Sulfate-resistant concrete offers enhanced durability against sulfate-rich soil conditions, making it ideal for roads exposed to aggressive environments. Roller-compacted concrete provides superior compressive strength and rapid construction benefits, making it suitable for high-traffic road surfaces requiring quick installation.
Table of Comparison
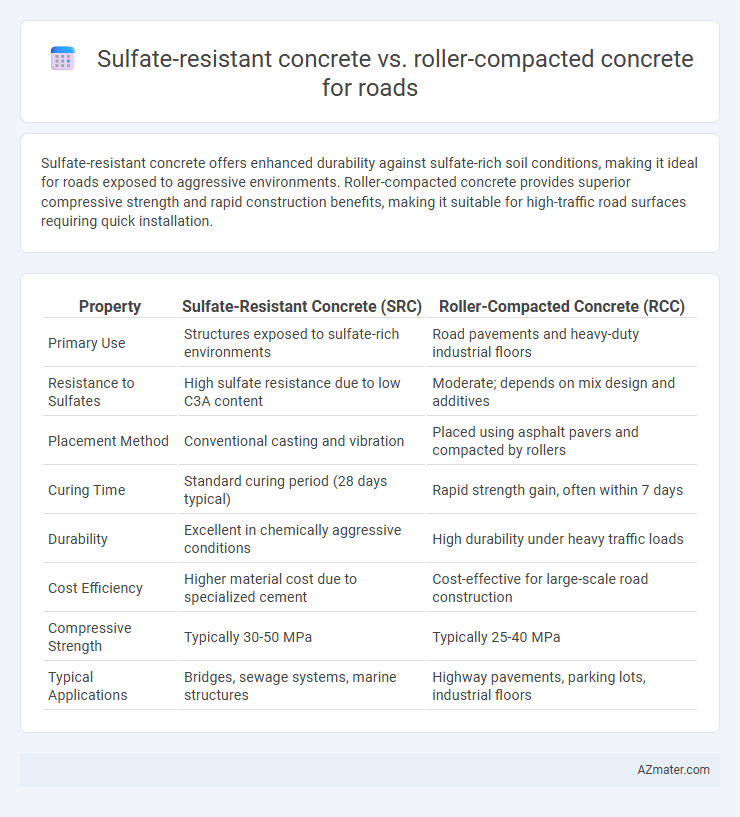
| Property | Sulfate-Resistant Concrete (SRC) | Roller-Compacted Concrete (RCC) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Structures exposed to sulfate-rich environments | Road pavements and heavy-duty industrial floors |
| Resistance to Sulfates | High sulfate resistance due to low C3A content | Moderate; depends on mix design and additives |
| Placement Method | Conventional casting and vibration | Placed using asphalt pavers and compacted by rollers |
| Curing Time | Standard curing period (28 days typical) | Rapid strength gain, often within 7 days |
| Durability | Excellent in chemically aggressive conditions | High durability under heavy traffic loads |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher material cost due to specialized cement | Cost-effective for large-scale road construction |
| Compressive Strength | Typically 30-50 MPa | Typically 25-40 MPa |
| Typical Applications | Bridges, sewage systems, marine structures | Highway pavements, parking lots, industrial floors |
Introduction to Sulfate-Resistant and Roller-Compacted Concrete
Sulfate-resistant concrete is specifically engineered to withstand high sulfate environments, making it ideal for road construction in areas with sulfate-rich soils or groundwater. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) is a dry mix concrete placed and compacted with heavy rollers, offering high durability and rapid construction for roads and pavements. Both types enhance road longevity but serve different environmental and structural requirements based on site conditions.
Key Properties of Sulfate-Resistant Concrete
Sulfate-resistant concrete is specifically designed with low tricalcium aluminate content, enhancing its durability against sulfate attacks commonly found in aggressive soil and groundwater environments. Its key properties include high chemical resistance, reduced permeability, and increased long-term strength retention, making it ideal for extending the lifespan of road infrastructure exposed to sulfate-rich conditions. Unlike roller-compacted concrete, which emphasizes rapid construction and high compressive strength, sulfate-resistant concrete prioritizes chemical stability and durability critical for sulfate-laden environments.
Essential Characteristics of Roller-Compacted Concrete
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) for roads is characterized by its low water content, high density, and rapid compaction using heavy rollers, resulting in exceptional strength and durability. RCC exhibits excellent resistance to deformation under heavy loads and superior permeability reduction compared to sulfate-resistant concrete, making it ideal for high-traffic pavements. Its essential characteristics also include fast-setting properties and minimal shrinkage, which contribute to reduced construction time and long-term performance in harsh environments.
Chemical Resistance: Sulfate Attacks in Road Construction
Sulfate-resistant concrete is specifically formulated with low C3A content and supplementary cementitious materials like fly ash or slag to enhance resistance against aggressive sulfate ions found in soil and groundwater, making it ideal for roads exposed to sulfate-rich environments. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers rapid construction and high compressive strength but may require additives or sealants to improve chemical resistance, as its dense matrix alone does not guarantee sulfate durability. Choosing sulfate-resistant concrete over standard RCC ensures enhanced long-term performance and durability when sulfate attack is a primary concern in road construction projects.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Sulfate-resistant concrete exhibits superior chemical durability, effectively resisting sulfate attack in aggressive soil and groundwater environments, which enhances long-term durability for road structures. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) provides high early strength and excellent load-bearing capacity due to its dry mix and compaction process, making it ideal for rapid construction of road pavements. While RCC offers enhanced mechanical strength, sulfate-resistant concrete ensures prolonged structural integrity in sulfate-rich conditions, making the choice dependent on environmental exposure and specific project durability requirements.
Construction Methods and Placement Techniques
Sulfate-resistant concrete requires precise mixing with low water-to-cement ratios and the use of sulfate-resisting cement to enhance durability in aggressive soil or groundwater conditions, typically placed using standard cast-in-place methods with vibration to ensure density. Roller-compacted concrete employs a zero-slump mixture compacted with vibratory rollers, allowing rapid placement and immediate traffic loading ideal for large-scale road projects. Construction efficiency differs as sulfate-resistant concrete demands careful curing to prevent sulfate attack, whereas roller-compacted concrete focuses on swift layering and compaction without forms or finishing.
Cost Analysis: Material and Labor Considerations
Sulfate-resistant concrete typically incurs higher material costs due to specialized cement blends designed to withstand aggressive sulfate environments, impacting overall project budgets for road construction. Roller-compacted concrete offers cost savings by utilizing a drier mix and faster placement techniques, reducing labor hours and equipment usage. Evaluating both options requires analyzing project-specific soil sulfate levels and production efficiencies to optimize material expenses and labor investments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Sulfate-resistant concrete minimizes environmental degradation by reducing repair frequency in sulfate-rich soils, enhancing road durability and lowering lifecycle carbon emissions. Roller-compacted concrete offers a sustainable solution through rapid construction, decreased cement content, and reduced energy consumption while maintaining structural integrity. Both materials contribute to eco-friendly road infrastructure, with sulfate-resistant concrete excelling in chemical resistance and roller-compacted concrete prioritizing resource efficiency.
Suitable Applications for Each Concrete Type
Sulfate-resistant concrete is ideal for road structures exposed to high sulfate environments, such as coastal highways and areas with sulfate-rich soils, due to its enhanced durability against chemical attack. Roller-compacted concrete suits heavy-load-bearing roads and pavements, including industrial yards and highways, thanks to its high strength and rapid construction capability. Selecting between these concretes depends on environmental sulfate exposure and structural load requirements, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Concrete for Road Projects
Sulfate-resistant concrete offers superior durability in environments with high sulfate exposure, making it ideal for roads in aggressive soil or groundwater conditions. Roller-compacted concrete provides rapid construction and high compressive strength, suitable for heavy-duty roadways requiring fast project turnaround. Selecting the right concrete depends on site-specific chemical exposure, load demands, and construction timelines to ensure long-lasting road performance and cost-efficiency.
Infographic: Sulfate-resistant concrete vs Roller-compacted concrete for Road
 azmater.com
azmater.com