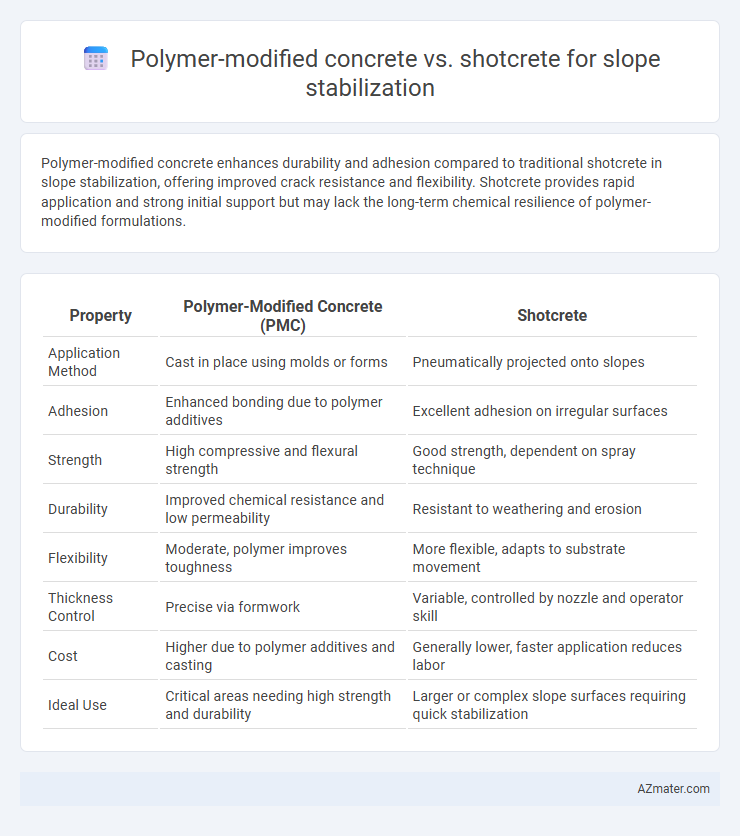
Polymer-modified concrete enhances durability and adhesion compared to traditional shotcrete in slope stabilization, offering improved crack resistance and flexibility. Shotcrete provides rapid application and strong initial support but may lack the long-term chemical resilience of polymer-modified formulations.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polymer-Modified Concrete (PMC) | Shotcrete |
|---|---|---|
| Application Method | Cast in place using molds or forms | Pneumatically projected onto slopes |
| Adhesion | Enhanced bonding due to polymer additives | Excellent adhesion on irregular surfaces |
| Strength | High compressive and flexural strength | Good strength, dependent on spray technique |
| Durability | Improved chemical resistance and low permeability | Resistant to weathering and erosion |
| Flexibility | Moderate, polymer improves toughness | More flexible, adapts to substrate movement |
| Thickness Control | Precise via formwork | Variable, controlled by nozzle and operator skill |
| Cost | Higher due to polymer additives and casting | Generally lower, faster application reduces labor |
| Ideal Use | Critical areas needing high strength and durability | Larger or complex slope surfaces requiring quick stabilization |
Introduction to Slope Stabilization Techniques
Slope stabilization techniques employ various materials and methods to prevent soil erosion and landslides, with polymer-modified concrete and shotcrete being prominent options. Polymer-modified concrete enhances strength and durability by incorporating polymers that improve adhesion and flexibility, making it suitable for reinforcing steep slopes and irregular surfaces. Shotcrete, a pneumatically applied concrete, offers rapid application and excellent adaptability to complex geometries, providing effective surface protection and structural support in slope stabilization projects.
Overview of Polymer-Modified Concrete
Polymer-modified concrete enhances traditional concrete by incorporating polymers, improving its adhesion, flexibility, and resistance to environmental degradation, making it ideal for slope stabilization. This material offers superior tensile and flexural strength compared to conventional concrete, reducing cracking and increasing durability on steep or unstable slopes. Its ability to bond with various substrates and resist water infiltration helps prevent erosion and slope failure in critical infrastructure projects.
Fundamentals of Shotcrete Application
Shotcrete application in slope stabilization relies on pneumatically projecting concrete or mortar onto a surface, ensuring rapid strength gain and excellent adhesion to irregular slopes. Polymer-modified concrete enhances shotcrete by increasing durability, flexibility, and resistance to cracking, which is critical for long-term slope integrity under environmental stresses. Proper shotcrete fundamentals include surface preparation, correct mix design, and optimal nozzle technique to maximize bonding and minimize rebound waste.
Material Properties: Polymer-Modified Concrete vs Shotcrete
Polymer-modified concrete exhibits enhanced bonding strength, increased flexural capacity, and superior resistance to water penetration compared to traditional shotcrete, making it highly effective for slope stabilization in aggressive environmental conditions. Shotcrete offers rapid application and excellent adaptability to complex slope geometries, but its material properties generally provide lower tensile strength and durability without polymer additives. The inclusion of polymers in concrete formulations significantly improves toughness, shrinkage control, and long-term durability, distinguishing polymer-modified concrete as a more resilient solution for slope reinforcement.
Installation Methods and Equipment Requirements
Polymer-modified concrete offers enhanced adhesion and flexibility for slope stabilization, requiring conventional concrete mixers and spraying equipment for precise application in challenging terrains. Shotcrete, applied pneumatically through spray nozzles, enables rapid placement and compaction on inclined or irregular surfaces, often utilizing portable compressors and hoses for efficient installation. Both methods demand skilled operators and robust equipment, but shotcrete typically allows faster installation, especially in confined or steep slope environments.
Durability and Long-Term Performance
Polymer-modified concrete demonstrates superior durability in slope stabilization due to its enhanced resistance to water ingress, chemical attack, and freeze-thaw cycles, resulting in extended service life compared to traditional materials. Shotcrete offers rapid application and strong initial adhesion but may experience reduced long-term performance without adequate polymer modification or proper curing. Long-term performance of polymer-modified concrete outperforms shotcrete by maintaining structural integrity and minimizing maintenance in harsh environmental conditions.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Polymer-modified concrete generally incurs higher initial material costs compared to conventional shotcrete due to specialized additives enhancing durability and adhesion properties. Shotcrete offers cost efficiency in slope stabilization by reducing labor and formwork expenses through its sprayed application method, making it favorable for complex geometries and rapid deployment. Economic considerations must include lifecycle costs, where polymer-modified concrete's increased resistance to environmental degradation can reduce maintenance expenses and extend service life, potentially offsetting the upfront investment.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polymer-modified concrete reduces permeability and enhances durability, minimizing the need for frequent repairs and lowering long-term environmental impact in slope stabilization projects. Shotcrete offers rapid application and strong adhesion, but its higher cement content contributes to increased carbon emissions compared to polymer-modified concrete. Both materials improve slope stability, yet polymer-modified concrete provides a more sustainable solution by extending service life and reducing the carbon footprint associated with maintenance and material production.
Case Studies: Successful Slope Stabilization Projects
Case studies of polymer-modified concrete demonstrate enhanced durability and adhesion in slope stabilization projects, improving resistance to water infiltration and erosion. Shotcrete applications in mountain tunnels of the Austrian Alps provide proven rapid application and flexibility in irregular terrain, supporting immediate slope support with minimal excavation. Comparative analyses reveal polymer-modified concrete suits long-term stabilization under harsh environmental conditions, while shotcrete excels in emergency repairs and complex geometries.
Choosing the Right Solution: Key Factors to Consider
Polymer-modified concrete offers enhanced durability, flexibility, and adhesion, making it ideal for long-term slope stabilization in environments exposed to moisture and temperature fluctuations. Shotcrete provides rapid application and excellent conformity to complex slope geometries, facilitating quick erosion control and structural reinforcement. Selecting between these methods depends on project-specific factors such as slope condition, environmental exposure, application speed, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Polymer-modified concrete vs Shotcrete for Slope stabilization
 azmater.com
azmater.com