Aramid fibers offer exceptional strength and heat resistance, making them ideal for high-performance protective stretch fabrics, while Spandex provides superior elasticity and comfort for everyday wear. Choosing between Aramid and Spandex depends on whether durability or stretchability is the primary requirement.
Table of Comparison
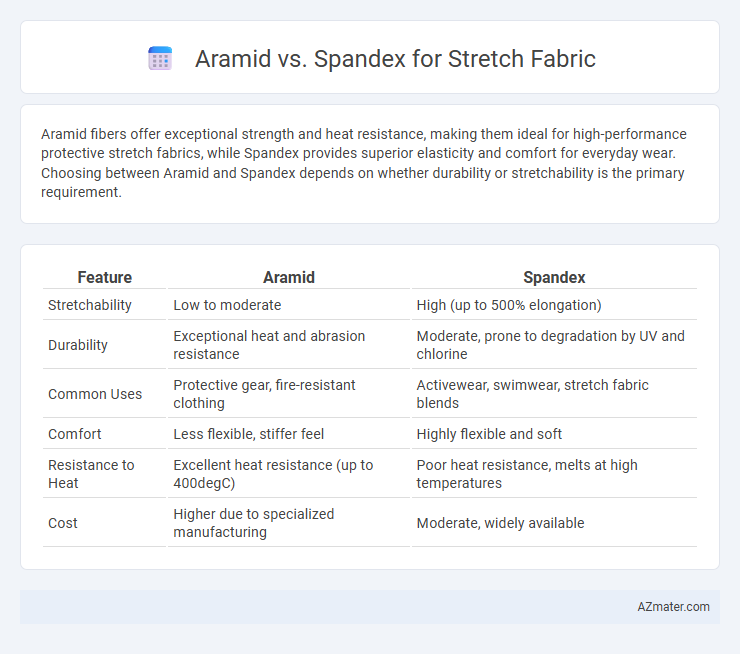
| Feature | Aramid | Spandex |
|---|---|---|
| Stretchability | Low to moderate | High (up to 500% elongation) |
| Durability | Exceptional heat and abrasion resistance | Moderate, prone to degradation by UV and chlorine |
| Common Uses | Protective gear, fire-resistant clothing | Activewear, swimwear, stretch fabric blends |
| Comfort | Less flexible, stiffer feel | Highly flexible and soft |
| Resistance to Heat | Excellent heat resistance (up to 400degC) | Poor heat resistance, melts at high temperatures |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized manufacturing | Moderate, widely available |
Introduction to Stretch Fabrics
Stretch fabrics combine elasticity and durability to enhance comfort and fit in clothing, with Aramid and Spandex being prominent materials. Aramid fibers offer exceptional strength and heat resistance, making them ideal for protective wear and high-performance applications. Spandex delivers superior stretch and recovery, providing flexible and form-fitting qualities favored in activewear and fashion industries.
Overview of Aramid Fibers
Aramid fibers, known for their exceptional strength and heat resistance, are synthetic fibers commonly used in protective clothing and industrial applications. Unlike spandex, which offers superior elasticity and comfort for stretch fabrics, aramid fibers provide high tensile strength and durability while maintaining limited stretchability. These fibers are often incorporated in composite materials to enhance overall fabric performance in demanding environments.
Overview of Spandex Fibers
Spandex fibers, known for their exceptional elasticity, can stretch up to 500% while maintaining shape and resilience, making them ideal for stretch fabrics in activewear and performance apparel. Unlike Aramid fibers, which prioritize heat resistance and strength in protective gear, Spandex offers superior comfort, flexibility, and durability in garments requiring freedom of movement. Its lightweight, chlorine-resistant properties also contribute to long-lasting stretch and recovery in swimwear and fitness clothing.
Key Differences Between Aramid and Spandex
Aramid fibers, known for high tensile strength and heat resistance, are commonly used in protective gear and industrial applications, while Spandex offers superior elasticity and comfort, making it ideal for activewear and stretch fabrics. Aramid resists abrasion and chemical exposure, maintaining durability under extreme conditions, whereas Spandex stretches up to 500% without losing shape, providing flexibility and fit. The primary difference lies in Aramid's durability and resistance properties compared to Spandex's exceptional stretchability and softness.
Durability Comparison: Aramid vs Spandex
Aramid fibers exhibit superior durability compared to spandex, offering exceptional resistance to abrasion, heat, and chemicals, making them ideal for protective clothing and industrial applications. Spandex provides excellent elasticity and stretch recovery but tends to degrade faster under UV exposure and repeated mechanical stress. The long-lasting structural integrity of aramid surpasses spandex, ensuring robust performance in demanding environments where durability is critical.
Stretch and Elasticity: Which Performs Better?
Aramid fibers exhibit high tensile strength and excellent durability but have limited stretch and elasticity compared to spandex, which is specifically engineered for superior stretchability and recovery. Spandex can stretch up to 500% of its original length and quickly return to its shape, making it ideal for garments requiring maximum flexibility. In contrast, aramid's minimal elongation under stress limits its use in applications where significant stretch and elasticity are critical.
Heat and Chemical Resistance
Aramid fibers exhibit exceptional heat resistance, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures above 400degC, making them ideal for high-heat applications. Spandex offers superior elasticity but degrades rapidly when exposed to high temperatures and harsh chemicals such as chlorine and solvents. For stretch fabrics requiring durability against heat and chemical exposure, aramid-based materials provide significantly greater resistance compared to spandex.
Applications in the Textile Industry
Aramid fibers offer exceptional heat resistance and tensile strength, making them ideal for protective clothing and industrial textiles requiring durability and safety. Spandex provides superior elasticity and comfort, widely used in activewear, lingerie, and performance fabrics where stretch and recovery are critical. Combining aramid with spandex enhances both protective properties and flexibility, expanding applications in advanced textile products such as firefighter suits and athletic gear.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Aramid fibers, known for their high strength and heat resistance, are significantly more expensive than spandex due to complex manufacturing processes and limited production scale. Spandex offers widespread availability and affordability, making it the preferred choice for mass-market stretch fabrics. The cost difference positions spandex as the dominant option in everyday apparel, while aramid remains reserved for specialized industrial and protective applications.
Choosing the Right Fiber for Your Needs
Aramid fibers offer exceptional heat resistance, durability, and strength, making them ideal for protective clothing and industrial applications requiring high-performance stretch fabrics. Spandex, known for its superior elasticity and comfort, excels in activewear and everyday garments where flexibility and softness are priorities. Choosing between aramid and spandex depends on specific needs: prioritize aramid for safety and durability, spandex for flexibility and comfort in stretch fabrics.
Infographic: Aramid vs Spandex for Stretch Fabric
 azmater.com
azmater.com