Roller-compacted concrete offers high durability and rapid placement with lower water content, while green concrete incorporates recycled materials and industrial by-products to significantly reduce carbon emissions in eco-friendly construction. Choosing green concrete enhances sustainability by minimizing environmental impact, whereas roller-compacted concrete provides efficient structural performance.
Table of Comparison
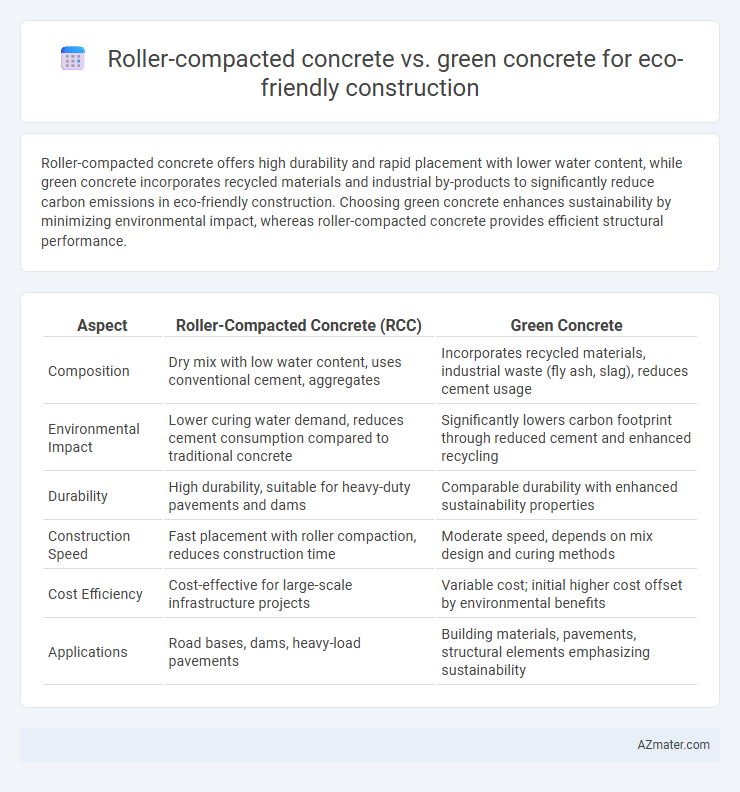
| Aspect | Roller-Compacted Concrete (RCC) | Green Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Dry mix with low water content, uses conventional cement, aggregates | Incorporates recycled materials, industrial waste (fly ash, slag), reduces cement usage |
| Environmental Impact | Lower curing water demand, reduces cement consumption compared to traditional concrete | Significantly lowers carbon footprint through reduced cement and enhanced recycling |
| Durability | High durability, suitable for heavy-duty pavements and dams | Comparable durability with enhanced sustainability properties |
| Construction Speed | Fast placement with roller compaction, reduces construction time | Moderate speed, depends on mix design and curing methods |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for large-scale infrastructure projects | Variable cost; initial higher cost offset by environmental benefits |
| Applications | Road bases, dams, heavy-load pavements | Building materials, pavements, structural elements emphasizing sustainability |
Introduction to Eco-Friendly Construction Materials
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) and green concrete are pivotal in eco-friendly construction, each offering sustainable alternatives to traditional concrete by minimizing environmental impact. RCC utilizes a dry mix and requires less water and cement, reducing carbon emissions, while green concrete incorporates recycled materials and industrial by-products to enhance durability and lower ecological footprints. Both materials contribute significantly to resource conservation and waste reduction in sustainable building practices.
Overview of Roller-Compacted Concrete (RCC)
Roller-Compacted Concrete (RCC) is a zero-slump concrete mixture characterized by its low water content and high density, enabling rapid placement and compaction using heavy rollers, which significantly reduces curing time and labor costs. RCC's durability and reduced cement usage make it an eco-friendly alternative, particularly suitable for large-scale infrastructure projects such as dams, pavements, and industrial floors. Its lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional concrete highlight RCC's potential to minimize the carbon footprint in sustainable construction practices.
What is Green Concrete?
Green concrete is an eco-friendly building material designed to reduce environmental impact by incorporating recycled industrial waste, such as fly ash, slag, and silica fume, thereby minimizing the use of traditional Portland cement. It enhances sustainability through lower carbon emissions, energy consumption, and improved durability compared to conventional concrete. Green concrete supports energy-efficient construction practices and promotes the circular economy by utilizing waste by-products in the concrete mix.
Composition and Production Methods
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) is composed of a drier mix with lower water content, using conventional concrete ingredients such as cement, aggregates, and fly ash, compacted by heavy rollers during production to achieve high density and strength while minimizing energy use. Green concrete incorporates industrial by-products like fly ash, slag, and recycled aggregates, emphasizing eco-friendly binders such as geopolymer or low-carbon cement, produced using energy-efficient processes to reduce carbon emissions. Production methods for RCC involve rapid placement and compaction suitable for large-scale infrastructure, whereas green concrete focuses on sustainable sourcing and curing techniques that lower environmental impact throughout the material lifecycle.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) typically has lower water usage and reduced cement content compared to traditional concrete, leading to decreased carbon dioxide emissions during production. Green concrete incorporates waste materials such as fly ash, slag, or recycled aggregates, significantly reducing natural resource depletion and landfill waste. Both RCC and green concrete contribute to eco-friendly construction by minimizing environmental impact, but green concrete offers enhanced sustainability through the utilization of industrial byproducts.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers high compressive strength and excellent durability due to its dense, low-porosity matrix, making it ideal for heavy-duty infrastructure projects. Green concrete incorporates industrial by-products like fly ash and slag, enhancing sustainability while maintaining competitive strength levels and improved resistance to chemical attack and cracking over time. Comparative analyses indicate RCC excels in load-bearing capacity, whereas green concrete provides superior long-term durability and environmental benefits essential for eco-friendly construction.
Cost Efficiency and Resource Utilization
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers cost efficiency through reduced cement usage and lower labor costs due to its fast placement and compaction methods, making it ideal for large-scale eco-friendly construction. Green concrete emphasizes incorporating industrial by-products like fly ash or slag, significantly reducing natural resource consumption and carbon footprint while maintaining structural integrity. Both methods optimize resource utilization, but RCC excels in rapid construction and cost savings, whereas green concrete prioritizes material sustainability and environmental impact reduction.
Application Areas in Sustainable Projects
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) is widely applied in infrastructure projects such as dams, highways, and industrial pavements due to its durability and rapid construction capabilities, contributing to resource-efficient building. Green concrete, incorporating recycled materials and industrial by-products, is favored in residential buildings and urban development projects where reducing carbon footprint and enhancing thermal insulation are critical. Both materials support sustainable construction by minimizing environmental impact, with RCC excelling in heavy-duty applications and green concrete promoting eco-friendly practices in architectural design.
Challenges and Limitations
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) faces challenges such as lower workability and limited mix design flexibility, which can affect structural performance and finish quality in eco-friendly construction. Green concrete encounters limitations related to the variability of recycled or waste materials and slower strength gain, impacting its consistency and durability. Both materials require careful quality control and innovative mix formulations to overcome these constraints while maintaining sustainability goals.
Future Trends in Eco-Friendly Concrete Solutions
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers high durability and rapid construction benefits, while green concrete integrates recycled materials and low-carbon binders to minimize environmental impact. Future trends emphasize hybrid formulations combining RCC's strength with green concrete's sustainability, leveraging industrial by-products like fly ash and slag to reduce CO2 emissions. Innovations in nanomaterials and bio-based additives are expected to enhance performance and promote circular economy principles in eco-friendly concrete solutions.
Infographic: Roller-compacted concrete vs Green concrete for Eco-friendly construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com