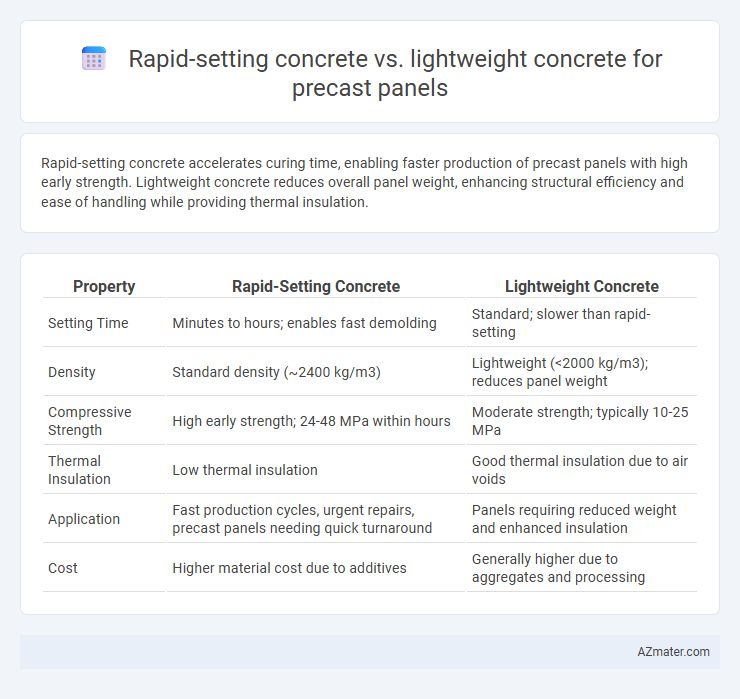
Rapid-setting concrete accelerates curing time, enabling faster production of precast panels with high early strength. Lightweight concrete reduces overall panel weight, enhancing structural efficiency and ease of handling while providing thermal insulation.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Rapid-Setting Concrete | Lightweight Concrete |
|---|---|---|
| Setting Time | Minutes to hours; enables fast demolding | Standard; slower than rapid-setting |
| Density | Standard density (~2400 kg/m3) | Lightweight (<2000 kg/m3); reduces panel weight |
| Compressive Strength | High early strength; 24-48 MPa within hours | Moderate strength; typically 10-25 MPa |
| Thermal Insulation | Low thermal insulation | Good thermal insulation due to air voids |
| Application | Fast production cycles, urgent repairs, precast panels needing quick turnaround | Panels requiring reduced weight and enhanced insulation |
| Cost | Higher material cost due to additives | Generally higher due to aggregates and processing |
Introduction to Precast Concrete Panels
Precast concrete panels are manufactured in controlled factory environments, enabling precise quality control and rapid installation on-site. Rapid-setting concrete accelerates the curing process, reducing production time and allowing faster turnaround for precast panel fabrication. Lightweight concrete offers reduced structural load and enhanced thermal insulation, making it ideal for energy-efficient building envelopes in precast applications.
Overview of Rapid-setting Concrete
Rapid-setting concrete offers accelerated curing times, allowing precast panels to be demolded and transported within hours, significantly increasing production efficiency. Its high early strength, achieved through specialized cementitious materials and chemical admixtures, ensures structural integrity and durability in precast applications. This type of concrete is particularly advantageous for projects requiring fast turnaround without compromising the mechanical performance of precast panels.
Overview of Lightweight Concrete
Lightweight concrete for precast panels is engineered by incorporating lightweight aggregates such as expanded clay, shale, or pumice to reduce density while maintaining structural integrity. This type of concrete offers enhanced thermal insulation, reduced dead load, and improved fire resistance compared to traditional or rapid-setting concrete. Its lower density facilitates easier handling and transportation in precast manufacturing, making it ideal for modular building components where weight reduction is critical.
Key Differences: Rapid-setting vs Lightweight Concrete
Rapid-setting concrete achieves high early strength within hours due to its specialized cement and chemical accelerators, making it ideal for fast turnaround in precast panel production. Lightweight concrete contains low-density aggregates such as expanded clay or shale, reducing panel weight for improved handling, thermal insulation, and structural efficiency. The key difference lies in rapid-setting concrete prioritizing quick curing and strength development, while lightweight concrete emphasizes reduced weight and enhanced insulation properties.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Rapid-setting concrete for precast panels offers high early strength, typically achieving compressive strengths of 20-30 MPa within 24 hours, enabling faster construction cycles and early load application. Lightweight concrete, with densities ranging from 1600 to 1800 kg/m3, provides lower compressive strength, generally between 10-25 MPa, but enhances thermal insulation and reduces dead load on structures. Durability of rapid-setting concrete is superior in aggressive environments due to its dense microstructure, while lightweight concrete requires careful mix design to maintain durability, especially in freeze-thaw and sulfate exposure conditions.
Speed of Construction and Curing Time
Rapid-setting concrete offers significantly faster curing times, typically achieving initial strength within 1 to 3 hours, which accelerates the speed of construction in precast panel applications by reducing production cycle times. In contrast, lightweight concrete generally requires longer curing periods--often 7 to 28 days--due to its lower density and air-entrained structure, which slows strength development. Choosing rapid-setting concrete optimizes project timelines by enabling earlier demolding and handling, whereas lightweight concrete provides benefits in thermal insulation and reduced weight but at the expense of longer curing durations.
Weight and Handling Considerations
Rapid-setting concrete typically has higher density, resulting in heavier precast panels that require robust handling equipment and careful transportation logistics. Lightweight concrete reduces panel weight by incorporating air-entrained aggregates or lightweight fillers, enhancing ease of handling and decreasing structural load without compromising durability. Choosing lightweight concrete improves installation efficiency on-site and reduces crane capacity needs while rapid-setting concrete benefits fast project turnaround despite heavier weight challenges.
Cost Analysis and Budget Implications
Rapid-setting concrete for precast panels typically incurs higher initial material costs due to specialized additives accelerating curing time, which can reduce labor and formwork expenses by enabling faster production cycles. Lightweight concrete, while often less expensive per cubic meter, may require additional reinforcement or insulation layers that increase overall project costs and impact budget allocation. Comparing both, rapid-setting concrete offers better cost efficiency in tight schedules, whereas lightweight concrete benefits projects prioritizing structural weight reduction and thermal performance within moderate budget constraints.
Applications and Suitability for Precast Panels
Rapid-setting concrete excels in precast panel applications requiring quick turnaround times and early strength gain, making it ideal for tight construction schedules and emergency repairs. Lightweight concrete is preferred for precast panels where reduced structural load and improved thermal insulation are critical, offering enhanced energy efficiency and ease of handling. Both materials suit different project demands: rapid-setting concrete for speed and load capacity, lightweight concrete for durability coupled with weight reduction.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Concrete Type for Precast Projects
Selecting the appropriate concrete type for precast panels depends on project requirements such as strength, weight, and curing time. Rapid-setting concrete is ideal for fast turnaround and early strength gain, while lightweight concrete offers benefits in reducing panel weight and improving thermal insulation. Evaluating structural load, installation speed, and environmental factors ensures optimal material performance and cost-efficiency in precast applications.
Infographic: Rapid-setting concrete vs Lightweight concrete for Precast panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com