Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) offers superior durability, compressive strength exceeding 150 MPa, and enhanced resistance to abrasion compared to roller-compacted concrete (RCC), which provides faster placement and lower initial costs. UHPC is ideal for high-stress, long-lasting pavements, while RCC suits large-scale projects requiring rapid construction and moderate performance.
Table of Comparison
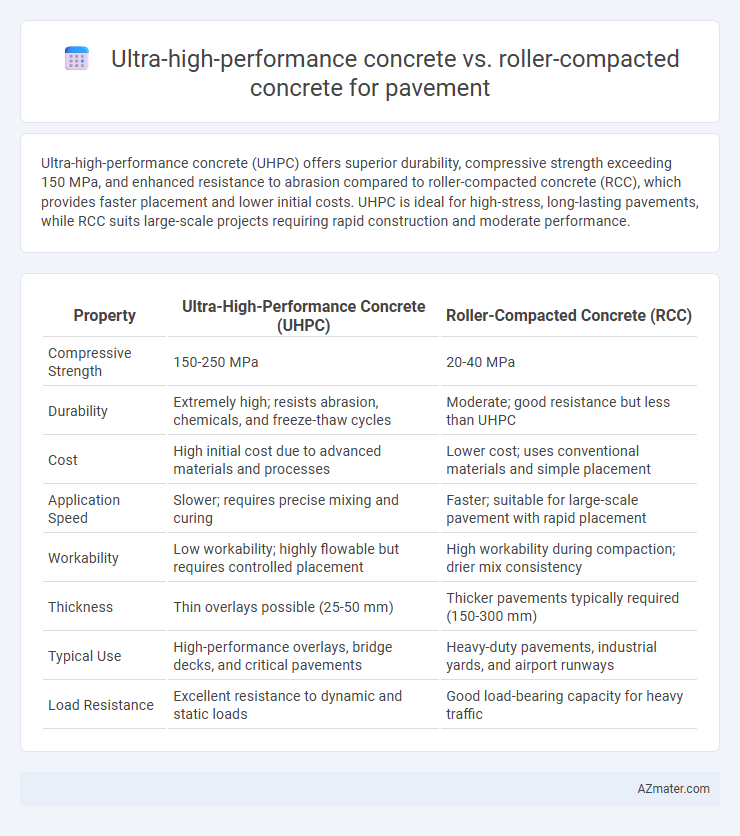
| Property | Ultra-High-Performance Concrete (UHPC) | Roller-Compacted Concrete (RCC) |
|---|---|---|
| Compressive Strength | 150-250 MPa | 20-40 MPa |
| Durability | Extremely high; resists abrasion, chemicals, and freeze-thaw cycles | Moderate; good resistance but less than UHPC |
| Cost | High initial cost due to advanced materials and processes | Lower cost; uses conventional materials and simple placement |
| Application Speed | Slower; requires precise mixing and curing | Faster; suitable for large-scale pavement with rapid placement |
| Workability | Low workability; highly flowable but requires controlled placement | High workability during compaction; drier mix consistency |
| Thickness | Thin overlays possible (25-50 mm) | Thicker pavements typically required (150-300 mm) |
| Typical Use | High-performance overlays, bridge decks, and critical pavements | Heavy-duty pavements, industrial yards, and airport runways |
| Load Resistance | Excellent resistance to dynamic and static loads | Good load-bearing capacity for heavy traffic |
Introduction to Ultra-High-Performance Concrete and Roller-Compacted Concrete
Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) is a class of advanced cementitious material characterized by exceptional strength, durability, and enhanced tensile properties, often exceeding 150 MPa compressive strength and incorporating fiber reinforcement for improved toughness. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) is a no-slump concrete mix designed for rapid construction of pavements and earth dams, recognized for its high density and lower cement content, providing cost-effective and durable solutions with compressive strengths typically ranging from 20 to 40 MPa. The distinct material compositions and mechanical properties of UHPC and RCC significantly influence their application in pavement engineering, with UHPC suited for high-performance, long-life surface layers and RCC optimal for heavy-duty base or structural layers requiring fast placement and economy.
Material Composition and Key Properties
Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) contains a dense matrix of fine powders, including cement, silica fume, quartz flour, and fine silica sand, combined with steel fibers, offering exceptional compressive strengths exceeding 150 MPa and superior durability. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) consists of a zero-slump blend of cement, coarse aggregates, and water with little to no fine aggregate, facilitating rapid placement and densities comparable to traditional concrete but with compressive strengths typically ranging from 20 to 40 MPa. UHPC's ultra-dense microstructure provides high abrasion resistance and low permeability ideal for heavy-duty pavements, while RCC prioritizes economical construction and rapid laying over mechanical properties.
Manufacturing and Placement Techniques
Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) manufacturing involves precise batching of high cementitious content, fine powders, and steel fibers, requiring advanced mixing equipment to achieve its dense microstructure. Placement of UHPC demands controlled pumping and specialized formworks to ensure consolidation without segregation, often utilizing self-consolidating properties. In contrast, roller-compacted concrete (RCC) employs a drier mix with lower cement content, placed using conventional asphalt pavers and compacted with rollers, enabling faster and more economical pavement construction.
Structural Performance Comparison
Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) exhibits superior compressive strength exceeding 150 MPa and exceptional durability under heavy traffic loads, making it ideal for long-span bridge decks and high-stress pavements. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC), with compressive strengths typically between 20-40 MPa, offers cost-effective and rapid construction but demonstrates lower tensile strength and fatigue resistance compared to UHPC. Structural performance comparisons reveal that UHPC provides enhanced crack resistance and longer service life under dynamic loading, whereas RCC is better suited for base layers and lightly trafficked pavement due to its lower mechanical properties.
Durability and Longevity in Pavement Applications
Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) offers superior durability with its dense microstructure, high compressive strength exceeding 150 MPa, and excellent resistance to freeze-thaw cycles, chemical attack, and abrasion, making it ideal for long-lasting pavement applications. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) provides cost-effective durability through high-density placement and low water content, achieving compressive strengths around 30-70 MPa, suitable for heavy traffic pavements but with comparatively lower resistance to environmental degradation than UHPC. The extended longevity of UHPC pavements results in reduced maintenance frequency and lifecycle costs, while RCC pavements deliver balanced durability and economic benefits for large-scale infrastructure projects.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) exhibits higher initial costs due to specialized materials and processing but offers superior durability and reduced maintenance expenses over the pavement lifecycle. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) provides a cost-effective solution with lower material and placement costs, suitable for large-scale applications requiring rapid construction. Economic considerations favor UHPC in scenarios demanding long-term performance and reduced total ownership costs, while RCC is optimal for budget-sensitive projects prioritizing upfront affordability.
Maintenance Requirements and Lifecycle Costs
Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) offers superior durability and significantly reduces maintenance requirements due to its high compressive strength and resistance to wear, leading to lower lifecycle costs despite higher initial investment. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) provides cost efficiency with faster construction times but generally demands more frequent maintenance and repairs because of its lower tensile strength and susceptibility to cracking under heavy traffic loads. Lifecycle cost analysis typically favors UHPC for long-term pavement infrastructure where reduced maintenance intervals translate to substantial savings over decades.
Environmental Impact Assessment
Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) offers superior durability and reduced maintenance requirements compared to roller-compacted concrete (RCC), resulting in a longer pavement lifespan and lower lifecycle carbon emissions. RCC typically requires less energy-intensive production and allows faster construction, which reduces on-site emissions and minimizes traffic disruptions. Environmental impact assessments highlight UHPC's potential for sustainability through resource efficiency, while RCC is favored for lower initial environmental costs and rapid deployment in large-scale pavement projects.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) demonstrates superior durability and load-bearing capacity in pavement applications, as evidenced by case studies from the U.S. Department of Transportation and European highways, where UHPC significantly extended service life under heavy traffic conditions. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers cost-effective and rapid construction benefits, with successful implementations in municipal roads and airport runways such as Texas's Loop 1604 and Denver International Airport, providing high structural strength with faster curing times. Comparative real-world analyses highlight UHPC's advantage in high-stress environments requiring long-term performance, while RCC remains a practical choice for large-area pavements demanding accelerated construction schedules.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Concrete for Pavements
Ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) offers superior durability, compressive strength exceeding 150 MPa, and exceptional resistance to environmental stressors, making it ideal for high-traffic or critical pavement applications. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) provides cost-effective construction with rapid placement and excellent load distribution, suitable for large-scale pavements requiring high structural capacity but less stringent aesthetic or durability demands. Selecting between UHPC and RCC depends on project priorities such as budget constraints, expected traffic loads, lifespan requirements, and maintenance considerations for optimized pavement performance.
Infographic: Ultra-high-performance concrete vs Roller-compacted concrete for Pavement
 azmater.com
azmater.com