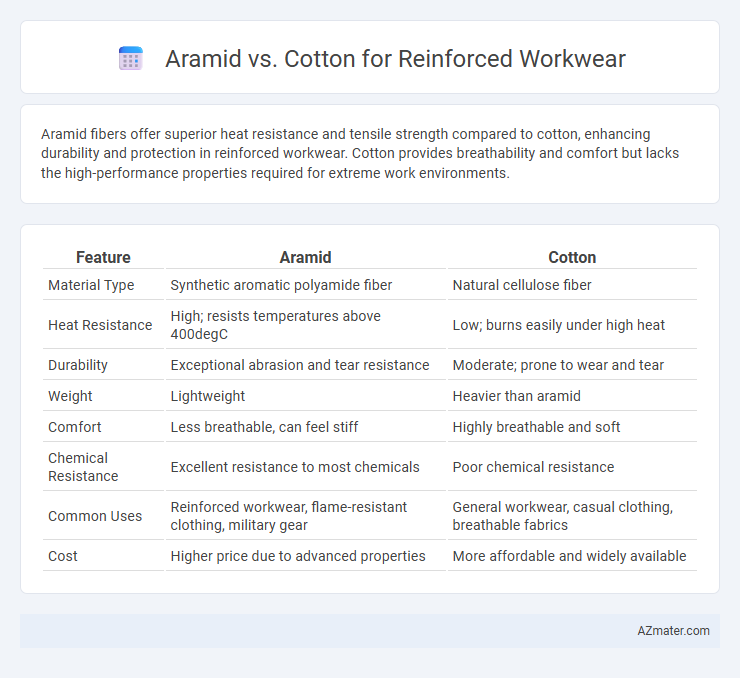
Aramid fibers offer superior heat resistance and tensile strength compared to cotton, enhancing durability and protection in reinforced workwear. Cotton provides breathability and comfort but lacks the high-performance properties required for extreme work environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Aramid | Cotton |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic aromatic polyamide fiber | Natural cellulose fiber |
| Heat Resistance | High; resists temperatures above 400degC | Low; burns easily under high heat |
| Durability | Exceptional abrasion and tear resistance | Moderate; prone to wear and tear |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier than aramid |
| Comfort | Less breathable, can feel stiff | Highly breathable and soft |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to most chemicals | Poor chemical resistance |
| Common Uses | Reinforced workwear, flame-resistant clothing, military gear | General workwear, casual clothing, breathable fabrics |
| Cost | Higher price due to advanced properties | More affordable and widely available |
Introduction to Reinforced Workwear Fabrics
Reinforced workwear fabrics such as aramid and cotton are essential for ensuring durability and safety in demanding work environments. Aramid fibers offer superior heat resistance, tensile strength, and abrasion resistance, making them ideal for protective clothing in high-risk industries. Cotton, while less resistant to extreme conditions, provides comfort, breathability, and cost-effectiveness, often used in blended fabrics to balance protection and wearability.
What is Aramid? Properties and Applications
Aramid fibers are synthetic polymers known for exceptional strength, heat resistance, and durability, often used in reinforced workwear to provide superior protection against cuts, flames, and abrasions. These fibers exhibit high tensile strength, excellent thermal stability up to 400degC, and resistance to chemical degradation, making them ideal for hazardous industrial environments. Common applications of aramid include firefighter suits, military uniforms, and industrial protective clothing where enhanced safety and longevity are critical.
Understanding Cotton in Workwear
Cotton in reinforced workwear offers natural breathability and comfort suitable for less hazardous environments, but it lacks the high-strength and heat-resistant properties found in aramid fibers. While cotton provides durability and moisture absorption, it is more prone to wear and tear under extreme conditions, limiting its effectiveness for heavy-duty applications. Understanding cotton's benefits and limitations helps workers select appropriate gear that balances comfort with safety requirements.
Aramid vs Cotton: Strength and Durability
Aramid fibers offer superior strength and durability compared to cotton, making them ideal for reinforced workwear subjected to extreme conditions. Aramid materials, such as Kevlar, resist cuts, abrasions, and heat, while cotton tends to wear down faster under heavy use and lacks inherent flame resistance. The high tensile strength and long-lasting resilience of aramid significantly enhance protective clothing performance, ensuring worker safety and garment longevity.
Fire and Heat Resistance Comparison
Aramid fibers, such as Nomex and Kevlar, offer superior fire and heat resistance compared to cotton, providing excellent protection against thermal hazards in reinforced workwear. Aramid materials can withstand temperatures up to 500degC (932degF) without melting or dripping, maintaining structural integrity during exposure to flames and radiant heat. Cotton, while breathable and comfortable, ignites more easily and lacks the inherent flame-resistant properties found in aramid fibers, making it less suitable for high-heat or fire-exposure environments.
Comfort and Breathability: Cotton vs Aramid
Cotton fibers provide superior comfort and breathability in reinforced workwear due to their natural moisture-wicking properties and softness against the skin. Aramid, while offering exceptional flame resistance and durability, tends to be less breathable and may cause increased heat retention during prolonged wear. Balancing comfort and protective features, many manufacturers blend cotton with aramid fibers to optimize breathability without compromising safety.
Cost and Accessibility of Aramid and Cotton
Aramid fiber workwear generally comes at a higher cost due to its superior strength, heat resistance, and durability, making it more suitable for high-risk industrial environments. Cotton workwear is more affordable and widely accessible, offering breathability and comfort but lacking the advanced protective properties of aramid. While aramid garments require specialized manufacturing and sourcing, cotton fabrics are readily available and easier to maintain, impacting their overall accessibility in various markets.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Aramid fibers offer superior durability and flame resistance compared to cotton, significantly reducing the frequency of garment replacement and waste generation. Cotton cultivation demands extensive water and pesticide use, contributing to environmental degradation, whereas aramid's synthetic origin, although energy-intensive, supports longer garment lifecycles that mitigate overall environmental impact. Choosing aramid-reinforced workwear enhances sustainability by balancing resource consumption with extended product lifespan and reduced waste in industrial settings.
Best Applications: When to Choose Aramid or Cotton
Aramid fibers are ideal for reinforced workwear in high-heat, flame-resistant environments such as firefighting, welding, and electrical jobs due to their exceptional thermal stability and durability. Cotton excels in applications requiring comfort, breathability, and moderate protection, making it suitable for construction, agriculture, and light industrial tasks. Choosing aramid ensures maximum safety in hazardous conditions, while cotton offers better moisture absorption and flexibility for extended wear in less extreme environments.
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Reinforced Workwear Fabric
Aramid fibers provide superior heat resistance, durability, and cut protection compared to cotton, making them ideal for high-risk industrial environments. Cotton offers breathability and comfort but lacks the advanced protective properties necessary for extreme conditions. Selecting reinforced workwear fabric depends on balancing protection requirements with comfort, with aramid being optimal for hazardous tasks and cotton suitable for lighter duties.
Infographic: Aramid vs Cotton for Reinforced Workwear
 azmater.com
azmater.com