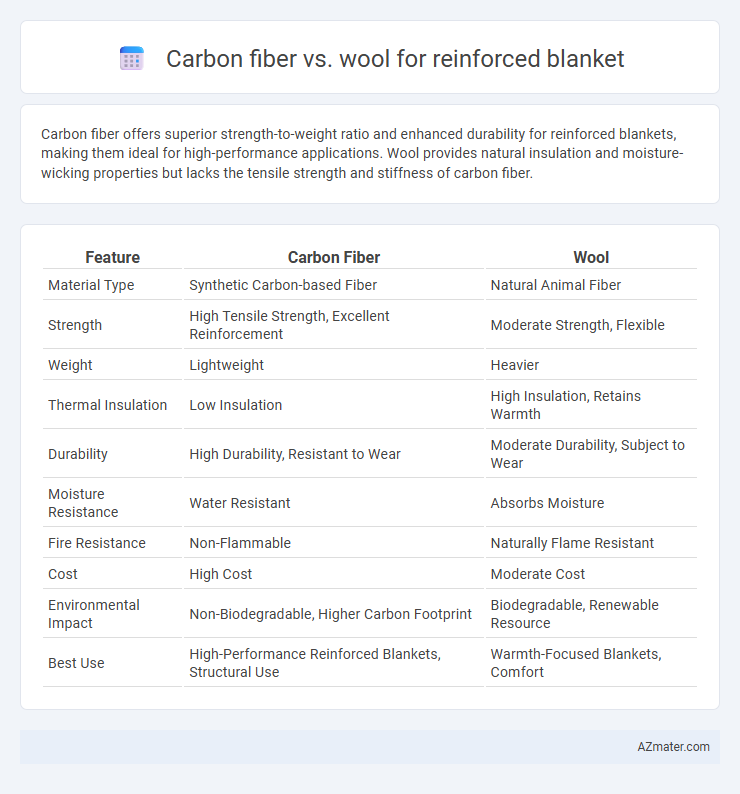
Carbon fiber offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced durability for reinforced blankets, making them ideal for high-performance applications. Wool provides natural insulation and moisture-wicking properties but lacks the tensile strength and stiffness of carbon fiber.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Carbon Fiber | Wool |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic Carbon-based Fiber | Natural Animal Fiber |
| Strength | High Tensile Strength, Excellent Reinforcement | Moderate Strength, Flexible |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Thermal Insulation | Low Insulation | High Insulation, Retains Warmth |
| Durability | High Durability, Resistant to Wear | Moderate Durability, Subject to Wear |
| Moisture Resistance | Water Resistant | Absorbs Moisture |
| Fire Resistance | Non-Flammable | Naturally Flame Resistant |
| Cost | High Cost | Moderate Cost |
| Environmental Impact | Non-Biodegradable, Higher Carbon Footprint | Biodegradable, Renewable Resource |
| Best Use | High-Performance Reinforced Blankets, Structural Use | Warmth-Focused Blankets, Comfort |
Introduction: The Need for Reinforced Blankets
Reinforced blankets require materials that balance strength, durability, and weight. Carbon fiber offers exceptional tensile strength and lightweight properties, making it ideal for high-performance reinforcement. Wool provides natural insulation and flexibility but lacks the mechanical strength necessary for demanding applications in reinforced blankets.
Material Overview: Carbon Fiber vs Wool
Carbon fiber is a high-strength, lightweight material known for its exceptional tensile strength and durability, making it ideal for reinforced blankets requiring superior structural reinforcement and resistance to wear. Wool, a natural fiber, offers excellent thermal insulation, moisture-wicking properties, and flexibility but lacks the mechanical strength and rigidity of carbon fiber. Combining carbon fiber with wool can enhance blanket performance by integrating the strength and durability of synthetic fibers with the comfort and insulation properties of natural fibers.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Carbon fiber demonstrates significantly higher tensile strength and stiffness compared to wool, making it ideal for reinforced blankets requiring exceptional durability and resistance to mechanical stress. While wool offers natural flexibility and moderate tensile strength, carbon fiber's superior modulus of elasticity ensures enhanced load-bearing capacity and minimal deformation under strain. The integration of carbon fiber in reinforced blankets provides unmatched mechanical performance for applications demanding lightweight and robust materials.
Thermal Insulation Performance
Carbon fiber offers superior thermal insulation performance for reinforced blankets due to its low thermal conductivity and excellent heat retention properties, effectively reducing heat loss in extreme conditions. Wool, while naturally insulating and moisture-wicking, tends to have higher thermal conductivity and can absorb moisture, which diminishes its insulating efficiency when wet. Combining carbon fiber with wool in reinforced blankets can enhance thermal regulation by leveraging carbon fiber's insulating strength and wool's temperature-adaptive characteristics.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Carbon fiber reinforced blankets typically weigh significantly less than wool counterparts, offering enhanced strength-to-weight ratio ideal for lightweight applications. The inherent rigidity of carbon fiber provides high tensile strength but reduces flexibility compared to wool, which remains highly pliable and adaptable under stress. Wool's natural crimp structure grants superior elasticity, making it better suited for applications requiring frequent bending without compromising integrity.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Carbon fiber offers superior durability and exceptional wear resistance compared to wool for reinforced blankets, making it ideal for high-stress applications and long-term use. Its lightweight yet strong properties ensure resistance to abrasion, punctures, and environmental degradation, far surpassing the natural fibers in wool. Wool, while naturally resilient and comfortable, tends to degrade faster under heavy wear and exposure to moisture, limiting its longevity in reinforced blanket applications.
Fire Resistance and Safety Factors
Carbon fiber offers superior fire resistance compared to wool due to its high melting point exceeding 3,000degC and non-flammable properties, making it ideal for reinforced blankets used in high-temperature environments. Wool, naturally flame-retardant with a decomposition temperature around 570degC, provides excellent insulation but can char and smolder under extreme heat, posing potential safety risks. Reinforced blankets combining carbon fiber maximize fire resistance and durability, whereas wool blankets emphasize comfort with moderate thermal protection and safer smoldering behavior.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbon fiber reinforced blankets offer high durability and strength with a lower weight, but their production relies on energy-intensive processes and non-renewable petroleum-based resources, resulting in a higher carbon footprint. Wool, a natural and biodegradable fiber, supports sustainable farming practices and enhances soil health, although its production can involve significant water use and methane emissions from sheep. Choosing wool over carbon fiber for reinforced blankets reduces environmental impact through renewability and biodegradability, making it a more sustainable option despite some agricultural challenges.
Cost and Accessibility
Carbon fiber reinforced blankets typically cost significantly more than wool due to advanced manufacturing processes and raw material expenses, making them less accessible for general consumers. Wool blankets offer wider availability and affordability, benefiting from abundant natural resources and simpler production methods. Cost-efficiency and accessibility make wool a preferred choice for everyday uses, while carbon fiber suits specialized, high-performance applications despite higher prices.
Choosing the Right Material for Reinforced Blankets
Choosing the right material for reinforced blankets depends on the specific application requirements such as strength, durability, and thermal insulation. Carbon fiber offers superior tensile strength, lightweight properties, and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for high-performance reinforcement in extreme conditions. Wool, on the other hand, provides excellent thermal insulation, flexibility, and natural moisture regulation, which suits applications needing comfort and moderate structural support.
Infographic: Carbon fiber vs Wool for Reinforced blanket
 azmater.com
azmater.com