strength and impact resistance, supporting applications where flexibility and toughness are critical. Selecting the optimal fiber for structural wraps depends on specific project requirements, balancing basalt's longevity and temperature tolerance against aramid's strength and resilience.
Infographic: Basalt fiber vs Aramid fiber for structural wrap
 azmater.com
azmater.com