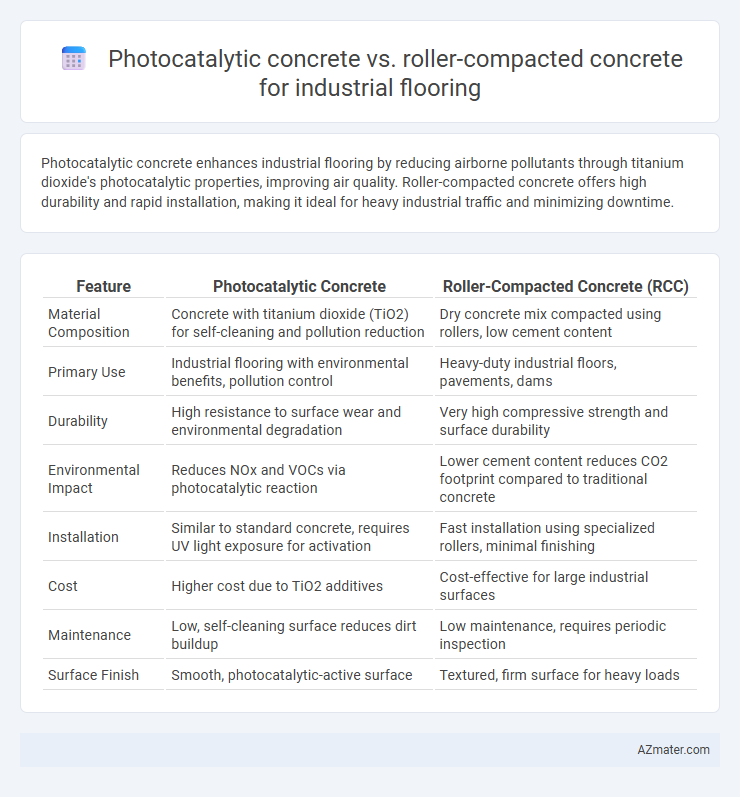
Photocatalytic concrete enhances industrial flooring by reducing airborne pollutants through titanium dioxide's photocatalytic properties, improving air quality. Roller-compacted concrete offers high durability and rapid installation, making it ideal for heavy industrial traffic and minimizing downtime.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Photocatalytic Concrete | Roller-Compacted Concrete (RCC) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Concrete with titanium dioxide (TiO2) for self-cleaning and pollution reduction | Dry concrete mix compacted using rollers, low cement content |
| Primary Use | Industrial flooring with environmental benefits, pollution control | Heavy-duty industrial floors, pavements, dams |
| Durability | High resistance to surface wear and environmental degradation | Very high compressive strength and surface durability |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces NOx and VOCs via photocatalytic reaction | Lower cement content reduces CO2 footprint compared to traditional concrete |
| Installation | Similar to standard concrete, requires UV light exposure for activation | Fast installation using specialized rollers, minimal finishing |
| Cost | Higher cost due to TiO2 additives | Cost-effective for large industrial surfaces |
| Maintenance | Low, self-cleaning surface reduces dirt buildup | Low maintenance, requires periodic inspection |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, photocatalytic-active surface | Textured, firm surface for heavy loads |
Introduction to Industrial Flooring Solutions
Photocatalytic concrete enhances industrial flooring by integrating titanium dioxide to break down pollutants and maintain surface cleanliness, improving air quality and reducing maintenance efforts. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) provides high strength and durability with rapid setting properties, ideal for heavy industrial loads and fast construction timelines. Both materials offer distinct advantages for industrial flooring, with photocatalytic concrete focusing on environmental benefits and RCC emphasizing structural performance.
Overview of Photocatalytic Concrete
Photocatalytic concrete incorporates titanium dioxide (TiO2) that activates under UV light to break down pollutants and improve air quality, making it ideal for sustainable industrial flooring. Its self-cleaning surface reduces maintenance costs and enhances durability by preventing organic stains and surface degradation. Compared to roller-compacted concrete, photocatalytic concrete offers environmental benefits through pollutant reduction while maintaining comparable strength and load-bearing capacity essential for industrial applications.
Key Features of Roller-Compacted Concrete
Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) for industrial flooring is characterized by its high density, low permeability, and rapid curing, providing exceptional durability and high load-bearing capacity. Its mix design includes low water content and coarse aggregates, which contribute to superior abrasion resistance and reduced maintenance costs compared to photocatalytic concrete. RCC's compaction by vibratory rollers ensures a smooth, uniform surface ideal for heavy industrial traffic, making it a cost-effective and robust solution for industrial flooring applications.
Environmental Benefits: Photocatalytic vs Roller-Compacted
Photocatalytic concrete offers significant environmental benefits for industrial flooring by actively reducing air pollutants like nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds through its TiO2 photocatalyst, improving local air quality. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC), while durable and cost-effective, lacks the pollutant-degrading properties of photocatalytic concrete and primarily contributes to environmental sustainability through reduced cement content and increased resource efficiency. Choosing photocatalytic concrete enhances environmental impact beyond structural performance by enabling floors that contribute to pollution mitigation in industrial settings.
Durability and Performance in Industrial Settings
Photocatalytic concrete enhances durability in industrial flooring through its self-cleaning and pollutant-degrading properties, reducing maintenance and extending surface life under heavy machinery and chemical exposure. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers superior compressive strength and abrasion resistance, ideal for withstanding intense mechanical loads and repeated traffic in industrial environments. Both materials excel in performance, but photocatalytic concrete provides added environmental benefits while RCC ensures robust structural integrity.
Installation Process and Time Comparison
Photocatalytic concrete for industrial flooring requires precise application of titanium dioxide coatings during mixing or surface finishing, which can extend curing times compared to traditional methods. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) benefits from rapid placement using heavy rollers without forms or finishing, significantly reducing installation time. RCC typically achieves faster construction cycles and earlier load-bearing capacity, while photocatalytic concrete offers environmental advantages but demands longer curing and careful handling during installation.
Maintenance Requirements and Longevity
Photocatalytic concrete for industrial flooring offers self-cleaning and pollution-reducing properties that significantly lower routine maintenance needs by breaking down organic contaminants and reducing surface dirt accumulation. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) provides exceptional durability and high compressive strength, making it ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications with minimal repair costs over time, though it lacks self-cleaning capabilities. While photocatalytic concrete enhances longevity through reduced surface degradation, RCC delivers superior structural longevity under intense mechanical stress, requiring periodic inspections to ensure optimal performance.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Lifecycle Expenses
Photocatalytic concrete generally incurs higher initial costs due to advanced materials and additives that enable pollution reduction and self-cleaning properties, whereas roller-compacted concrete (RCC) offers lower upfront expenses through its simplified placement and lower binder content. Lifecycle expenses for photocatalytic concrete can be reduced by decreased maintenance and cleaning costs attributed to its anti-pollutant surface, while RCC requires periodic surface treatments and repairs that may increase long-term operational costs. Industrial flooring projects must balance these factors, considering photocatalytic concrete's environmental benefits against RCC's economic advantages in terms of installation speed and initial investment.
Suitability for Specific Industrial Applications
Photocatalytic concrete excels in industrial flooring applications where air purification and pollution reduction are priorities, such as manufacturing plants prone to airborne contaminants and chemical emissions. Roller-compacted concrete (RCC) is better suited for heavy load-bearing environments like warehouses and distribution centers due to its high compressive strength and rapid installation capabilities. Selecting between photocatalytic concrete and RCC depends on balancing environmental benefits with structural demands specific to the industrial operation.
Future Trends in Industrial Concrete Flooring
Photocatalytic concrete incorporates titanium dioxide to reduce air pollutants, offering sustainable benefits for industrial flooring with self-cleaning and pollutant-degrading properties. Roller-compacted concrete provides rapid installation and high load-bearing capacity, ideal for heavy-duty industrial environments focusing on durability and cost efficiency. Future trends emphasize integrating photocatalytic technology into roller-compacted mixes to combine environmental sustainability with structural performance in industrial flooring applications.
Infographic: Photocatalytic concrete vs Roller-compacted concrete for Industrial flooring
 azmater.com
azmater.com