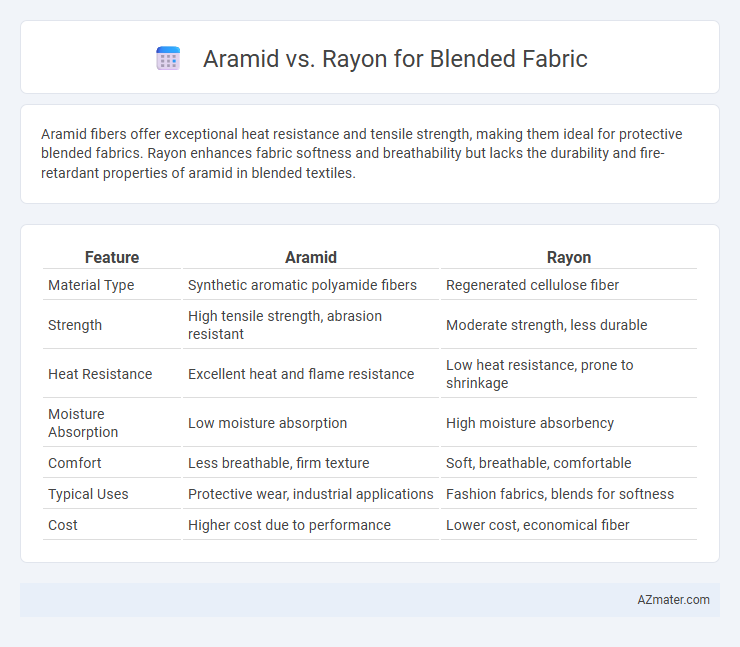
Aramid fibers offer exceptional heat resistance and tensile strength, making them ideal for protective blended fabrics. Rayon enhances fabric softness and breathability but lacks the durability and fire-retardant properties of aramid in blended textiles.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Aramid | Rayon |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic aromatic polyamide fibers | Regenerated cellulose fiber |
| Strength | High tensile strength, abrasion resistant | Moderate strength, less durable |
| Heat Resistance | Excellent heat and flame resistance | Low heat resistance, prone to shrinkage |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorption | High moisture absorbency |
| Comfort | Less breathable, firm texture | Soft, breathable, comfortable |
| Typical Uses | Protective wear, industrial applications | Fashion fabrics, blends for softness |
| Cost | Higher cost due to performance | Lower cost, economical fiber |
Introduction to Blended Fabrics
Blended fabrics combine fibers like aramid and rayon to enhance durability, comfort, and performance. Aramid fibers contribute high tensile strength, heat resistance, and chemical stability, making the fabric suitable for protective apparel. Rayon adds softness, moisture absorption, and breathability, creating a balanced textile ideal for industrial and everyday clothing applications.
What is Aramid Fiber?
Aramid fiber is a high-strength synthetic fiber known for its exceptional heat resistance, durability, and lightweight properties, commonly used in protective clothing and aerospace applications. Its molecular structure features aromatic polyamide chains that provide superior tensile strength and resistance to chemical degradation compared to rayon. When blended with rayon, aramid fibers enhance fabric resilience and thermal protection while maintaining softness and breathability.
What is Rayon Fiber?
Rayon fiber is a semi-synthetic material made from regenerated cellulose derived from wood pulp or cotton linters, known for its softness, breathability, and excellent moisture absorption. It is commonly blended with aramid fibers to enhance fabric comfort and flexibility while maintaining durability and heat resistance. Rayon's ability to mimic natural fibers like cotton makes it a popular choice in blended fabrics designed for activewear and protective clothing.
Key Properties of Aramid
Aramid fibers offer exceptional heat resistance, high tensile strength, and excellent durability, making them ideal for protective clothing and industrial applications in blended fabrics. Their inherent flame retardancy and resistance to abrasion outperform rayon, which is more prone to moisture absorption and lower tensile strength. Incorporating aramid into rayon blends enhances the fabric's thermal stability, mechanical strength, and longevity in demanding environments.
Key Properties of Rayon
Rayon in blended fabrics provides excellent moisture absorption and breathability, enhancing overall comfort and wearability. It offers a soft, smooth texture with high dye affinity, resulting in vibrant colors and a luxurious feel. However, rayon has lower tensile strength and durability compared to aramid, making it less resistant to abrasion and heat.
Aramid vs Rayon: Strength and Durability
Aramid fibers exhibit superior strength and exceptional durability compared to rayon, making them ideal for high-performance blended fabrics requiring enhanced abrasion resistance and tensile strength. Rayon, while softer and more breathable, lacks the inherent toughness and stability of aramid, resulting in reduced longevity under heavy mechanical stress and exposure to harsh environments. Blending aramid with rayon combines the toughness of aramid with the comfort and moisture absorbency of rayon, creating fabrics optimized for both durability and wearability.
Comfort and Breathability Comparison
Aramid fibers, known for their strength and heat resistance, offer less breathability and moderate comfort compared to rayon, which excels in moisture absorption and softness, enhancing fabric comfort. Blended fabrics with higher rayon content typically provide better airflow and a cooler feel, making them ideal for warm climates or activewear. Conversely, aramid-enhanced blends prioritize durability and protection, often sacrificing some breathability and comfort for performance in harsh environments.
Cost and Availability of Aramid and Rayon
Aramid fibers, known for high strength and heat resistance, generally come at a higher cost and limited availability compared to rayon, which is more affordable and widely accessible due to its cellulose-based origins. The price difference significantly impacts the overall cost of blended fabrics, making rayon a preferred choice for budget-sensitive applications, while aramid is favored where durability and performance are critical. Supply chain factors also influence procurement, with aramid often sourced from specialized manufacturers and rayon produced in large volumes globally.
Best Applications for Aramid-Rayon Blends
Aramid-rayon blended fabrics combine aramid's high strength, flame resistance, and durability with rayon's softness and moisture absorption, making them ideal for protective apparel that requires comfort and safety. These blends are best applied in industrial workwear, firefighting uniforms, and military clothing where thermal protection and breathability are crucial. The synergy between aramid's toughness and rayon's comfort enhances wearer endurance in hazardous environments without sacrificing mobility or skin comfort.
Choosing the Right Blend for Your Needs
Aramid fibers offer exceptional strength, heat resistance, and durability, making them ideal for protective clothing and industrial applications where safety is paramount. Rayon contributes softness, breathability, and moisture absorption, enhancing comfort and wearability in blended fabrics. Choosing the right blend depends on balancing performance requirements; prioritize higher aramid content for abrasion resistance and thermal protection, while increasing rayon for improved comfort and flexibility in everyday wear.
Infographic: Aramid vs Rayon for Blended Fabric
 azmater.com
azmater.com