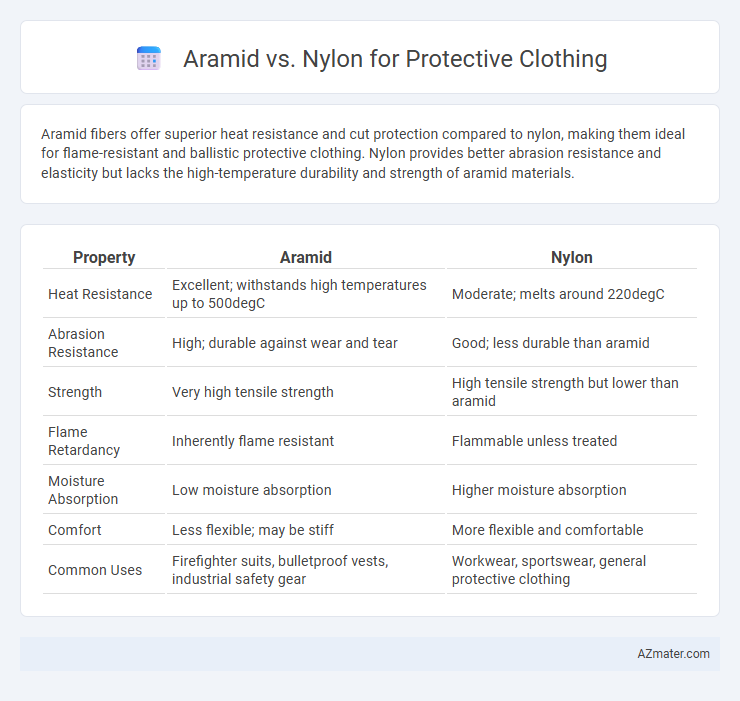
Aramid fibers offer superior heat resistance and cut protection compared to nylon, making them ideal for flame-resistant and ballistic protective clothing. Nylon provides better abrasion resistance and elasticity but lacks the high-temperature durability and strength of aramid materials.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aramid | Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Excellent; withstands high temperatures up to 500degC | Moderate; melts around 220degC |
| Abrasion Resistance | High; durable against wear and tear | Good; less durable than aramid |
| Strength | Very high tensile strength | High tensile strength but lower than aramid |
| Flame Retardancy | Inherently flame resistant | Flammable unless treated |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorption | Higher moisture absorption |
| Comfort | Less flexible; may be stiff | More flexible and comfortable |
| Common Uses | Firefighter suits, bulletproof vests, industrial safety gear | Workwear, sportswear, general protective clothing |
Introduction to Protective Clothing Materials
Protective clothing materials like aramid and nylon are engineered to provide essential safety features including flame resistance, durability, and impact protection. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, excel in high heat and abrasion resistance, making them ideal for firefighters, military, and industrial applications. Nylon offers excellent tensile strength and flexibility but generally lacks the inherent flame resistance of aramid, limiting its use in environments requiring advanced thermal protection.
Overview of Aramid Fibers
Aramid fibers, such as Nomex and Kevlar, are synthetic materials renowned for their exceptional heat resistance, high tensile strength, and flame-retardant properties, making them ideal for protective clothing in hazardous environments. These fibers maintain structural integrity under extreme heat and offer excellent resistance to abrasion and chemical exposure, outperforming conventional textiles like nylon in safety applications. Their lightweight, durable nature enhances wearer comfort while providing superior protection against thermal and mechanical hazards.
Key Features of Nylon Fibers
Nylon fibers offer high tensile strength, excellent abrasion resistance, and good elasticity, making them suitable for durable protective clothing. Their lightweight nature and moisture-wicking properties enhance comfort during extended wear in demanding environments. Nylon's resistance to chemicals and UV degradation further contributes to the longevity and reliability of protective garments in various industrial applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, exhibit superior strength and exceptional resistance to abrasion, heat, and chemical exposure, making them ideal for high-performance protective clothing. Nylon, while durable and elastic with good impact resistance, generally falls short of aramid's tensile strength and thermal stability under extreme conditions. The enhanced durability of aramid ensures longer-lasting protection in hazardous environments compared to nylon-based garments.
Fire and Heat Resistance
Aramid fibers like Kevlar and Nomex offer superior fire and heat resistance compared to nylon, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 500degC and providing inherent flame retardant properties without chemical treatment. Nylon melts and ignites at lower temperatures around 237degC, making it less effective for high-heat protective clothing applications. The exceptional thermal stability of aramid fabrics ensures enhanced protection for fire fighters and industrial workers exposed to extreme heat and open flames.
Chemical and Abrasion Resistance
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, exhibit superior chemical resistance and maintain high tensile strength when exposed to harsh solvents and acids, making them ideal for protective clothing in chemically hazardous environments. Nylon offers moderate chemical resistance but excels in abrasion resistance due to its toughness and flexibility, providing durability in applications requiring frequent physical contact. Protective garments combining aramid and nylon materials optimize both chemical protection and abrasion durability, enhancing overall performance in industrial safety gear.
Comfort and Wearability Factors
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, offer excellent heat resistance and superior durability, making them ideal for protective clothing in high-risk environments, but can feel stiff and less breathable compared to nylon. Nylon fibers provide greater flexibility, lighter weight, and enhanced moisture-wicking properties, improving comfort and wearability during extended use. Balancing aramid's protective qualities with nylon's comfort often involves blending both materials to optimize performance and user experience.
Cost and Availability
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, typically incur higher costs due to complex manufacturing processes and specialized applications in protective clothing, limiting widespread availability compared to nylon. Nylon is more affordable and widely available, making it a common choice for budget-conscious protective gear, though it offers less inherent flame and cut resistance than aramid. Industries requiring advanced protection often invest in aramid despite its price, while nylon remains prevalent in general-purpose protective clothing due to its cost-effectiveness and accessibility.
Common Applications in Protective Gear
Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar and Nomex, are commonly used in ballistic vests, firefighter suits, and cut-resistant gloves due to their exceptional heat resistance, high tensile strength, and flame retardancy. Nylon is frequently utilized in protective clothing for its abrasion resistance, flexibility, and durability, making it ideal for outer shells, backpacks, and tactical gear. Both materials are crucial in safety equipment, with aramids preferred for impact and heat protection while nylon excels in lightweight and wear-resistant applications.
Choosing the Right Material for Protective Clothing
Aramid fibers, known for their exceptional heat resistance and high tensile strength, provide superior protection against flames and abrasions, making them ideal for firefighting and industrial safety gear. Nylon offers durability and flexibility but lacks the fire-retardant properties of aramid, making it better suited for applications where comfort and stretch are prioritized over extreme heat protection. Selecting the right material depends on the specific hazard exposure, with aramid preferred for high-heat environments and nylon for impact resistance combined with lightweight wearability.
Infographic: Aramid vs Nylon for Protective Clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com