White concrete offers superior aesthetic appeal and high durability with excellent light reflectance, making it ideal for modular structures requiring a sleek finish. Precast concrete enables faster construction and consistent quality due to factory-controlled production, suited for modular projects emphasizing efficiency and precision.
Table of Comparison
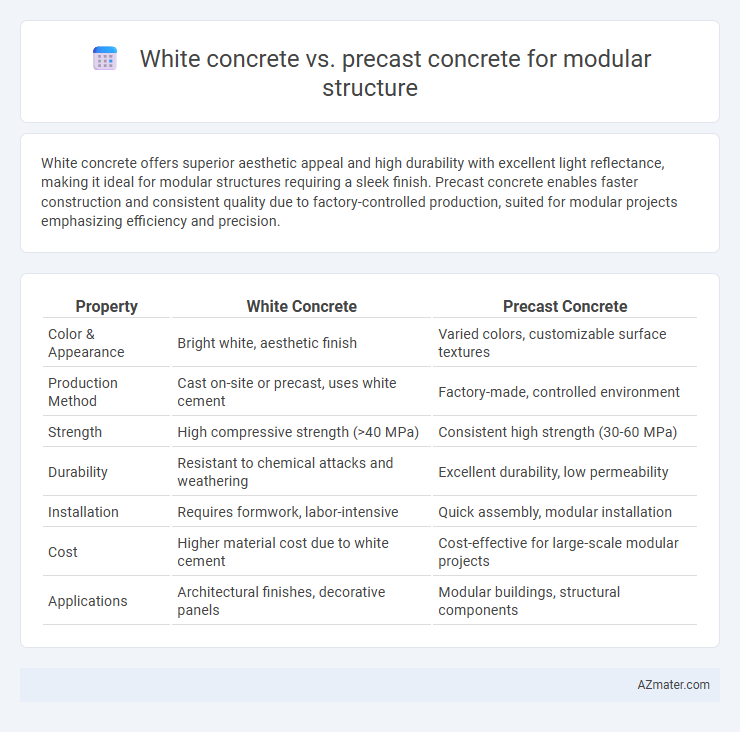
| Property | White Concrete | Precast Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Color & Appearance | Bright white, aesthetic finish | Varied colors, customizable surface textures |
| Production Method | Cast on-site or precast, uses white cement | Factory-made, controlled environment |
| Strength | High compressive strength (>40 MPa) | Consistent high strength (30-60 MPa) |
| Durability | Resistant to chemical attacks and weathering | Excellent durability, low permeability |
| Installation | Requires formwork, labor-intensive | Quick assembly, modular installation |
| Cost | Higher material cost due to white cement | Cost-effective for large-scale modular projects |
| Applications | Architectural finishes, decorative panels | Modular buildings, structural components |
Introduction to White Concrete and Precast Concrete
White concrete, characterized by its bright, reflective surface, is formulated using white cement and light-colored aggregates, enhancing aesthetic appeal and reducing heat absorption in modular structures. Precast concrete consists of factory-produced components cast in controlled environments, ensuring uniform quality and accelerating on-site assembly in modular construction. Both materials offer distinct advantages, with white concrete providing design flexibility and precast concrete delivering efficiency and durability for modular building applications.
Defining Modular Construction
White concrete offers superior aesthetic appeal and light-reflective properties, enhancing modular structures with a clean, modern finish. Precast concrete provides high precision and faster assembly times, enabling efficient, repeatable modules ideal for scalable construction projects. Both materials support modular construction by allowing factory-controlled production and streamlined on-site installation, reducing construction waste and time.
Composition and Properties of White Concrete
White concrete is composed of white Portland cement, light-colored aggregates such as quartz or limestone, and minimal iron content to maintain its bright appearance, offering high reflectivity and aesthetic appeal. Its properties include high compressive strength, low thermal conductivity, and superior durability against weathering and chemical attacks, making it ideal for exposed modular structures. Compared to precast concrete, white concrete provides enhanced visual quality and corrosion resistance but may require more precise mix control to achieve consistent coloration and performance.
Overview of Precast Concrete Techniques
Precast concrete techniques involve casting concrete elements in a controlled factory environment, ensuring consistent quality and accelerated construction timelines for modular structures. These methods utilize standardized molds and reinforcement, enabling precise dimensions and enhanced durability compared to on-site white concrete pours. The prefabricated components are transported to the site for quick assembly, reducing labor costs and minimizing construction waste.
Aesthetic Appeal: White Concrete vs Precast Concrete
White concrete offers a clean, bright surface that enhances architectural designs with a smooth, uniform finish ideal for modern modular structures. Precast concrete provides versatility with customizable textures and shapes, allowing for intricate patterns and finishes that elevate the visual complexity of modular buildings. The choice between white concrete and precast concrete depends on desired aesthetic outcomes, with white concrete favoring minimalistic elegance and precast concrete supporting detailed architectural expression.
Structural Performance Comparison
White concrete offers superior aesthetic appeal but generally exhibits lower compressive strength compared to precast concrete, which is engineered for high durability and load-bearing capacity. Precast concrete components are manufactured under controlled conditions, ensuring uniform structural performance critical for modular construction stability and seismic resistance. The enhanced density and reinforcement integration in precast concrete provide better flexural strength and reduced cracking potential, making it more suitable for complex modular assemblies requiring stringent structural reliability.
Durability and Maintenance Factors
White concrete offers superior aesthetic longevity and resistance to UV discoloration, making it ideal for modular structures requiring minimal surface maintenance. Precast concrete provides enhanced durability through controlled factory curing, reducing susceptibility to cracking and environmental damage over time. Maintenance demands are generally lower with precast units due to standardized manufacturing and quality control, ensuring consistent performance in modular construction applications.
Installation and Construction Speed
White concrete offers aesthetic benefits but typically requires longer curing times, potentially slowing installation in modular construction. Precast concrete is manufactured offsite with controlled conditions, enabling rapid on-site assembly and significantly reducing overall construction time. The modular structure benefits from precast concrete's precision and speed, making it the preferred choice for efficient installation and fast project completion.
Cost Considerations and Value
White concrete typically incurs higher material costs due to the use of white cement and specialized aggregates, but it offers aesthetic appeal and durability that enhance the value of modular structures. Precast concrete enables faster construction and reduces labor expenses through factory-controlled production, resulting in cost savings despite initial mold and transportation investments. Evaluating overall project budgets reveals that precast concrete can provide greater long-term value by minimizing on-site work and improving quality consistency in modular construction.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
White concrete offers higher reflectivity, reducing urban heat island effects and lowering cooling energy consumption, which contributes positively to environmental sustainability in modular construction. Precast concrete minimizes on-site waste and energy use due to factory-controlled production and precise material batching, enhancing eco-efficiency and reducing carbon footprint. Both materials support sustainable design goals, with white concrete optimizing daylighting and thermal performance, while precast concrete enables efficient recycling and reduced transportation emissions through modular assembly.
Infographic: White concrete vs Precast concrete for Modular structure
 azmater.com
azmater.com