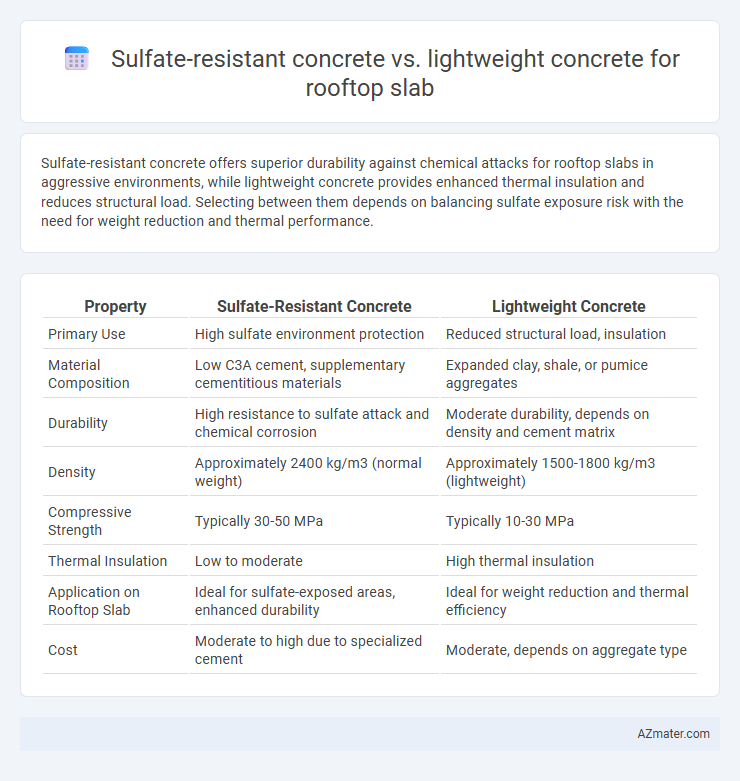
Sulfate-resistant concrete offers superior durability against chemical attacks for rooftop slabs in aggressive environments, while lightweight concrete provides enhanced thermal insulation and reduces structural load. Selecting between them depends on balancing sulfate exposure risk with the need for weight reduction and thermal performance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Sulfate-Resistant Concrete | Lightweight Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | High sulfate environment protection | Reduced structural load, insulation |
| Material Composition | Low C3A cement, supplementary cementitious materials | Expanded clay, shale, or pumice aggregates |
| Durability | High resistance to sulfate attack and chemical corrosion | Moderate durability, depends on density and cement matrix |
| Density | Approximately 2400 kg/m3 (normal weight) | Approximately 1500-1800 kg/m3 (lightweight) |
| Compressive Strength | Typically 30-50 MPa | Typically 10-30 MPa |
| Thermal Insulation | Low to moderate | High thermal insulation |
| Application on Rooftop Slab | Ideal for sulfate-exposed areas, enhanced durability | Ideal for weight reduction and thermal efficiency |
| Cost | Moderate to high due to specialized cement | Moderate, depends on aggregate type |
Introduction to Rooftop Slab Concrete Requirements
Rooftop slab concrete must possess high durability, resistance to environmental stressors, and adequate load-bearing capacity to support structural and weather elements. Sulfate-resistant concrete is engineered to withstand aggressive chemical exposure, making it ideal for roofs in industrial or coastal areas where sulfate attack is prevalent. Lightweight concrete reduces dead load on the structure, enhancing seismic performance and thermal insulation but may require additional protection against chemical degradation.
What is Sulfate-Resistant Concrete?
Sulfate-resistant concrete is specifically formulated to withstand exposure to high sulfate environments by using sulfate-resistant cement, reducing the risk of chemical attack and deterioration in rooftop slabs. It contains low tricalcium aluminate (C3A) content, typically less than 5%, which minimizes sulfate reactions and enhances durability against aggressive soil or water conditions. This type of concrete is ideal for rooftop slabs in areas with sulfate-rich groundwater or industrial pollution, ensuring long-term structural integrity.
Key Features of Lightweight Concrete
Lightweight concrete for rooftop slabs offers superior thermal insulation, reducing heat transfer and enhancing energy efficiency in buildings. Its lower density decreases structural load, which minimizes the need for heavy support systems and reduces construction costs. Compared to sulfate-resistant concrete, lightweight concrete provides better workability and ease of handling, making it ideal for rooftop applications exposed to moderate environmental conditions.
Sulfate Attack Risks in Rooftop Applications
Sulfate-resistant concrete contains low C3A cement, which enhances durability against sulfate attack in rooftop slabs exposed to aggressive environments such as acid rain or contaminated water. Lightweight concrete offers reduced structural load but may have higher porosity, increasing vulnerability to sulfate ingress and subsequent degradation unless properly treated or sealed. For rooftop applications prone to sulfate exposure, sulfate-resistant concrete provides superior chemical resistance, extending service life by minimizing expansion, cracking, and strength loss due to sulfate attack.
Weight Considerations for Rooftop Slabs
Sulfate-resistant concrete offers enhanced durability in aggressive soil or groundwater environments but is typically heavier than lightweight concrete, impacting the overall load on rooftop slabs. Lightweight concrete reduces dead load significantly due to its lower density, improving structural efficiency and reducing the need for heavy support systems. Selecting lightweight concrete for rooftop slabs ensures optimized weight management, critical for high-rise buildings or structures with stringent load limitations.
Durability Comparison: Sulfate-Resistant vs Lightweight Concrete
Sulfate-resistant concrete exhibits superior durability for rooftop slabs in aggressive sulfate-rich environments by minimizing chemical attacks that cause deterioration and spalling. In contrast, lightweight concrete offers advantages in reducing dead load but generally presents lower resistance to sulfate exposure due to its higher porosity and potential for increased permeability. For rooftop slabs requiring enhanced longevity and structural integrity under sulfate attack, sulfate-resistant concrete provides a more durable and resilient solution.
Structural Performance and Load-Bearing Capacity
Sulfate-resistant concrete offers superior durability and enhanced resistance to chemical attacks, making it ideal for rooftop slabs exposed to aggressive sulfate environments, maintaining long-term structural integrity. Lightweight concrete reduces dead load significantly, lowering the overall load on supporting structures and foundations, which can improve seismic performance but may have lower compressive strength compared to sulfate-resistant alternatives. For rooftop slabs, sulfate-resistant concrete provides higher load-bearing capacity and better structural performance under harsh exposure, while lightweight concrete benefits applications where weight reduction is critical without compromising insulation properties.
Thermal and Insulation Properties
Sulfate-resistant concrete offers superior chemical durability but has relatively low thermal insulation properties compared to lightweight concrete. Lightweight concrete significantly enhances thermal insulation due to its lower density and high air content, making it ideal for rooftop slabs in hot climates. Its insulative characteristics help reduce heat transfer, contributing to energy efficiency and improved indoor comfort.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Lifecycle Investment
Sulfate-resistant concrete typically incurs higher initial costs due to specialized cement and additives required for enhanced durability against sulfate exposure in rooftop slabs. Lightweight concrete offers cost savings through reduced structural load, lowering foundation and support expenses, but may necessitate more frequent maintenance, impacting lifecycle investment. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals sulfate-resistant concrete's higher upfront price is often offset by lower lifecycle repair costs, while lightweight concrete demands careful long-term durability assessment.
Recommended Applications and Selection Guidelines
Sulfate-resistant concrete is recommended for rooftop slabs exposed to sulfate-rich environments such as coastal regions or industrial areas, where durability against chemical attack is essential. Lightweight concrete suits rooftop slabs requiring reduced dead load, improved thermal insulation, and easier handling during construction, especially in seismic zones. Selection guidelines prioritize environmental exposure conditions, structural load capacity, and thermal performance requirements to determine the optimal concrete type for rooftop slab applications.
Infographic: Sulfate-resistant concrete vs Lightweight concrete for Rooftop slab
 azmater.com
azmater.com