Mass concrete offers superior structural strength and durability for tunnel lining due to its high compressive strength and low permeability. Shotcrete provides faster application and better adaptability to complex tunnel geometries, making it ideal for reinforcement and repair in tunnel construction.
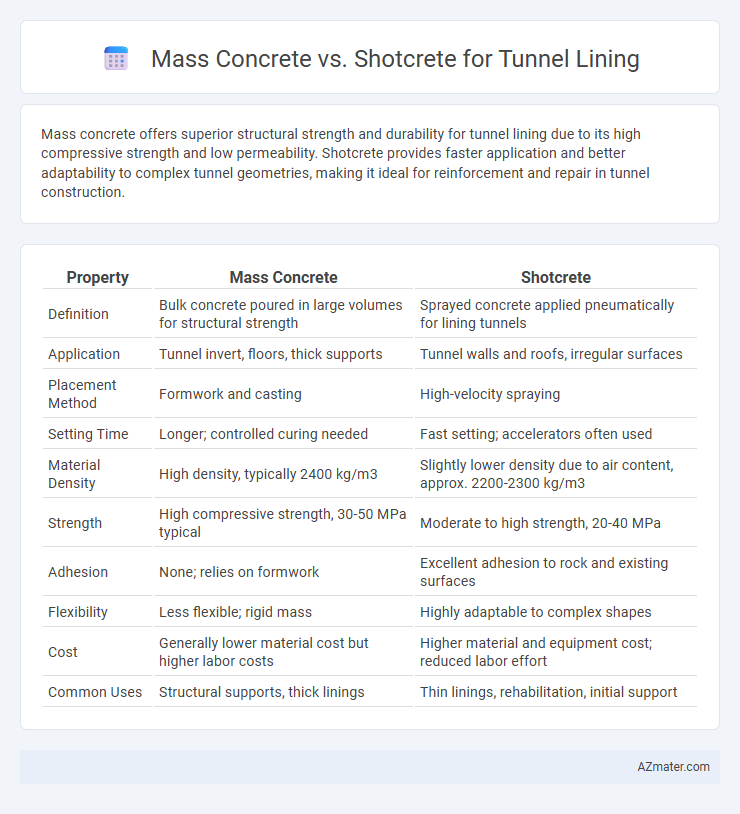
Table of Comparison
| Property | Mass Concrete | Shotcrete |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bulk concrete poured in large volumes for structural strength | Sprayed concrete applied pneumatically for lining tunnels |
| Application | Tunnel invert, floors, thick supports | Tunnel walls and roofs, irregular surfaces |
| Placement Method | Formwork and casting | High-velocity spraying |
| Setting Time | Longer; controlled curing needed | Fast setting; accelerators often used |
| Material Density | High density, typically 2400 kg/m3 | Slightly lower density due to air content, approx. 2200-2300 kg/m3 |
| Strength | High compressive strength, 30-50 MPa typical | Moderate to high strength, 20-40 MPa |
| Adhesion | None; relies on formwork | Excellent adhesion to rock and existing surfaces |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; rigid mass | Highly adaptable to complex shapes |
| Cost | Generally lower material cost but higher labor costs | Higher material and equipment cost; reduced labor effort |
| Common Uses | Structural supports, thick linings | Thin linings, rehabilitation, initial support |
Introduction to Tunnel Lining Methods
Tunnel lining methods primarily involve mass concrete and shotcrete, each with distinct applications based on structural and geological requirements. Mass concrete offers high strength and durability for permanent support, typically cast in situ using formwork, while shotcrete, sprayed at high velocity, provides quick application and adhesion for initial ground support and stabilization. Selection depends on factors like tunnel size, rock conditions, and construction speed, influencing durability, safety, and cost efficiency.
Overview of Mass Concrete and Shotcrete
Mass concrete for tunnel lining involves using large volumes of concrete poured in place to form a continuous, monolithic structure providing high compressive strength and durability. Shotcrete is a sprayed concrete technique applied pneumatically, offering rapid setting times and excellent adhesion to irregular surfaces, enhancing tunnel stability during excavation. The choice between mass concrete and shotcrete depends on project requirements such as structural demands, construction speed, and geological conditions.
Material Composition and Properties
Mass concrete for tunnel lining primarily consists of cement, aggregates, water, and admixtures tailored to achieve high compressive strength and durability, with a dense, homogeneous structure minimizing permeability and thermal cracking. Shotcrete combines cement, fine aggregates, and water with tailored admixtures, applied pneumatically to provide quick setting, high early strength, and excellent adhesion to irregular surfaces, often incorporating fibers to enhance tensile strength and control cracking. Both materials are selected based on specific structural and environmental demands, with mass concrete favoring large, monolithic sections and shotcrete offering flexibility and rapid application in complex geometries.
Application Techniques: Mass Concrete vs. Shotcrete
Mass concrete for tunnel lining involves placing large volumes of concrete in forms, requiring extensive formwork and longer curing times to achieve structural stability. Shotcrete application uses pneumatic spraying to rapidly apply concrete layers directly onto tunnel surfaces, offering faster placement, reduced formwork, and better adaptation to complex geometries. The choice between mass concrete and shotcrete depends on factors like tunnel shape, site constraints, and construction speed requirements.
Structural Performance and Durability
Mass concrete offers high compressive strength and excellent durability for tunnel lining, achieved through controlled casting and curing processes that minimize shrinkage and cracking. Shotcrete provides superior adhesion and rapid application, enhancing structural performance in complex geometries and reducing construction time, but may require fiber reinforcement to improve long-term durability against abrasion and environmental attack. Both methods can achieve robust tunnel lining performance, with mass concrete favored for large, uniform sections and shotcrete preferred for intricate or rehabilitation works.
Construction Speed and Efficiency
Mass concrete provides a robust and durable lining ideal for large tunnel sections but requires longer setting times, impacting overall construction speed. Shotcrete enables rapid application with minimal formwork, significantly accelerating tunnel lining installation and allowing for continuous progress in complex geometries. Efficiency gains with shotcrete come from reduced labor and equipment needs, making it the preferred choice for projects demanding swift turnaround.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Mass concrete for tunnel lining generally incurs higher initial costs due to extensive formwork, longer curing times, and labor-intensive placement, whereas shotcrete offers cost savings with faster application, reduced formwork requirements, and minimized labor expenses. Economic considerations include the potential for shotcrete to decrease project timelines, thereby lowering indirect costs such as equipment rentals and overhead, while mass concrete may provide durability benefits that reduce long-term maintenance expenses. Selecting between mass concrete and shotcrete depends on detailed cost-benefit analyses, factoring in material prices, labor rates, project scale, and lifecycle economic impacts.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Shotcrete offers a more environmentally sustainable option for tunnel lining compared to mass concrete due to its reduced material consumption and lower carbon emissions during application. The sprayed application technique minimizes waste and allows for precise layer thickness, decreasing the overall ecological footprint associated with cement production and transportation. Mass concrete's higher volume and energy-intensive curing process result in increased greenhouse gas emissions, making shotcrete a preferable choice for environmentally conscious tunnel construction projects.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Mass concrete and shotcrete are both widely used for tunnel lining but present unique challenges such as achieving uniform strength and controlling shrinkage cracks in mass concrete, while shotcrete often faces issues with rebound losses and inconsistent thickness. Solutions for mass concrete include optimized mix designs with low heat cement and proper curing methods to mitigate thermal cracking, whereas shotcrete benefits from improved nozzle techniques, the use of accelerators, and fiber reinforcement to enhance adhesion and durability. Both methods require precise quality control and monitoring to ensure structural integrity and longevity of the tunnel lining.
Choosing the Right Tunnel Lining Method
Mass concrete offers structural strength and durability for tunnel lining, making it ideal for large-scale projects requiring heavy load-bearing capacity and long-term stability. Shotcrete provides rapid application, excellent adhesion, and adaptability to complex tunnel geometries, which benefits repair works and tunnels with irregular shapes. Selecting the appropriate method depends on factors such as project scale, geological conditions, time constraints, and cost efficiency.
Infographic: Mass concrete vs Shotcrete for Tunnel lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com