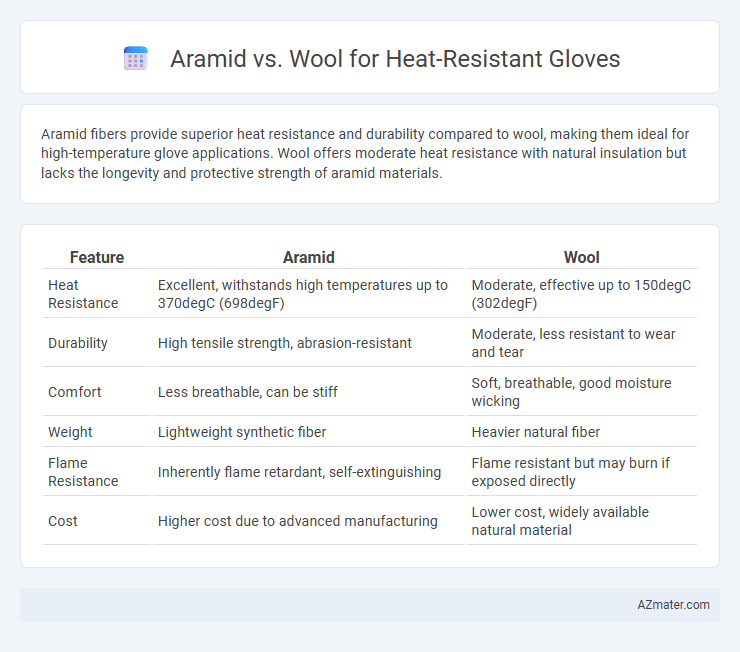
Aramid fibers provide superior heat resistance and durability compared to wool, making them ideal for high-temperature glove applications. Wool offers moderate heat resistance with natural insulation but lacks the longevity and protective strength of aramid materials.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Aramid | Wool |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Excellent, withstands high temperatures up to 370degC (698degF) | Moderate, effective up to 150degC (302degF) |
| Durability | High tensile strength, abrasion-resistant | Moderate, less resistant to wear and tear |
| Comfort | Less breathable, can be stiff | Soft, breathable, good moisture wicking |
| Weight | Lightweight synthetic fiber | Heavier natural fiber |
| Flame Resistance | Inherently flame retardant, self-extinguishing | Flame resistant but may burn if exposed directly |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced manufacturing | Lower cost, widely available natural material |
Introduction to Heat-resistant Gloves
Heat-resistant gloves are essential protective equipment designed to shield hands from extreme temperatures during industrial, culinary, and firefighting activities. Aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer superior heat resistance, high tensile strength, and excellent cut protection, making them ideal for gloves that withstand intense heat and mechanical hazards. Wool gloves provide natural insulation and flame resistance but lack the durability and thermal protection level found in aramid-based gloves, making them less suitable for heavy-duty heat exposure.
Overview of Aramid Fibers
Aramid fibers, known for their exceptional heat resistance and high tensile strength, are extensively used in heat-resistant gloves to protect against extreme temperatures and mechanical hazards. These synthetic fibers, including brands like Kevlar and Nomex, provide superior flame retardancy and thermal stability while remaining lightweight and durable. Unlike wool, aramid fibers do not absorb moisture, enhancing their protective performance in demanding industrial environments.
Properties of Wool for Heat Resistance
Wool exhibits excellent natural heat resistance due to its high ignition temperature and ability to char rather than melt, making it effective in protecting against moderate heat exposure. Its moisture-wicking properties also enhance thermal regulation, maintaining comfort during prolonged use. These characteristics make wool a reliable material for heat-resistant glove linings, especially in environments with low to medium heat hazards.
Thermal Protection: Aramid vs Wool
Aramid fibers offer superior thermal protection compared to wool, withstanding temperatures up to 500degC (932degF) without melting or burning, making them ideal for high-heat environments. Wool provides moderate heat resistance, self-extinguishing when removed from flame but typically tolerating temperatures only up to 200degC (392degF). For heat-resistant gloves, aramid blends enhance durability and thermal insulation, while wool contributes comfort and moisture-wicking properties, but aramid dominates in extreme heat scenarios.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Aramid fibers, known for their exceptional tensile strength and high thermal stability, offer superior durability and wear resistance compared to wool in heat-resistant gloves. Wool provides natural insulation but tends to degrade faster under extreme heat and abrasion, making it less effective for long-term heavy-duty use. Gloves reinforced with aramid consistently maintain structural integrity and resist wear in high-temperature industrial environments.
Comfort and Dexterity Comparison
Aramid fibers offer superior heat resistance and durability in gloves, maintaining flexibility under high temperatures for enhanced dexterity during precision tasks. Wool gloves provide natural insulation and breathability, delivering moderate heat resistance with greater comfort in cooler conditions but limited dexterity due to bulkiness. For heat-resistant gloves requiring optimal comfort and dexterity balance, aramid materials outperform wool by combining lightweight softness with thermal protection.
Moisture Management and Breathability
Aramid fibers excel in heat resistance but have limited moisture-wicking capabilities, making them less effective at managing sweat and moisture compared to wool. Wool naturally absorbs and releases moisture, enhancing breathability and keeping hands dry during prolonged use in heat-resistant gloves. Combining wool's superior moisture management with aramid's thermal protection offers optimal comfort and safety in high-temperature environments.
Cost-effectiveness and Availability
Aramid gloves offer superior heat resistance and durability at a higher price point, making them ideal for industries requiring extreme protection, while wool gloves provide moderate heat resistance at a lower cost and are more readily available for general-use applications. The cost-effectiveness of aramid gloves is justified by their longer lifespan and enhanced thermal protection, whereas wool gloves, though less expensive, may require more frequent replacement due to lower heat tolerance. Availability of wool gloves is widespread due to common material sourcing, whereas aramid gloves may face supply constraints and higher procurement costs in specialized markets.
Best Applications for Aramid Gloves
Aramid gloves, known for their exceptional heat resistance and cut protection, are ideal for high-temperature environments such as foundries, welding, and firefighting. Their lightweight, flame-retardant properties make them perfect for applications requiring dexterity and prolonged heat exposure, outperforming wool gloves in industrial heat safety. Aramid fibers, including Kevlar and Nomex, provide superior thermal stability and durability, ensuring maximum protection against burns and abrasions in extreme heat conditions.
Ideal Uses for Wool Gloves
Wool gloves excel in moderate heat resistance and are ideal for tasks involving brief exposure to warmth, such as handling hot objects in cooking or light industrial work. Their natural moisture-wicking and insulation properties provide comfort and breathability during extended wear. Wool gloves are preferred in environments requiring less intense heat protection combined with flexibility and dexterity.
Infographic: Aramid vs Wool for Heat-resistant Glove
 azmater.com
azmater.com