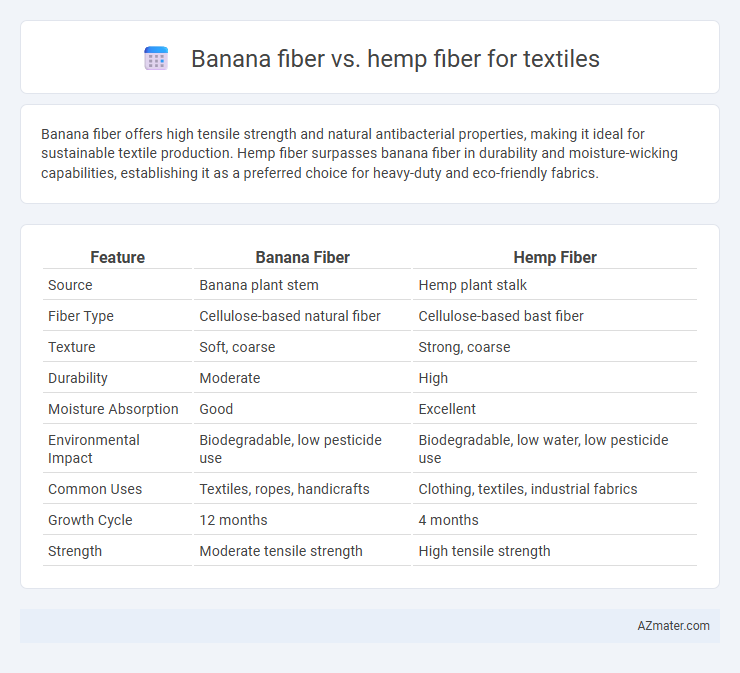
Banana fiber offers high tensile strength and natural antibacterial properties, making it ideal for sustainable textile production. Hemp fiber surpasses banana fiber in durability and moisture-wicking capabilities, establishing it as a preferred choice for heavy-duty and eco-friendly fabrics.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Banana Fiber | Hemp Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Banana plant stem | Hemp plant stalk |
| Fiber Type | Cellulose-based natural fiber | Cellulose-based bast fiber |
| Texture | Soft, coarse | Strong, coarse |
| Durability | Moderate | High |
| Moisture Absorption | Good | Excellent |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low pesticide use | Biodegradable, low water, low pesticide use |
| Common Uses | Textiles, ropes, handicrafts | Clothing, textiles, industrial fabrics |
| Growth Cycle | 12 months | 4 months |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | High tensile strength |
Introduction: The Rise of Sustainable Textile Fibers
Banana fiber and hemp fiber are emerging as sustainable alternatives in the textile industry due to their eco-friendly cultivation and biodegradability. Both fibers offer strong tensile strength and durability, with hemp providing superior resistance to UV and microbial damage, while banana fiber excels in softness and moisture absorption. Increasing consumer demand for organic and renewable materials drives the adoption of these natural fibers in eco-conscious textile production.
Overview of Banana Fiber and Hemp Fiber
Banana fiber, extracted from the pseudostem of the banana plant, is known for its strength, biodegradability, and natural sheen, making it suitable for eco-friendly textiles and composites. Hemp fiber, derived from the stalk of the Cannabis sativa plant, offers high tensile strength, durability, and resistance to UV light and microbial attacks, widely used in clothing, industrial fabrics, and sustainable products. Both fibers contribute to sustainable fashion by providing biodegradable alternatives to synthetic textiles, with banana fiber excelling in softness and hemp fiber renowned for its robustness and longevity.
Cultivation and Environmental Impact
Banana fiber cultivation utilizes the pseudostems of Musa plants, which are agricultural byproducts, reducing waste and requiring minimal water and pesticides compared to hemp that grows rapidly with low nutrient needs but can demand more land and specific climates. Banana fiber processing is labor-intensive but produces biodegradable, strong fibers with a low carbon footprint, while hemp fiber farming contributes to soil health through phytoremediation and sequesters more carbon due to its fast growth rate. Both fibers offer sustainable alternatives in textiles, but banana fiber excels in waste utilization, whereas hemp provides substantial environmental benefits through soil improvement and carbon capture.
Fiber Extraction Processes
Banana fiber extraction involves a manual or mechanical process where the outer layers of banana stems are stripped, followed by retting or scraping to separate the fibers, emphasizing gentle handling to preserve fiber strength. Hemp fiber extraction uses dew retting or water retting to break down pectins binding the fibers, combined with decortication machines to separate long bast fibers suitable for textiles. Both processes require specific retting techniques that impact fiber quality, with hemp generally yielding longer, stronger fibers due to its robust bast structure compared to banana's softer parenchyma fibers.
Physical and Mechanical Properties Comparison
Banana fiber exhibits a tensile strength of approximately 458 MPa and a density around 1.35 g/cm3, offering moderate elongation at break near 3-4%, making it suitable for lightweight textiles. Hemp fiber displays superior mechanical properties with tensile strength ranging from 550 to 900 MPa and a density of 1.48 g/cm3, alongside higher modulus values that contribute to enhanced durability and rigidity in fabric applications. Both fibers demonstrate good moisture absorption, but hemp's higher tensile strength and stiffness translate to greater resilience and longer lifespan in high-performance textile products.
Textile Applications and Versatility
Banana fiber exhibits superior softness and breathability, making it ideal for lightweight textiles such as summer clothing and upholstery, while hemp fiber offers exceptional durability and moisture-wicking properties suited for heavy-duty applications like workwear and home textiles. Hemp's natural resistance to pests and mold enhances its suitability for outdoor fabrics, whereas banana fiber's biodegradability and fine texture lend themselves well to eco-friendly fashion and luxury textile markets. Both fibers support sustainable production, yet hemp's versatility extends to rope, canvas, and technical textiles, complementing banana fiber's niche in delicate, high-value fabric blends.
Comfort and Wearability Factors
Banana fiber offers excellent breathability and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for comfortable, lightweight textiles. Hemp fiber provides superior durability and natural antimicrobial qualities, enhancing wearability for long-lasting garments. Both fibers support eco-friendly fashion, but banana fiber excels in softness while hemp ensures strength and resilience.
Cost Efficiency and Market Availability
Banana fiber offers moderate cost efficiency due to its abundance in tropical regions and relatively low processing requirements compared to hemp fiber, which tends to be more expensive because of its labor-intensive extraction and specialized processing techniques. Market availability of hemp fiber is more widespread in North America and Europe, driven by growing demand in sustainable textiles, while banana fiber is primarily accessible in Southeast Asia, limiting its global distribution. Both fibers present eco-friendly alternatives, but hemp fiber dominates the international market with higher scalability despite its higher production costs.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendliness
Banana fiber and hemp fiber both offer sustainable alternatives to conventional textiles due to their renewable nature and low environmental impact. Hemp fiber requires minimal pesticides and herbicides, thrives with less water, and promotes soil health through crop rotation, while banana fiber utilizes agricultural waste from banana plants, reducing waste and promoting circular economy principles. Both fibers biodegrade faster than synthetic textiles, but hemp's stronger durability supports longer garment life, enhancing overall eco-friendliness in textile applications.
Future Prospects and Industry Trends
Banana fiber and hemp fiber exhibit strong potential in the sustainable textile industry due to their biodegradability and renewable nature. Banana fiber offers high tensile strength and is gaining traction in eco-friendly fashion, while hemp fiber's durability and resistance to mold position it as a staple in performance textiles. Growing consumer demand for sustainable fabrics and advancements in fiber processing technologies are expected to accelerate adoption rates for both fibers in global textile markets.
Infographic: Banana fiber vs Hemp fiber for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com